This Article supports SDG 3 by estimating the avoidable health and economic burden of physical inactivity, and highlighting how further investments in and implementation of known and effective policy interventions will support countries to reach the SDG 3 goal of reduction of NCD mortality by 2030.
This Review supports SDG 3 by investigating how licensing could successfully improve the affordability of and timely access to biotherapeutics in low-income and middle-income countries, by identifying key elements needed to support access to affordable biosimilars in these countries.
This article supports SDG's 2, 3 and 12 by considering production steps (cell extraction, cell line establishment, cell culture and scaffolding) and challenges (technology limitations, consumer acceptance & law and legislation) for the development of lLab-based meat, which is more sustainable and safer to consume than conventional meat.
This study examined the cross-sectional and retrospective longitudinal associations between erythrocyte omege 3 (ω-3) index and cognition, brain imaging, and biomarkers among older adults. Longitudinally, low ω-3 index was associated with greater Aβ accumulation and WMS cognitive decline but unexpectedly with lower total Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale cognitive subscale (ADAS-Cog) cognitive decline. Although no associations were cross-sectionally found in the whole population, low ω-3 index was associated with lower WMS cognition and higher tau accumulation among ApoE ε4 carriers.
Chen and Holtzman review the emerging roles of both innate and adaptive immunity, their alterations, their interplay, and their contributions to the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. They proposed that targeting dysregulated innate and adaptive immune responses in both brain parenchyma and border structures could lead to important therapeutics for preventing and treating the disease.
This Article supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by assessing the contribution of smoking to the social inequalities in dementia. The results suggest that smoking in midlife does mediate some of this inequality.
How to determinemicroplatsctis in samples in a green way? Often sample preparation steps involve environmentally harmful chemicals. This artcile decsibes a robust, efficient and green sample preparation with a high separation quality.
This Article supports SDG 3 and 7 by providing robust evidence of an increased risk of cardiovascular or respiratory disease within 24 h after exposure to air pollution or temperature.
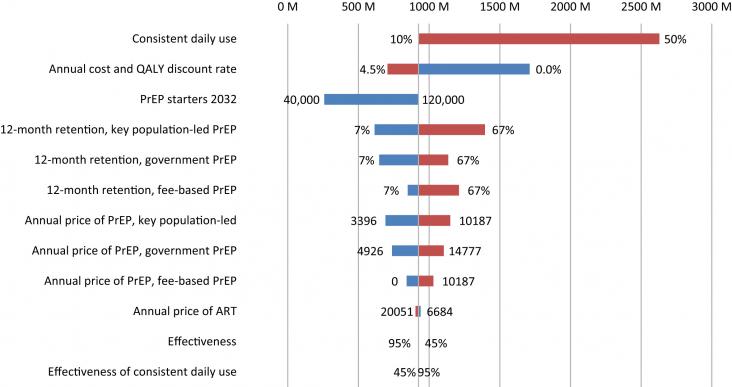
PrEp interventions led by Key populations are more cost effective in delivering these services.
This viewpoint supports SDGs 3, 5, 10 and 16, focusing on the drivers of Black maternal mortality and advocating the collection of disaggregated data to support improvements in Black maternal health.
