Neurobiology of Brain Disorders (Second Edition), Biological Basis of Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders, 2022, Pages 313-336
This book chapter advances SDG #3 and #10 by reviewing several key topics that influence our understanding of pathogenic mechanisms and lead to the identification of novel therapeutic strategies. These include the diagnostic spectrum of MCI and AD, genetic risk alleles associated with late-onset AD, structures of gamma-secretase and tau, imaging and fluid biomarkers, the role of microglia and neuroinflammation, and novel animal models of AD.
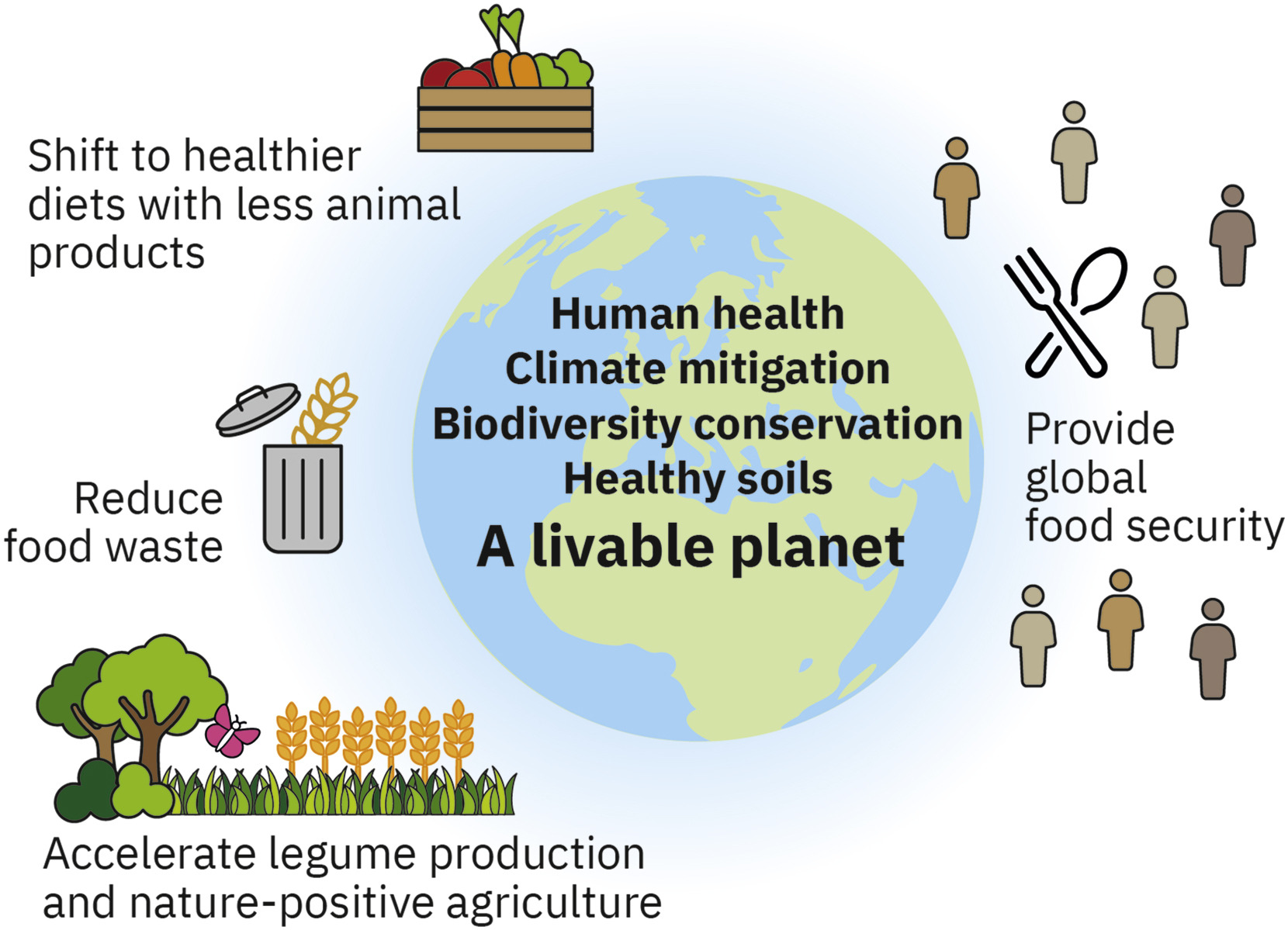
The transformation toward a healthy, just, and environmentally friendly food system needs to be reinforced—and not abandoned—in the face of the Russia-Ukraine war. We need comprehensive solutions that bring short-term relief and also avert the existential threat our food system poses to the health of people and the planet.
Background: The effect of long-term exposure to air pollution on the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is still controversial, and the role of the interactions of air pollution with genetic risk and lifestyle in COPD risk is unclear. Methods: We included 452762 participants derived from the UK Biobank. Annual concentrations of air pollutions, including particle matter (PM2.5, PM10), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), were assessed using land-use regression model.
This article supports SDGs 5, 7 and 10 by integrating the principles of equality, diversity, and inclusivity (EDI) into all aspects to correct historical and structural inequalities, and establishing an inclusive culture to achieve the justice urgently needed for the global transition to net zero. the progress can be made in the fields of energy and artificial intelligence.
Refugees need a place where both their physical and mental security is assured. This study looks at how the UN HCR program to resettle refugees is helping.
Climate policy targets.
The results in this paper have implications for consumers and policy makers, as well as other food system actors. Consumers following individual strategies can make important contributions towards more sustainable food systems. To facilitate this shift, changes in food environments are needed and a coordinated action plan with coherent policies that targets a thorough redesign of the food system, including several of the proposed strategies, is needed to achieve large systemic effects. This could encompass suitable education measures, incentives, as well as rules for production, processing, retail, gastronomy, transport, and consumption.