Contested racial identity— self-identified race not matching socially-assigned race—may be an indication of experiences with racism.
Study objective: This scoping review was conducted to collate and summarize the published research literature addressing sexual and gender minority care in the emergency department (ED).
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 10 by assessing SARS-CoV-2 incidence in six ethnic groups in Amsterdam, and showing that incidence was highest in the largest minority ethnic groups. The findings suggest that prevention measures and vaccination should be especially encouraged in these groups.
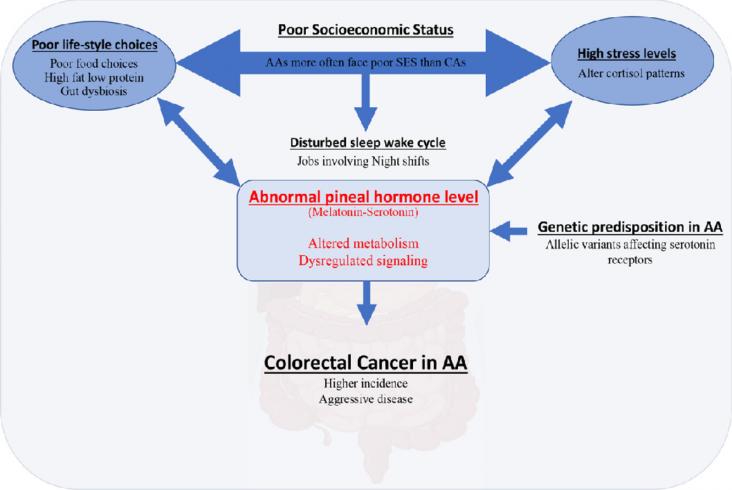
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States.

Research4Life has been providing free and low-cost access to scientific research in the developing world for 20 years. Read this insightful story about the history of Research4Life, and its new strategy for the future with the aim to help researchers in the developing world fully participate in the global research community. This relates to SDG 4, 10 & 17.
Race and kidney function.
This Review supports SDG 3 and 10 by highlighting how genomics research intersects with existing racial and ethnic inequalities and forms of exclusion; there is no universally accepted, consistently applied method for categorising genomic data, which the authors argue is problematic, both from a clinical and scientific perspective, but more fundamentally in terms of the ability of genomics research to achieve the core ethical values of equity and justice.
HIV-1 viral load assays are essential tools for clinical management of people living with HIV-1. The cobas HIV-1 assay is highly sensitive, accurate and suitable for use in clinical practice.
A review article discusses various drugs and plant extracts for Alzheimer's disease, and further discusses plant species that can be researched for treatment.
This study, relevant to Goals 3, 10, and 13, examined how often and in which countries health considerations were factored into a country’s Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC’s) for climate commitments. They found that countries with the greatest vulnerability to climate change health effects – largely countries with the fewest resources – considered health effects the most. The authors recommend that considering health, even in higher resourced countries, can increase public backing for ambitious climate goals.
