To advance goal 6 (clean water and sanitation), this chapter explores different desalination processes to make seawater drinkable, which is an obvious solution to any water shortages. Given the high-polluting energy required in the desalination process, solar-desalination technologies is considered.
Elsevier,
Competition for Water Resources: Experiences and Management Approaches in the US and Europe, 2017, Pages 19-35
This book chapter addresses goals 6 and 12 by providing an overview of water resources in Europe and the associated anthropogenic and natural pressures. It further introduces the main instrument of the European Union (the Water Framework Directive) initiated as a response to the expected water crisis.
Professor Paul T. Anastas holds the Teresa and H.
The detection of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs), known as emerging contaminants (ECs), in the environment has attracted growing concern due to their toxicity and potential h
London's ability to remain a world-leading city in an increasingly globalised economy is dependent on it being an efficient, low-risk place to do business and a desirable place to live.
This study sought to assess the relationship between regulatory and educational approaches to nutrient management and homeowner behaviors, perceptions, and knowledge of best management practices (BMPs
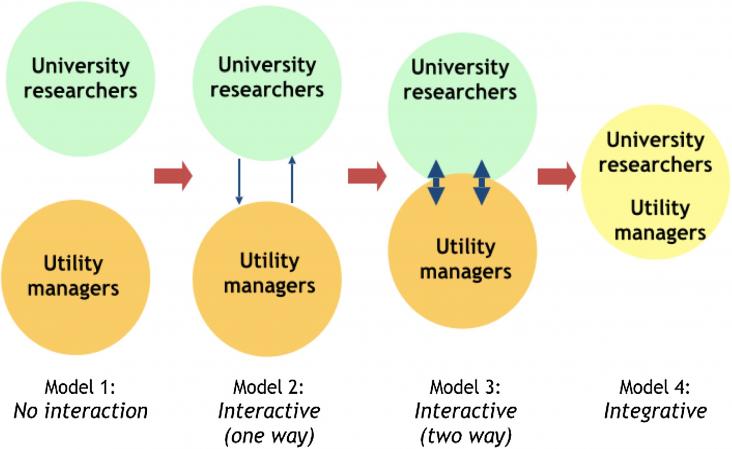
In the face of intensifying stresses such as climate change, rapid urban population growth, land use change, and public concern with rates and use restrictions, water management is becoming increasing
Ensuring future water security requires broad community support for changes in policy, practice, and technology, such as those involved in delivering alternative water schemes.
Access to water in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) continues to be a challenge to the extent that there are more people without access to water in 2015 than in 1990.
This paper uses ‘Medieval’ drought conditions from the 12th Century to simulate the implications of severe and persistent drought for the future of water resource management in metropolitan Phoenix
