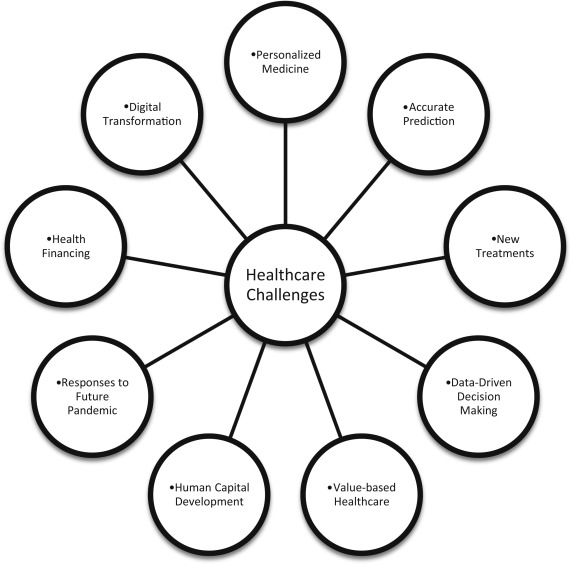
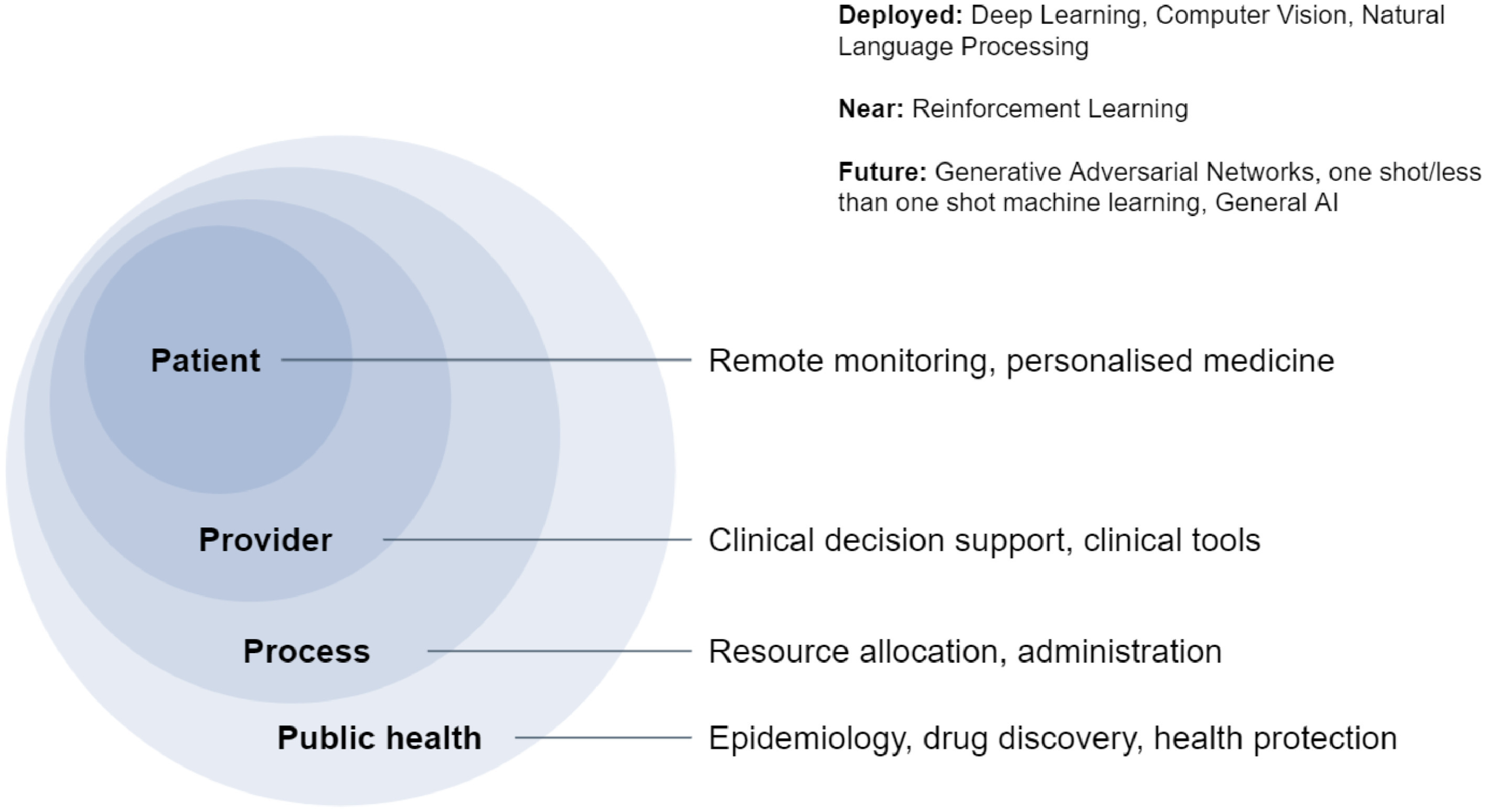
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool in advancing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity by 2030. AI's capabilities, ranging from data analysis to predictive modeling, offer unprecedented opportunities to address complex global challenges outlined in the SDGs. For instance, AI can analyze vast datasets to identify trends and insights related to poverty, hunger, health, education, and environmental degradation, enabling targeted interventions and resource allocation. In the realm of healthcare, AI-powered tools and systems are revolutionizing diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient monitoring, contributing significantly to SDG 3, which aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. By analyzing medical data, AI can identify disease patterns, predict outbreaks, and suggest preventive measures, thereby enhancing healthcare accessibility and affordability.
Moreover, AI's role in climate action (SDG 13) is another area where its impact is profound. Through the analysis of climate data, AI helps in predicting weather patterns, assessing the impact of climate change, and optimizing the use of renewable energy sources. This aids in developing more effective strategies for disaster risk reduction, sustainable agriculture, and energy consumption, aligning with the goals to combat climate change and its impacts. Additionally, AI contributes to achieving SDG 4 (quality education) by personalizing learning experiences through adaptive learning platforms that cater to the individual needs of students, thus improving access to quality education globally. However, the integration of AI into SDG efforts also presents challenges, including ethical considerations, data privacy concerns, and the digital divide. Ensuring that AI technologies are inclusive, transparent, and aligned with human rights is crucial to leveraging AI for the global good without exacerbating inequalities or undermining privacy and security.
The relationship between AI and the SDGs is symbiotic; while AI offers tools and solutions to accelerate progress towards the SDGs, the pursuit of these goals provides a framework for developing and implementing AI technologies responsibly and ethically. As we harness AI's potential, it is imperative to adopt a multi-stakeholder approach that includes governments, the private sector, academia, and civil society. This collaborative effort is essential to create policies, standards, and practices that ensure AI's benefits are widely distributed and its challenges are effectively managed. By doing so, we can maximize AI's contribution to sustainable development, creating a more equitable, resilient, and prosperous world for all.
Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice, How AI Technologies Impact Medical Research and Clinics
2024, Pages 395-399
Emerging Practices in Telehealth
Best Practices in a Rapidly Changing Field
2023, Pages 163-182
The field of digital histopathology has seen incredible growth in recent years. Digital pathology is becoming a relevant tool in healthcare, industrial and research sectors to reduce the saturation of pathology departments and improve the productivity of pathologists by increasing diagnostic accuracy and reducing turnaround times. Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms may be used for the identification of relevant regions, extraction of features from a histological image and overall classification of images into specific classes.
Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics for Smart Healthcare, Next Gen Tech Driven Personalized Med&Smart Healthcare, 2021, Pages 1-9