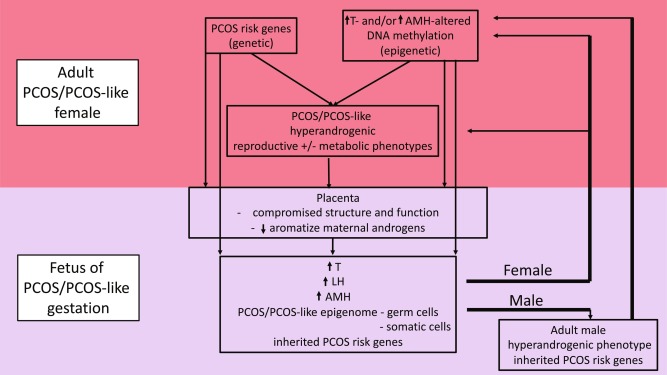
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, Challenging Issues in the Modern Era of Individualized Medicine, 2022, Pages 23-38
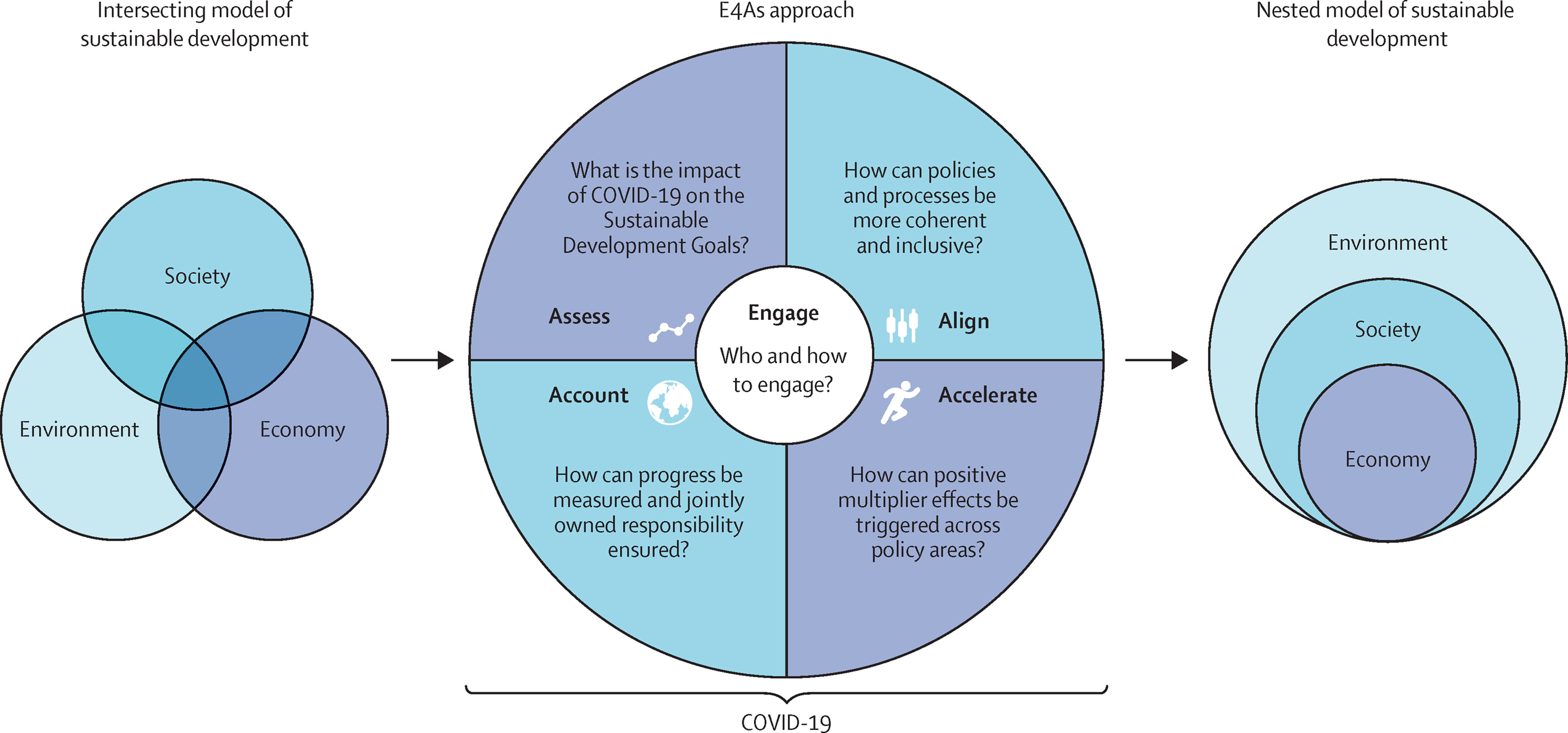
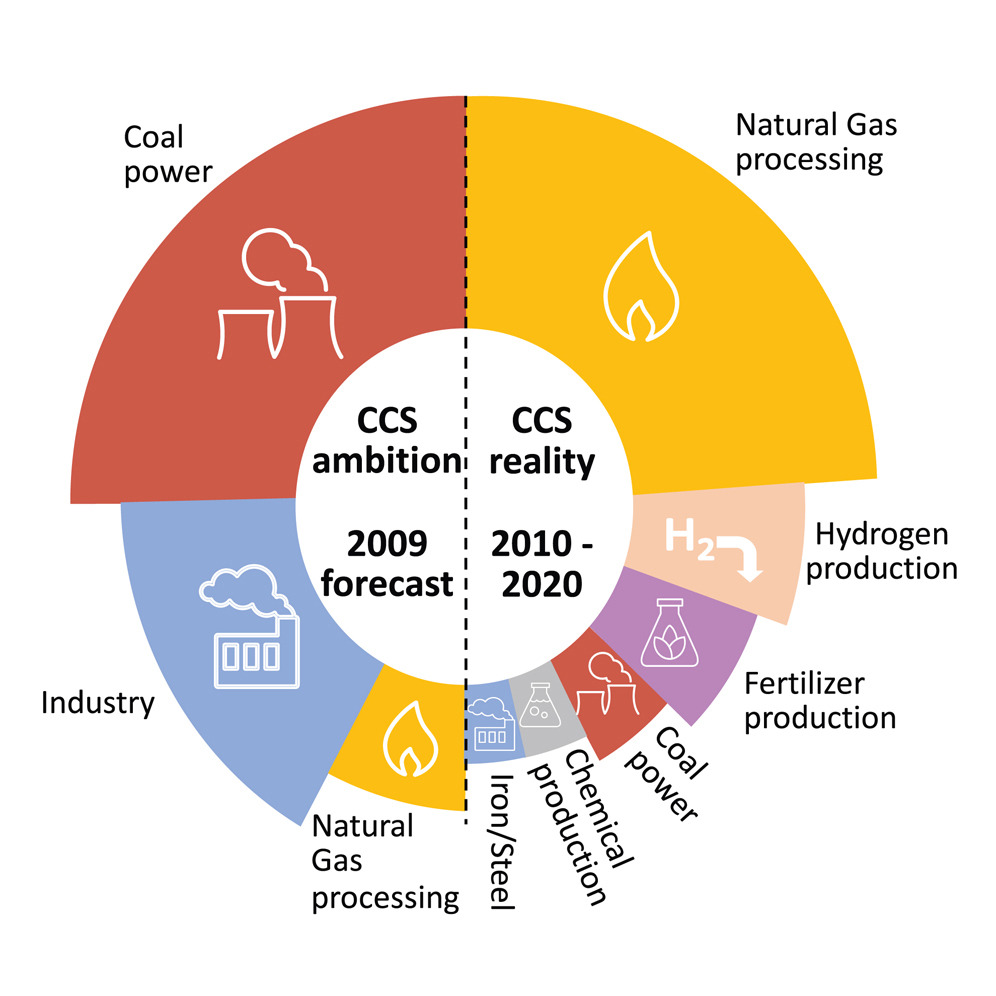
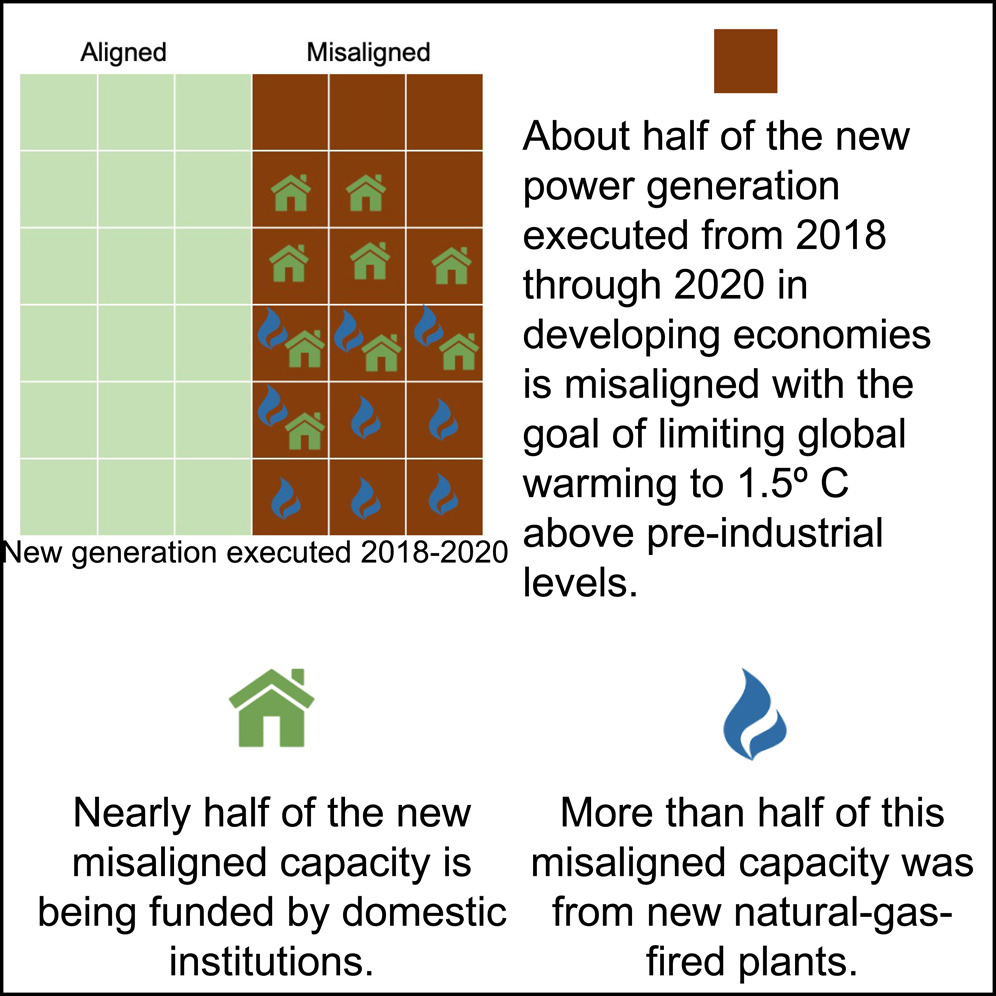
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, Challenging Issues in the Modern Era of Individualized Medicine, 2022, Pages 187-216
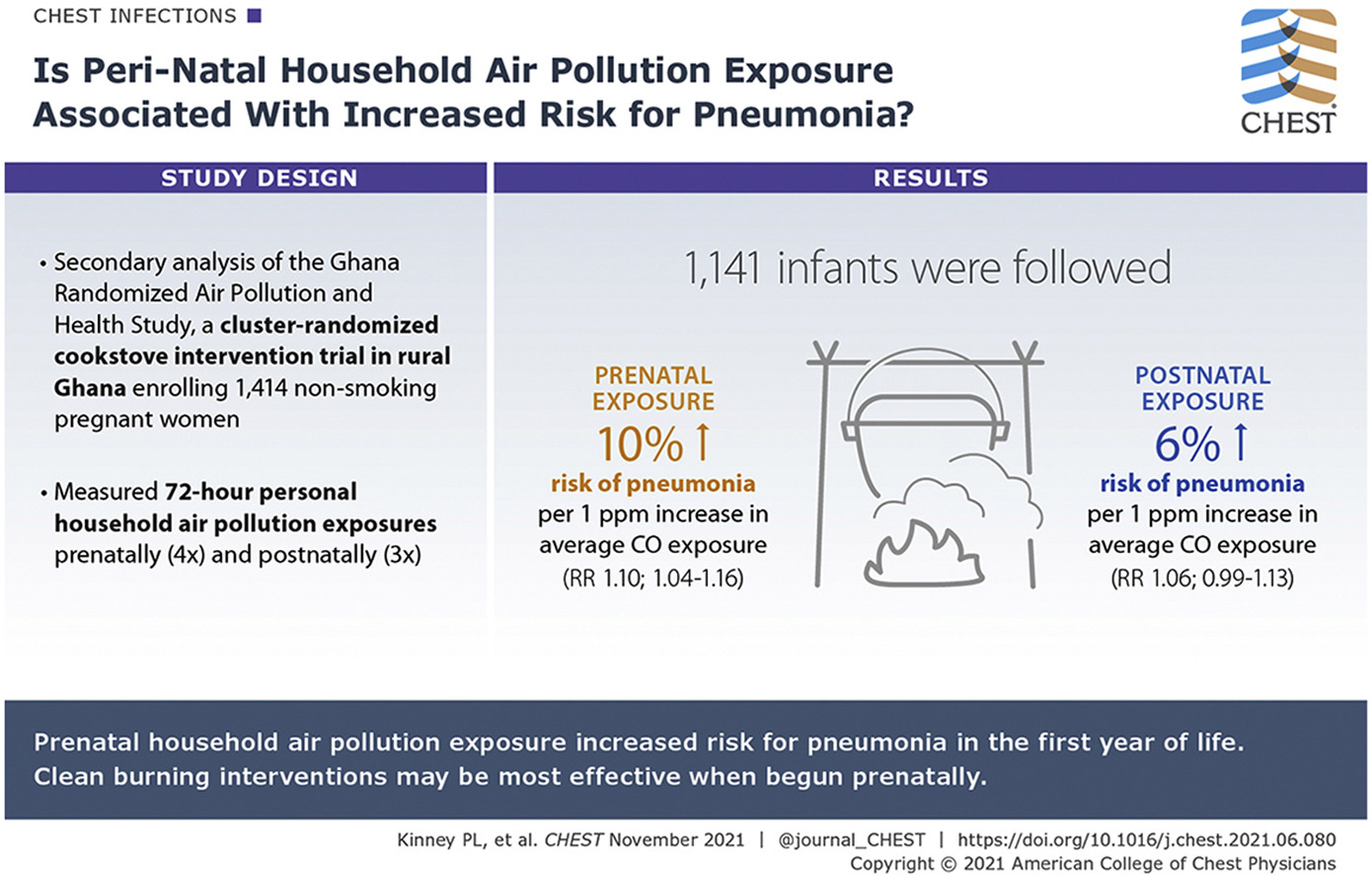
Background: Nearly 40% of the world's population is exposed daily to household air pollution. The relative impact of prenatal and postnatal household air pollution exposure on early childhood pneumonia, a leading cause of mortality, is unknown. Research Question: Are prenatal or postnatal household air pollution, or both, associated with pneumonia risk in the first year of life? Study Design and Methods: The Ghana Randomized Air Pollution and Health Study enrolled 1,414 nonsmoking, pregnant women before 24 weeks’ gestation with prospective follow-up to the child's age of 1 year.