Given the growing interest in systemic design, there is a demand for designerly approaches that can aid practitioners in catalyzing social systems change. The purpose of this research is to develop an initial portfolio of designerly approaches that acknowledges social structures as a key leverage point for influencing social systems. This article presents learnings from experimentation with a host of designerly approaches for shaping social structures and identifies four design principles to guide systemic design practitioners in doing this work.
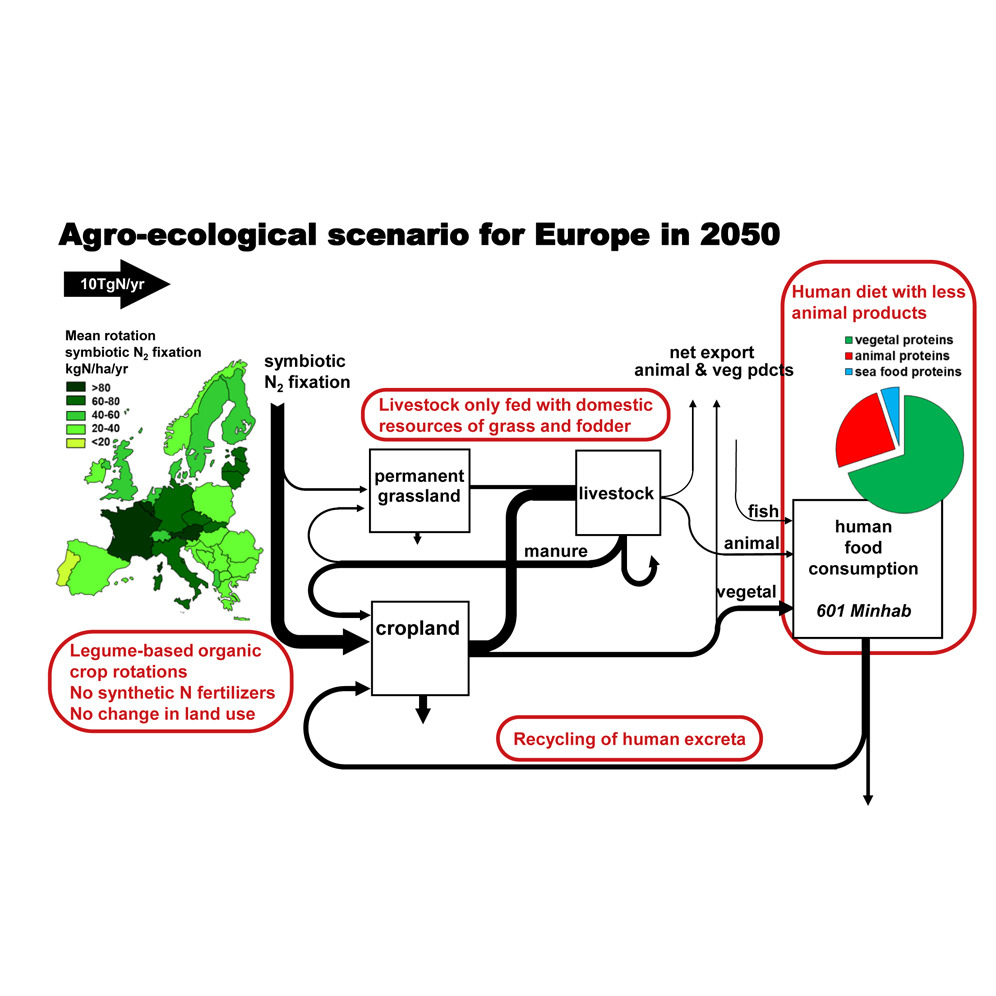
After World War II, the evolution of Europe's agro-food system has been marked by intensified use of synthetic fertilizers, territorial specialization, and integration in global food and feed markets. This evolution led to increased nitrogen (N) losses to aquatic environments and the atmosphere, which, despite increasing environmental regulations, continues to harm ecosystems and human well-being.
The processes of salinisation and alkalinisation of soil that caused the formation of different types of saline (halomorphic) soils are characteristic of the northern part of Serbia — the area of Vojvodina. These soils are characterized by poor physical and chemical properties due to a high content of salt and/or adsorbed Na+ ions because of which are being used to a limited extent in agricultural production, and more as pastures.
Background: The prevalence of head injury is estimated to be as high as 55% in women in prison and might be a risk factor for violent offending, but evidence is equivocal. The extent of persisting disability is unknown, making decisions about service needs difficult. The UN recognises vulnerabilities in women in prison, but does not include head injury. This study aimed to investigate relationships among head injury, comorbidities, disability, and offending in women in prison.
Background: Ovarian cancer continues to have a poor prognosis with the majority of women diagnosed with advanced disease. Therefore, we undertook the UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening (UKCTOCS) to determine if population screening can reduce deaths due to the disease. We report on ovarian cancer mortality after long-term follow-up in UKCTOCS. Methods: In this randomised controlled trial, postmenopausal women aged 50–74 years were recruited from 13 centres in National Health Service trusts in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
To exceed in sugar consumption is one of the main causes of overweight and obesity, especially for children and adolescent. However, sugar reduction, especially in baked goods, is challenging due to its effect not only on sensorial properties but also for other quality parameters. Multiple technological strategies to obtain muffins at low sugar content addressed for children were studied.
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has affected mental health, psychological wellbeing, and social interactions. People with physical disabilities might be particularly likely to be negatively affected, but evidence is scarce. Our aim was to evaluate the emotional and social experience of older people with physical disabilities during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic in England.
This book chapter advances SDG 3 and 10 by discussing the importance of social support and psychological flexibility to act as a buffer between the effects of COVID-19 on psychological distress and mental health.
This book chapter advances SDG 3 and 10 reviewing the extent to which coronavirus lockdown and restrictions have affected the life of the people of Ghana
This book chapter advances SDG 3 and 10 by exploring the gap within research literature in which the intersectional complexities of South Asian Muslims lie by examining the historical and geopolitical contexts of South Asian Muslim experiences in the United States. This chapter discusses the ways in which contemporary South Asian Muslim American experiences are further complicated when navigating additional marginalized identities such as gender and sexual orientation, age and generational influences, disability status, class, and national origin.