RELX Group has published a new analysis, conducted by Elsevier, on SDG4: Quality education. This new graphic builds on Elsevier’s 2015 Sustainability Science in a Global Landscape Report, and its 2017 update Sustainability Science in graphic form. Looking specifically at SDG 4, this graphic provides insight into peer-reviewed research on education as related to the themes of the goal.
The LexisNexis Newsdesk® app featuring human rights is a free app which tracks news about the 17 SDGs and brings relevant stories from across the world in real time to your mobile device. Media monitoring using LexisNexis technology provides insights and news that will inform all those who are working to advance the SDGs. Target SDG 17.16 includes encouraging multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of the sustainable development goals in all countries.
Working mothers often find themselves in a difficult situation when trying to balance work and family responsibilities and to manage expectations about their work and parental effectiveness. Family-friendly policies such as maternity leave have been introduced to address this issue. But how are women who then make the decision to go or not go on maternity leave evaluated?
Previous research suggests that when individuals encounter new information, they interpret it through perceptual ‘filters’ of prior beliefs, relevant social identities, and messenger credibility. In short, evaluations are not based solely on message accuracy, but also on the extent to which the message and messenger are amenable to the values of one's social groups. Here, we use the release of Pope Francis's 2015 encyclical as the context for a natural experiment to examine the role of prior values in climate change cognition.
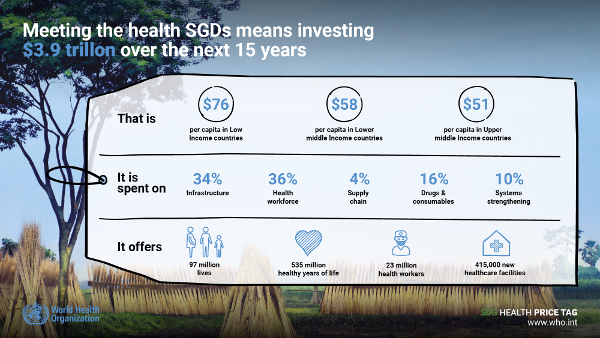
Background The ambitious development agenda of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) requires substantial investments across several sectors, including for SDG 3 (healthy lives and wellbeing). No estimates of the additional resources needed to strengthen comprehensive health service delivery towards the attainment of SDG 3 and universal health coverage in low-income and middle-income countries have been published. Methods We developed a framework for health systems strengthening, within which population-level and individual-level health service coverage is gradually scaled up over time.
A climate mitigation comprehensive solution is presented through the first high yield, low energy synthesis of macroscopic length carbon nanotube (“CNT”) wool from CO2 by molten carbonate electrolysis. The CNT wool is of length suitable for weaving into carbon composites and textiles. Growing CO2 concentrations, and the concurrent climate change and species extinction, can be addressed if CO2 becomes a sought resource rather than a greenhouse pollutant.
Nanoscience is an inspiring and influential discipline of science which have accessible numerous novel and cost-effective yields and applications. Currently, nanotechnology research has been empowering more in agricultural sector, food process and medicinal industries. The surface area to volume ratio of nanoparticles is quite large which have 1–100 nm size. Nanomaterials have superior bioavailability than larger particles, resulting in greater utilization in single cells, tissues and organs.
We develop roadmaps to transform the all-purpose energy infrastructures (electricity, transportation, heating/cooling, industry, agriculture/forestry/fishing) of 139 countries to ones powered by wind, water, and sunlight (WWS). The roadmaps envision 80% conversion by 2030 and 100% by 2050. WWS not only replaces business-as-usual (BAU) power, but also reduces it ∼42.5% because the work: energy ratio of WWS electricity exceeds that of combustion (23.0%), WWS requires no mining, transporting, or processing of fuels (12.6%), and WWS end-use efficiency is assumed to exceed that of BAU (6.9%).
Background Urban transport related exposures and practices are associated with a significant burden of morbidity and premature mortality, which could be prevented by changing current practices. Cities now have access to an increasingly wide range of transport policy measures which continue to expand. However, the health impacts of these measures are not always explicitly defined or well understood and therefore may not be sufficiently considered when selecting policy measures.
Megacities contain at least 10 million people whose wellbeing largely depends on ecosystem services provided by remote natural areas. What is, however, most often disregarded is that nature conservation in the city can also contribute to human wellbeing benefits. The most common mind set separates cities from the rest of nature, as if they were not special kinds of natural habitats.