This article advances SDG # 15 and SDG # 11 by examining the large number of animals killed on road and establish how best to assess the problem so as to improve mitigation.
Elsevier,
Manzoor Qadir, Christopher A. Scott, Trade-offs of wastewater irrigation, Editor(s): Michael J. Goss, Margaret Oliver, Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment (Second Edition), Academic Press, 2023, Pages 277-287, ISBN 9780323951333, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822974-3.00018-5.
This chapter aligns with Goal 11 and 6 by analysing the use of wastewater for irrigation, balancing positive outcomes and trade-offs. There is a large variation between developed and developing countries as well as among countries within different economic groups regarding safe management of wastewater.
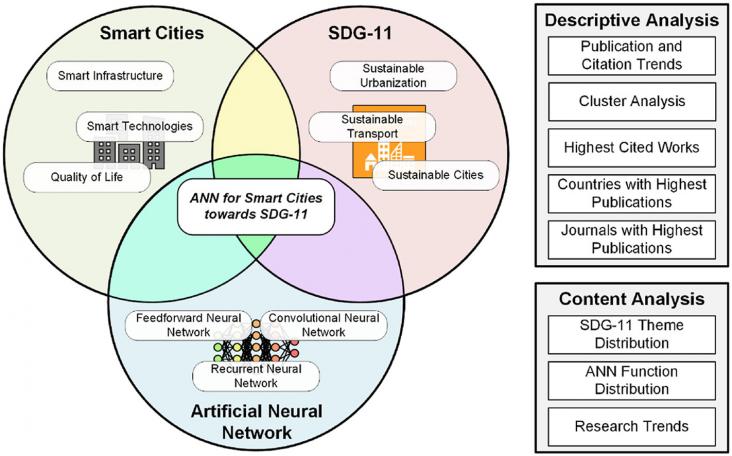
This review assessed the academic landscape on the use of ANN for Smart Cities towards SDG-11. A keyword-based methodological framework was used to retrieve the relevant documents. The documents were assessed using descriptive and content analysis. Results revealed significant research interest on the topic and is on an increasing trend. Research works on the topic are expected to increase as clusters on specific topics have formed. This review identified the SDG-11 themes Environmental Impact, Transport Systems, and Urbanization among the most prominent. Research gaps were identified in the SDG-11 themes on Green and Public Spaces, and Natural and Cultural Heritage.
This study links multiple models for a comprehensive assessment of the economic-environmental-health co-benefits of renewable energy development in China. The results show that developing renewable energy can avoid 0.6 million premature mortalities, 151 million morbidities, and 111 million work-loss days in 2050.
Explores the impact and consequences of not being able to make trips because of transport disadvantage. Explicitly does so in relation to SDG goal 11.2.
This paper is particularly relevant to investigations into the spread of organisms that remain close to shore over timescales of days-to-weeks, e.g., the spread of marine non-native species and pathogenetic parasites, but is equally relevant to simulations tracking the dispersal of eDNA or coastal pollutants such as oil and plastics.
This One Earth Research Article shows how residential socioeconomic and racial segregation, in part due to historic redlining and unequal investment in green spaces, has led to disparities in heat exposure in the United States. This is expected to worsen as the climate warms, highlighting the need fro climate mitigation and adaptation (SDG 13), with additional implications for improving climate resilient and equitable infrastructure in cities (SDG 11) and public health interventions to reduce heat exposure (SDG 3).
Cities and communities can be understood as "climate sensitive systems." This One Earth Perspective article proposes a research paradigm for assessing compounding and cascading risks, which is important for developing sustainable and resilient cities (SDG 11) and climate adaptation (SDG 13).
Migration, e.g., from rural to urban areas, from coastal areas inland, or between countries, is one potential adaptation to climate change (SDG 13), with potential impacts on poverty (SDG 1) and hunger (SDG 2). This One Earth Perspectives article offers criteria for evaluating whether it is successful or maladaptive.
World Intellectual Property Day 2024 is highlighting the critical importance of intellectual property (IP) in catalyzing the human innovation and creativity needed for achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This paper integrates innovation research with intellectual property law to explore how such a systemic collaboration for sustainable innovation should be characterised, and how the intellectual property rights (IPR) system could be shaped to support it. The paper highlights that reaching sustainability objectives depends on system-level innovations; system-level innovation for sustainability calls for new forms of collaboration; current IPR regime limits systemic collaborations for sustainable innovations and new IPR system and tools are needed to facilitate systemic collaboration.
