Objective imaging-based biomarker discovery for psychiatric conditions is critical for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Background: Access to safe sanitation and the elimination of open defecation are pre-conditions for improved child health and nutrition and wider achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (S
This study supports SDGs 3 and 6 by analysing data from 88 low-income and middle-income countries and showing geographical disparities in access to clean water and sanitation facilities. These findings identify where efforts to increase access to safe water and sanitation have been successful over time, and highlight the need for targeted and tailored interventions to reach those communities and regions that have been left behind.

World Alzheimer's Day is an international campaign organised by Alzheimer's Disease International to raise awareness and highlight issues faced by people affected by dementia. It takes place every year on September 21st and is the focus of World Alzheimer's Month. In support of this year’s theme – ‘Let’s talk about dementia’ - Elsevier presents a curated, open access collection of 25 journal articles and book chapters focused on challenging the fear and stigma associated with dementia.
Patients with burning mouth syndrome (BMS) have burning sensation of the oral mucosa and occurs more commonly in middle-aged and elderly women. This study determines that gastric parietal cell antibody+BMS patients have significantly higher frequencies of macrocytosis, blood Hb and serum vitamin B12 deficiencies, and hyperhomocysteinemia than healthy control subjects or GPCA−BMS patients.
This book chapter advances SDGs 3 and 10 by explaining how to develop a comprehensive understanding of the epidemiology of obesity, and that it is important to consider the social circumstances and environmental exposures that are related to obesity, given that these contribute to a combined 20% of premature deaths.

On Monday 24 August 2020 – at the beginning of World Water Week - RELX announced the winners of the 2020 RELX Environmental Challenge. Now in its 10th year, the RELX Environmental Challenge supports innovative solutions that improve sustainable access to safe water and sanitation where it is at risk, contributing to SDGs 1, 3, 6 and 10.

Although financial wellness benefits have been rising in popularity for some time, the demand for them has grown exponentially this year due to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and resulting recession. Such benefits can be a vital resource for employees during this stressful time. Advancing SDG 3, this article covers employer considerations around designing a successful financial wellness programme.
Eradicating food insecurity is necessary for achieving global health goals. Liberal trade policies might increase food supplies but how these policies influence individual-level food insecurity remains uncertain. We aimed to assess the association between liberal trade policies and food insecurity at the individual level, and whether this association varies across country-income and household-income groups.
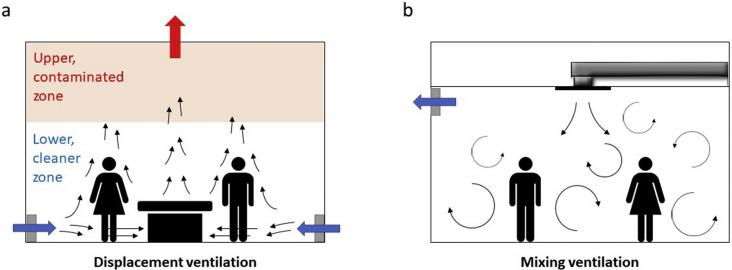
Within a time span of only a few months, the SARS-CoV-2 virus has managed to spread across the world.
