Industry holds an indispensable relationship with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) formulated by the United Nations, illuminating the fact that sustainable industrial development plays a vital role in achieving these global objectives. Industry, particularly manufacturing, serves as a critical driver for economic growth, employment, and technological advancement. SDG 9, specifically, underlines the importance of industry, innovation, and infrastructure, underscoring the need for resilient infrastructure, inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and fostering innovation. However, the intricate interlinkages between industry and other SDGs must not be overlooked.
For instance, clean and sustainable industrial processes contribute significantly to SDG 13, aiming at climate action, by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving energy efficiency, and adopting clean and environmentally sound technologies. Similarly, SDG 12, responsible consumption and production, demands the industries to promote resource and energy efficiency, sustainable infrastructure, and provide access to basic services, green and decent jobs, and a better quality of life for all. It motivates industries to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
The role of industries extends to SDG 8 (Decent work and Economic Growth) as industries stimulate economic activities that lead to job creation and thus, improve living standards. Also, in respect to SDG 5 (Gender Equality), industrial sectors have the potential to provide opportunities for women in the workforce and help bridge the gender wage gap.
Nevertheless, the transformation to a more sustainable industry is not without challenges. The demands of rapid technological changes, the need for significant capital investments in green technologies, and the transition to a circular economy are some of the hurdles industry faces. Further, this transformation requires a multilevel and multi-stakeholder approach, calling for cooperation among governments, private sectors, academia, and civil society to pave the path to achieving SDGs.
John A. Gladysz is a Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at Texas A&M University, where he holds the Dow Chair in Chemical Invention. He began his academic career at the University of California, Los Angeles and has also held appointments at the University of Utah and Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg. His group's current research centers around organometallic chemistry and branches into catalysis, organic synthesis, enantioselective reactions, stereochemistry, mechanism, and materials and green chemistry. John A.
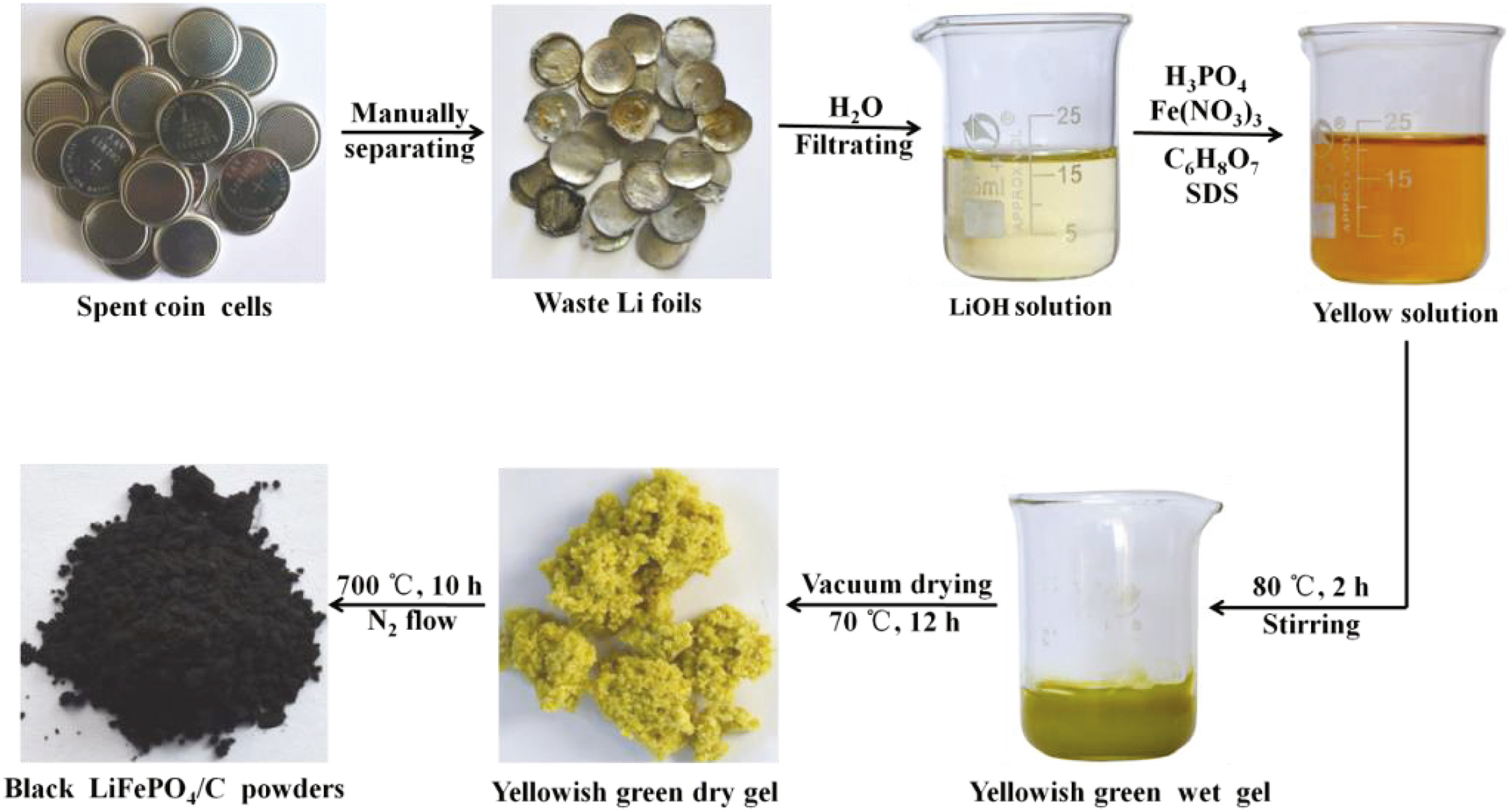
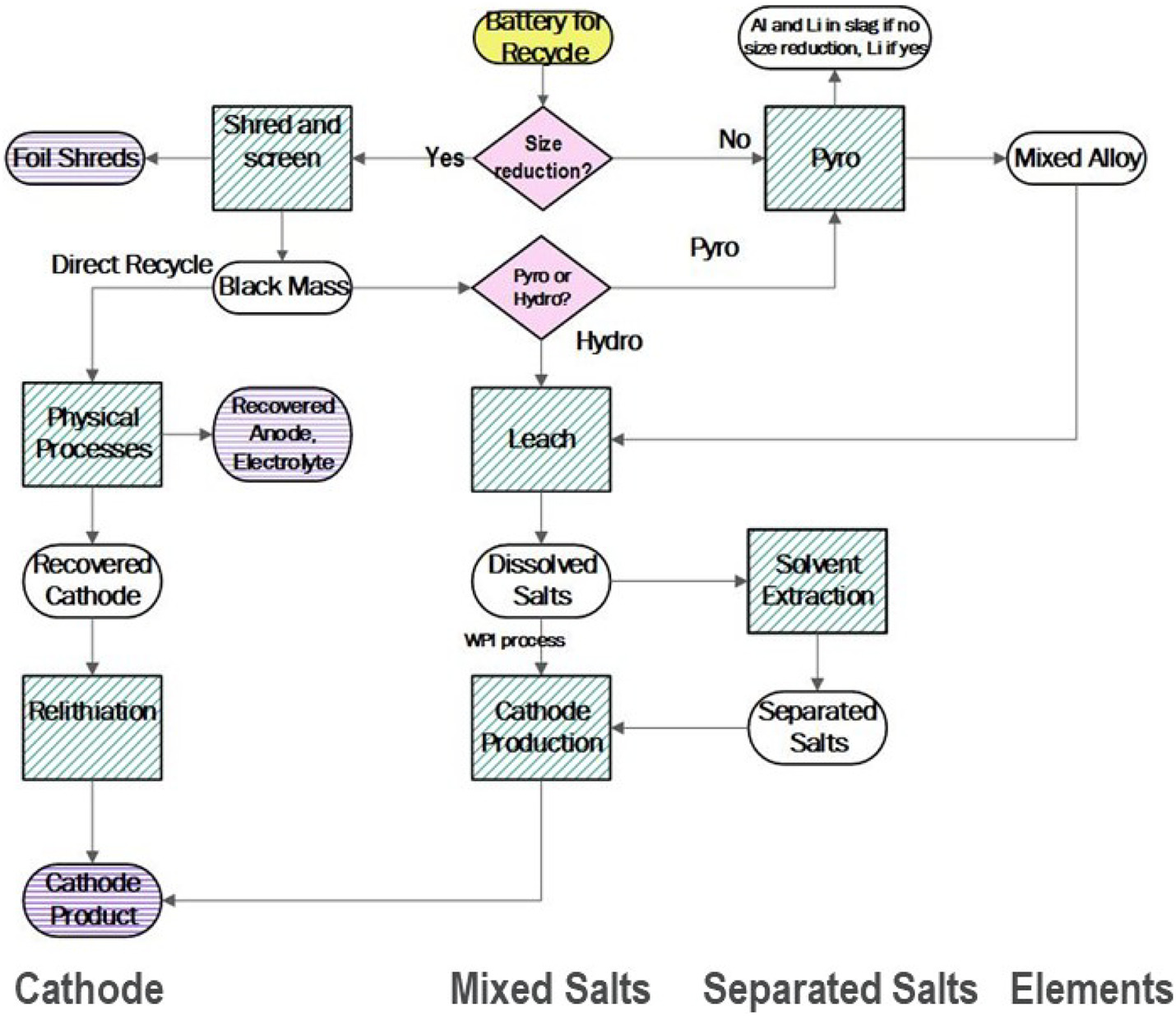
There is a need to develop technology to enable a resource-efficient and economically feasible recycling system for lithium-ion batteries and thus assure the future supply of the component materials. Lithium-ion batteries are complex products, and designs and materials are still evolving, which makes planning for future recovery more challenging. Several processes for recycling are proposed or operating, and each has advantages and disadvantages. This paper compares these processes on technical and economic bases, elucidating differences in benefits as a function of cathode composition.