Over US$60 trillion is predicted to be spent on new infrastructure globally by 2040.
A new threat now confronts the Amazon in the form of a massive infrastructure program, the Initiative for the Integration of the Regional Infrastructure of South America, or IIRSA.
Economic development projects are increasingly applying the mitigation hierarchy to achieve No Net Loss, or even a Net Gain, of biodiversity.
To conserve the bulk of Earth's ecological heritage across the Anthropocene, setting aside half of Earth's land is just a start.
Economic development projects are increasingly applying the mitigation hierarchy to achieve No Net Loss, or even a Net Gain, of biodiversity.
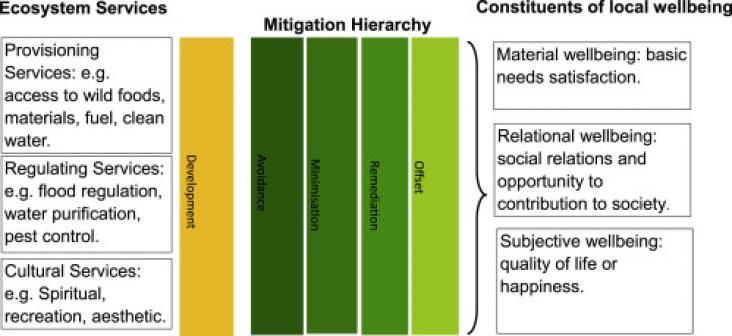
Economic development projects are increasingly applying the mitigation hierarchy to achieve No Net Loss, or even a Net Gain, of biodiversity.
This book chapter addresses goals 13, 14, and 15 by focusing on how changing environmental temperatures affect species adaptation.
Conservation of biodiversity and ecosystem services in natural environments requires careful management choices.
The no-tillage system combining winter cover crops and crop rotation may increase the efficiency use of soil P and phosphate fertilizer.
Soils host the vast majority of life on Earth including microorganisms and animals, and supporting all terrestrial vegetation.
