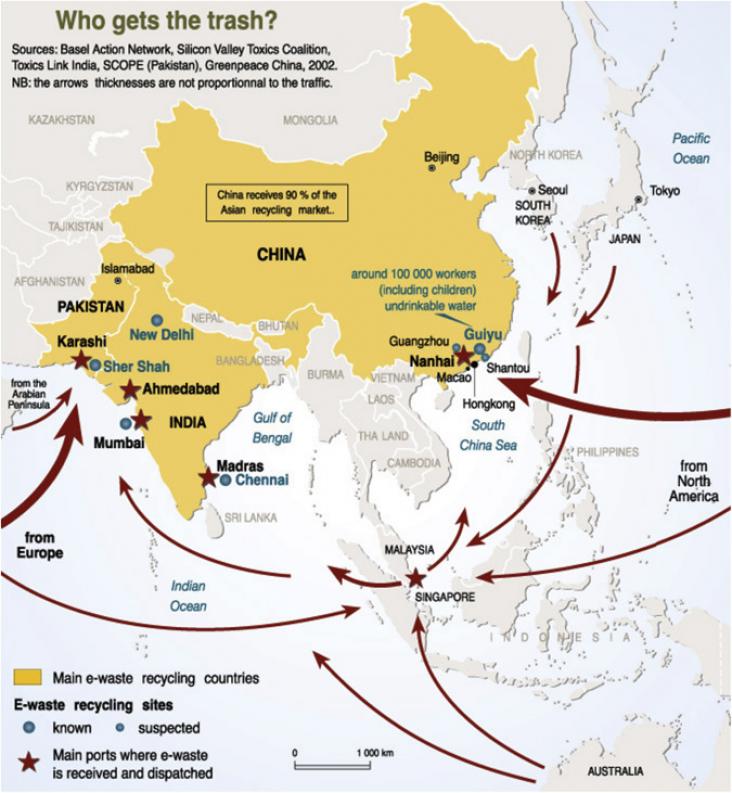
Chapter on the public health problem of how to effectively deal with or dispose of the ever-increasing number of old or outdated electronic devices (e-waste) in a safe manner. The goal of SDG target 3.9 is to substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination
This chapter will attempt brief review on some of the known factors which define populations, particulary developing countries, at special risk for chemical toxicity from e-waste. The goal of SDG target 3.9 is to substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination
Although it is one of the poorest countries in the world, devastated by the 1994 Genocide against the Tutsi and heavily aid-dependent, Rwanda has achieved most of its Millennium Development targets fo
Objectives malaria causes complications during 80% of all pregnancies in Uganda.
Background The burden of HIV in transgender women (transwomen) in Brazil remains unknown.
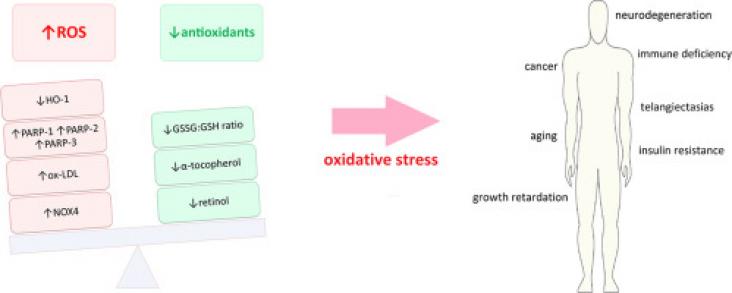
Rare pleiotropic genetic disorders, Ataxia-telangiectasia (A-T), Bloom syndrome (BS) and Nijmegen breakage syndrome (NBS) are characterised by immunodeficiency, extreme radiosensitivity, higher cancer
Thirty years of public health research have demonstrated that improved indoor environmental quality is associated with better health outcomes.
Background The 69th World Health Assembly approved the Global Health Sector Strategy to eliminate hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection by 2030, which can become a reality with the recent launch of direct
