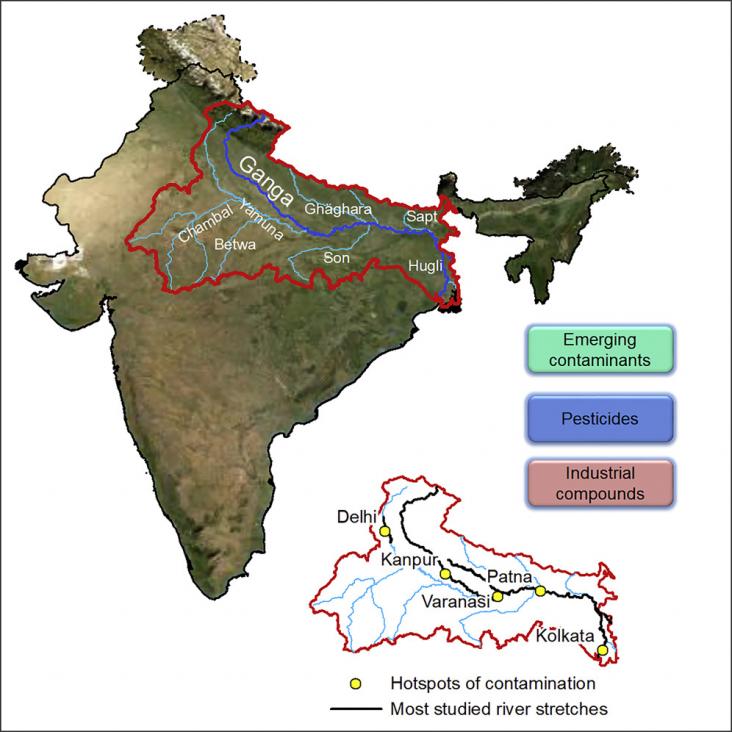
The Ganga basin includes some of the most densely populated areas in the world, in a region characterized by extremely high demographic and economic growth rates.
The National Biogas Policy of Ethiopia introduces plans for the implementation of biogas technologies in rural areas.
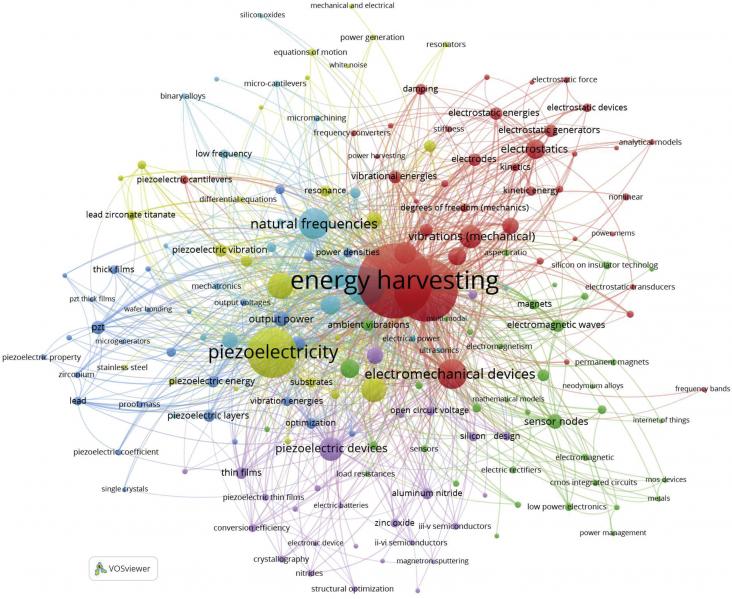
Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) energy harvester's research interests have been increasing rapidly, indicating that the topic has given significant contributions to the sustainable development
Vehicle driving patterns greatly impact the sustainability of the transportation system.
Background: Ambient air pollution is a major environmental cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Cities are generally hotspots for air pollution and disease.
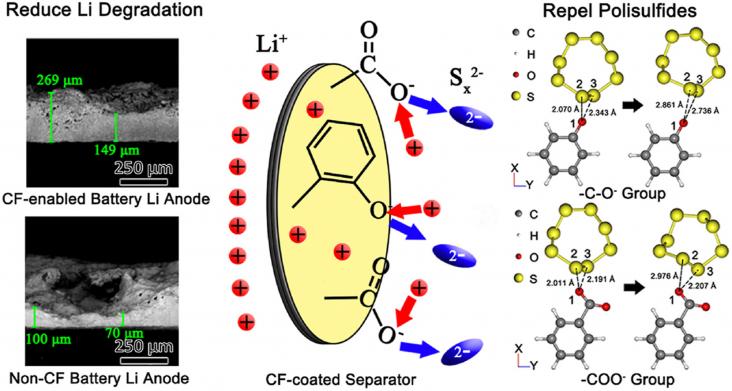
The fast-expanding electric vehicle market demands eco-friendly, high-performance, and low-cost energy storage systems.
The climate emergency and population growth are challenging water security and sustainable urban design in cities worldwide.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are widely regarded as the key to finally making private mobility clean, yet virtually no research is being conducted on their potential contribution to the expansion of imp
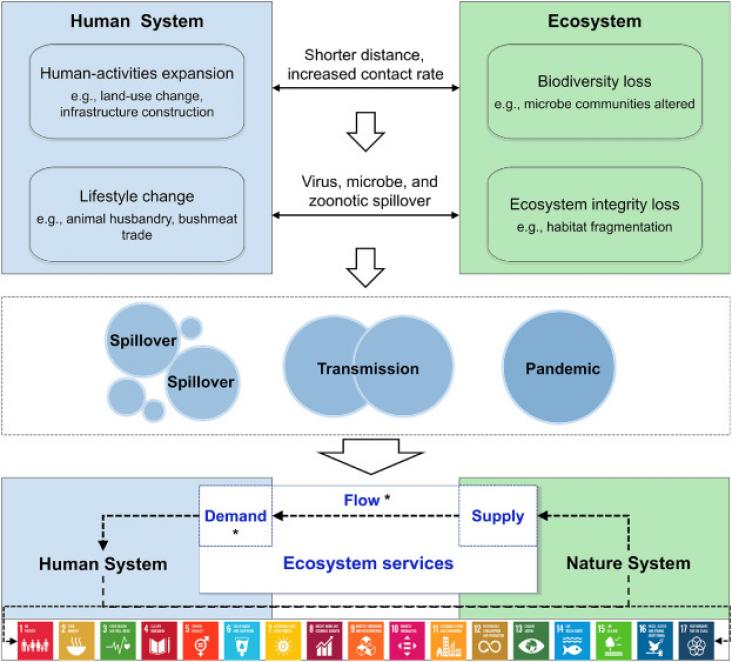
The COVID-19 pandemic has stalled and rolled back progress on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
This article supports SDGs 7, 9 and 11 by utilizing solar photovoltaic, wind energy, solar thermal energy, and battery energy storage, and the special emphasis is placed on the schedulable value of concentrated solar power generation to provide more economical and environmentally friendly energy supply, while integrating multiple renewable energy technologies through artificial intelligence technology to shape the future of cities.
