The concept of “Smart City” has been proposed by governments, the business community, advocacy groups, and research institutions as a means to solve common urban problems and improve the quality of life for citizens. Although a Smart City has the potential to change our cities for the better, it also may unintentionally reinforce existing inequalities. In particular, without appropriate strategies that support inclusion, persons with disabilities and seniors may experience social and digital exclusion in communities.
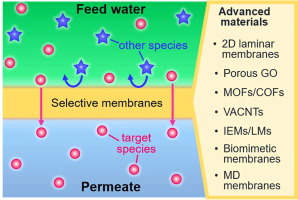
In this review, the authors discuss the drivers, fundamental science, and potential enabling materials for high selectivity membranes, as well as their applications in different water treatment processes.
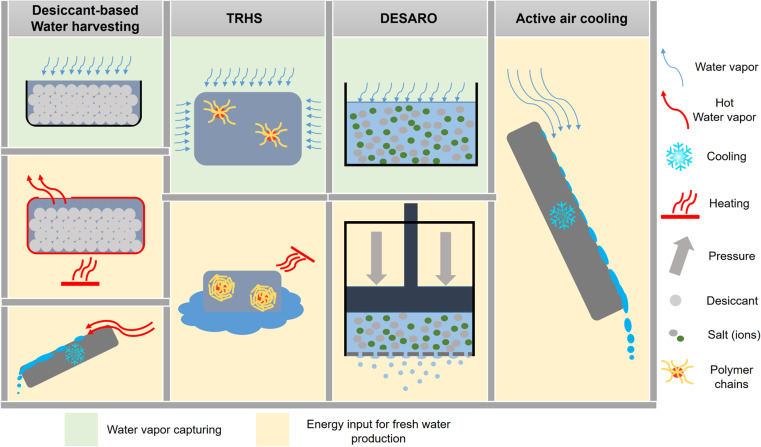
Producing clean, fresh drinking water from atmospheric water vapor can play an important role in alleviating water scarcity in drought-prone regions of the world. This perspective explores the current trends and future outlook for atmospheric water harvesting technologies.
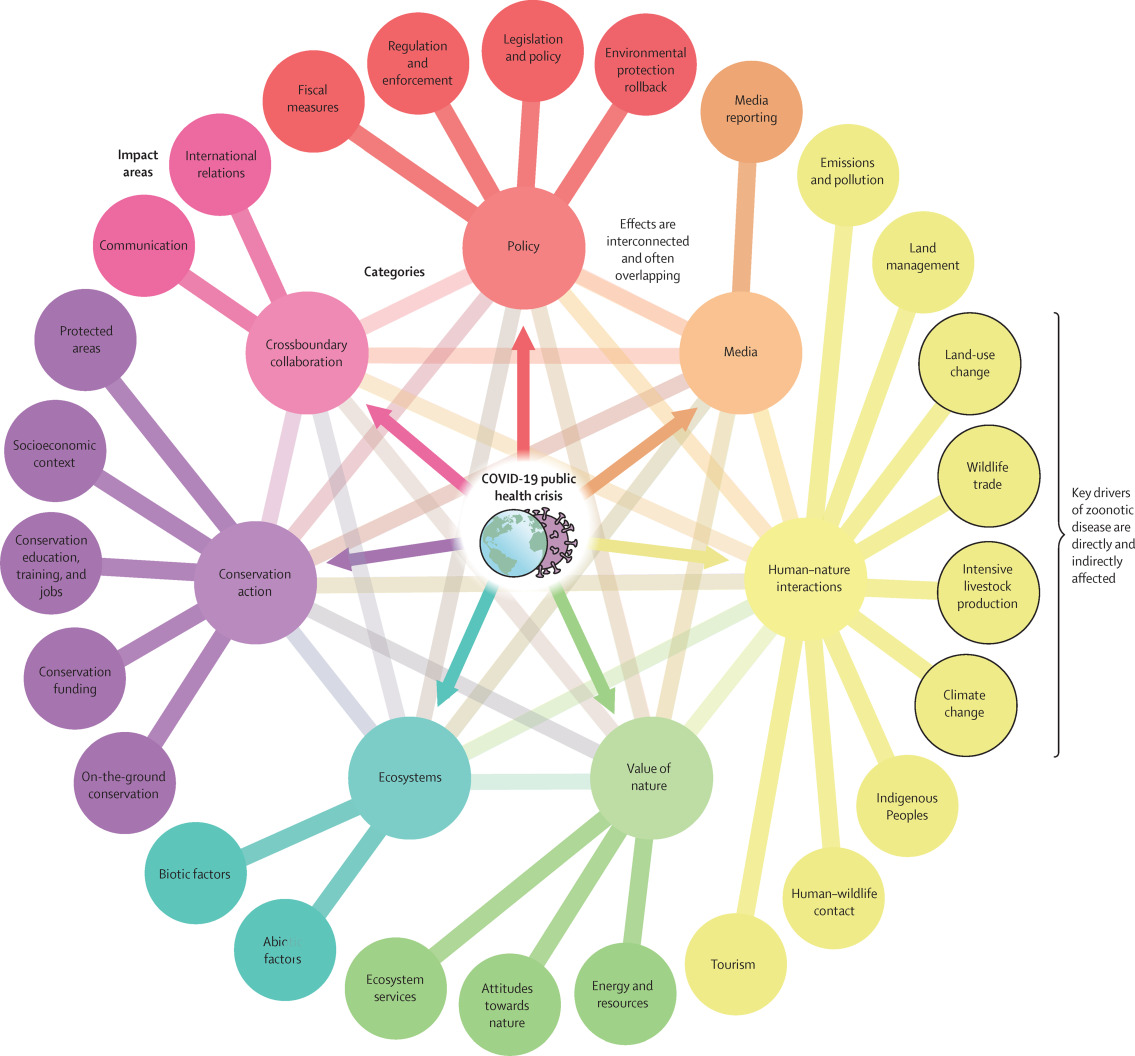
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, caused by zoonotic SARS-CoV-2, has important links to biodiversity loss and ecosystem health. These links range from anthropogenic activities driving zoonotic disease emergence and extend to the pandemic affecting biodiversity conservation, environmental policy, ecosystem services, and multiple conservation facets. Crucially, such effects can exacerbate the initial drivers, resulting in feedback loops that are likely to promote future zoonotic disease outbreaks.
This articles describes an investigative study in a suspected wildlife hunting incident in which molecular biology techniques were employed to identify the species involved. The genetic analysis in this study was suitable for diagnosing the species and concluding a criminal investigation. Molecular forensic techniques can, therefore, provide an important tool that enables local law enforcement agencies to apprehend poachers.
This book chapter advances SDG3 Good Health and Wellbeing and SDG10 Reducing Inequalities by focusing on educationally meaningful methods to develop programs that exploit voice recognition engines, based on cloud services, so that a smartphone device can remotely trigger typical farming actions or query the values of several critical parameters of the farm specifically for the elderly and disabled.
A Review in support of SDG 12, summarising the advantages and dsiadvantages of different models used to label foods according to their environmental and nutritional impact. This review highlights the need to develop reference values for the classifiation of sustainable foods
An Article in support of SDGs 2 and 12, assessing the financial costs of healthy and sustainable diets in countries with different income levels
To date, much of the literature on the clinical effectiveness of digital mental health interventions has come from higher income settings, but there is less evidence from low-resource settings. Notwithstanding varied access and gaps in access or connectivity, especially in rural areas, digital technologies offer unparalleled opportunities for transforming the delivery and use of mental health interventions in low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs).
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health and Wellbeing by providing an overview of current pain trends among PWH, treatment guidelines, and suggestions for how to best fulfill the needs to decrease pain, prevent opioid misuse, and improve quality of life for this unique patient population.