The role of agriculture in flood risk mitigation has been largely overlooked in the UK government’s national flood resilience review. Farm leaders are concerned that the review contains little mention of agriculture, rural communities or food security. This highlights the need to address flood risk mitigation holistically to support SDG 13.1 to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters, and SDG 2.4 to implement resilient agricultural practices that strengthen capacity for adaptation to climate change, including flooding.
Transportation geotechnics associated with constructing and maintaining properly functioning transportation infrastructure is a very resource intensive activity.
Energy geotechnics involves the use of geotechnical principles to understand and engineer the coupled thermo-hydro-chemo-mechanical processes encountered in collecting, exchanging, storing, and protec
Global and regional health effects of future food production under climate change: A modelling study
Background One of the most important consequences of climate change could be its effects on agriculture.
The internal combustion engine (ICE) does not efficiently convert chemical energy into mechanical energy. A majority of this energy is dissipated as heat in the exhaust and coolant.
Studies of waste-to-energy systems have applied a varying range of indicators to assess their sustainability.
Effective implementation of rules on reduced emission from avoided deforestation and forest degradation (REDD.
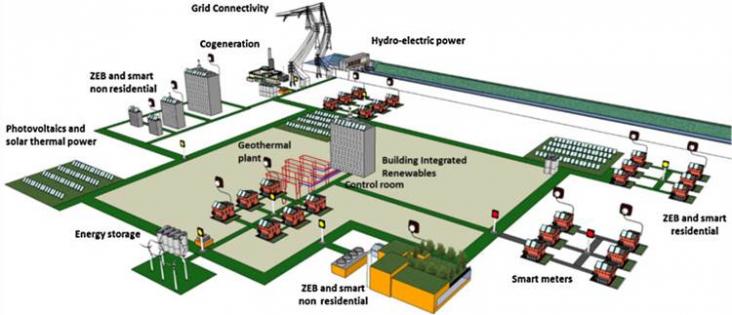
The smart grids are modern electric power grid infrastructure for enhanced efficiency and reliability through automated control, high-power converters, modern communications infrastructure, sensing
This book chapter advances SDGs 3 and 13 by discussing the public health preparedness aspects of preparing for and recovering from severe winter storms.
This book chapter advances SDGs 3 and 13 by explaining the factors contributing to wildfire morbidity and mortality.
