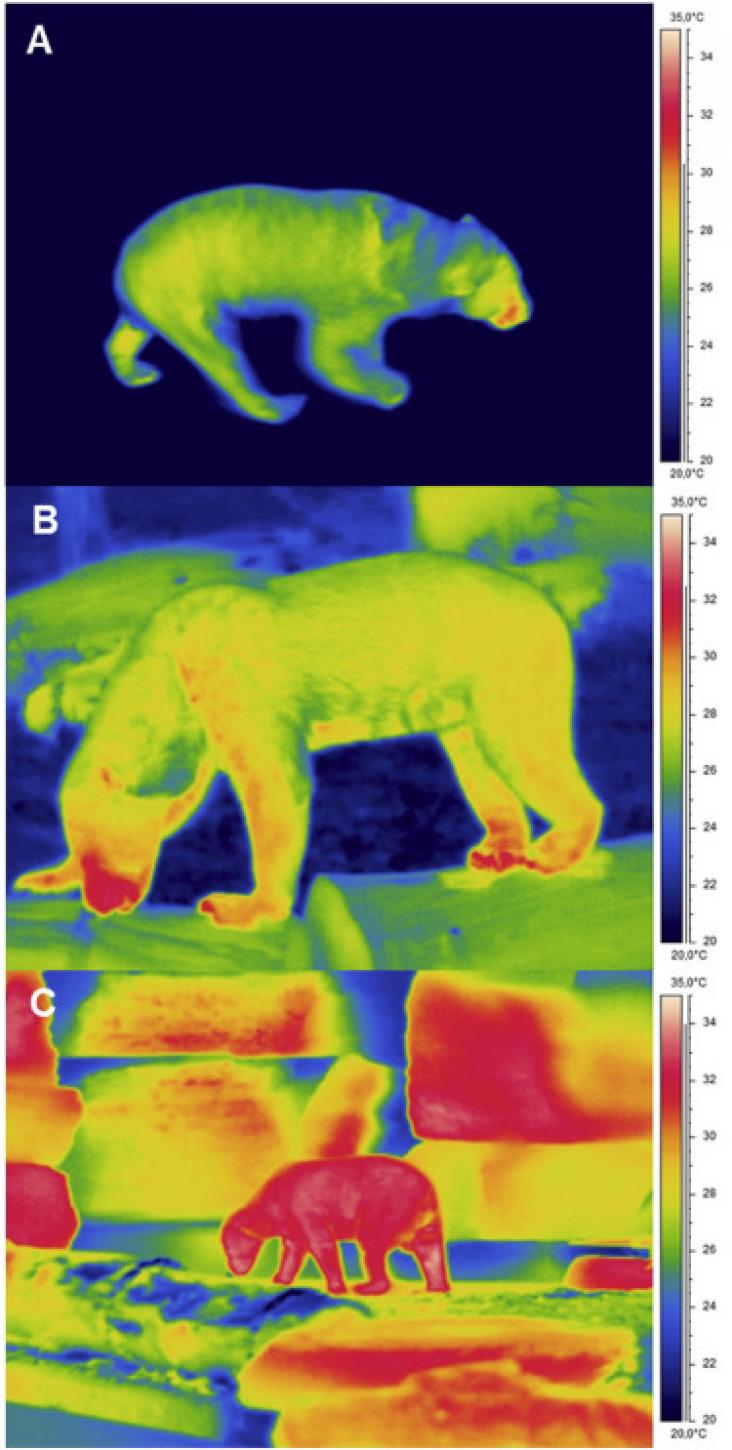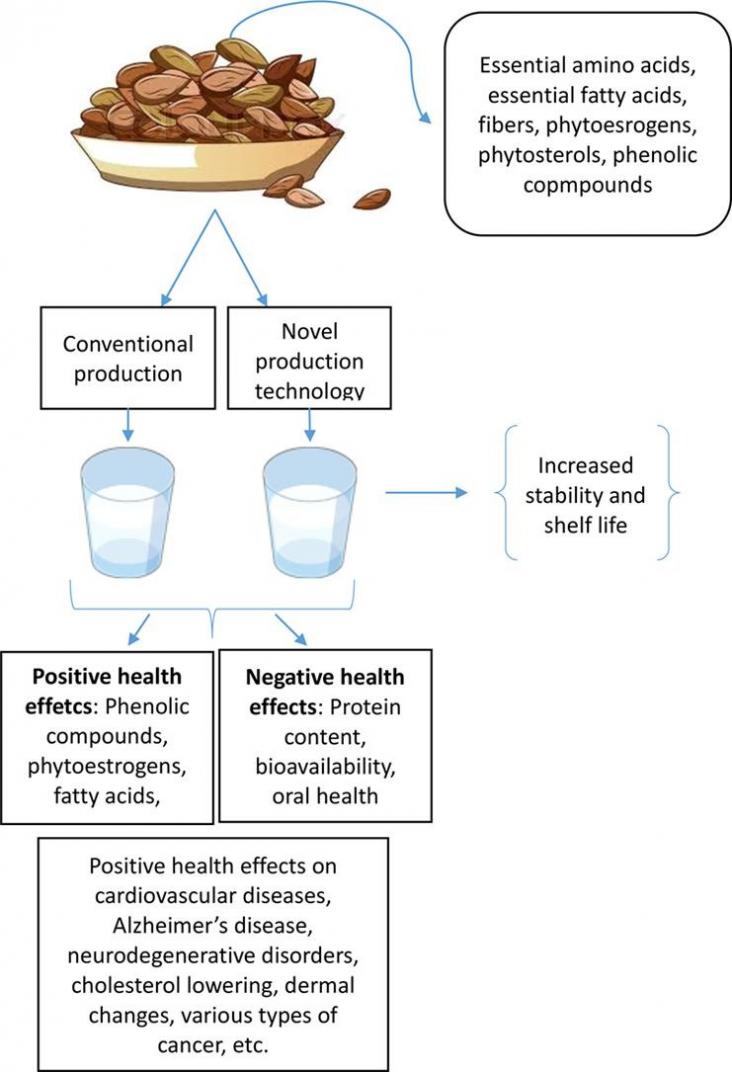
The consumption of plant-based milk substitutes has spread rapidly around the world due to its numerous positive health effects on the human body.
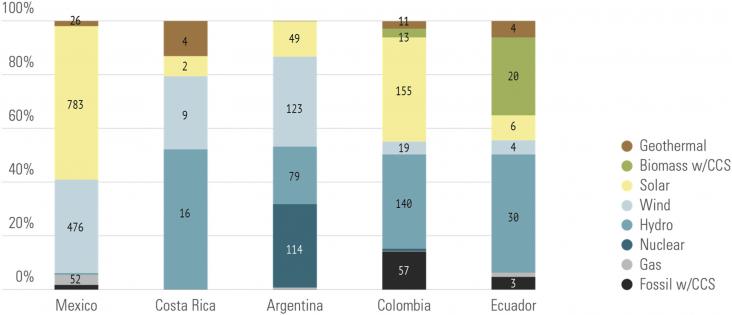
This synthesis paper presents the objectives, approach and cross-cutting results of the Latin American Deep Decarbonization Pathways project (DDP-LAC).
The COVID-19 pandemic has had growing environmental consequences related to plastic use and follow-up waste, but more urgent health issues have far overshadowed the potential impacts.
Pathways towards a defossilated sustainable power system for West Africa within the time horizon of 2015–2050 is researched, by applying linear optimisation modelling to determine the cost optimal
The destruction of natural habitats is causing loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
The process industries have been facing ever increasing pressure in the monitoring and control of gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds and hazardous air pollutants.
Bio-based aerogels with customizable porosities and functionalities constitute a significant potential for CO2 capture.

