Biodiversity and ecosystems, encompassing the vast variety of life on Earth and the natural systems they inhabit, are fundamental to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Their importance is acknowledged explicitly in several SDGs due to their critical role in maintaining environmental balance and supporting human life and well-being.
SDG 14 (Life Below Water) and SDG 15 (Life on Land) are directly focused on the conservation and sustainable use of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, respectively. These goals recognize the intrinsic value of biodiversity and the vital services ecosystems provide, such as habitat for wildlife, carbon sequestration, and soil formation. The preservation and restoration of ecosystems like forests, wetlands, and coral reefs are essential for maintaining biodiversity, which in turn supports ecological resilience and the sustenance of human life.
The role of biodiversity and ecosystems in achieving SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) is significant. The variety of life forms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, underpins agricultural productivity. Pollinators, soil organisms, and genetic diversity of crops are all crucial for food production and agricultural resilience. Ecosystems support agriculture not just in terms of crop yield but also in sustaining the natural resources like soil and water, upon which agriculture depends.
Similarly, SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation) is closely tied to the health of ecosystems. Natural habitats such as forests and wetlands play a key role in filtering and purifying water, maintaining the water cycle, and regulating water flow. This natural filtration process is vital for providing clean drinking water and supporting sanitation systems.
Biodiversity and ecosystems are also crucial for SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being). Natural environments regulate diseases by supporting a balance among species that, in turn, can control pest and disease outbreaks. Additionally, a vast number of medical discoveries, including medicines and treatments, have their origins in biological resources, underscoring the potential of biodiversity in contributing to human health and well-being.
Moreover, biodiversity and ecosystems play a significant role in addressing climate change, linking to SDG 13 (Climate Action). Ecosystems such as forests and oceans are major carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Protecting and restoring these ecosystems are vital strategies for climate change mitigation. Additionally, healthy ecosystems provide crucial services for climate change adaptation, such as protecting against extreme weather events and helping communities adjust to changing environmental conditions.
However, achieving these goals requires addressing threats to biodiversity and ecosystems, such as habitat destruction, pollution, overfishing, and invasive species. It also involves balancing the needs of human development with environmental conservation, ensuring sustainable use of natural resources.
Biodiversity and ecosystems are integral to achieving multiple SDGs. Their conservation and sustainable use not only benefit the environment but are essential for food security, water purity, human health, and combating climate change. The protection and restoration of biodiversity and ecosystems are therefore crucial steps towards sustainable development and ensuring the well-being of current and future generations.
The Paris Agreement to keep global temperature increase to well-below 2 °C and to pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5 °C requires to formulate ambitious climate-change mitigation scenarios to reduce CO2 emissions and to enhance carbon sequestration. These scenarios likely require significant land-use change. Failing to mitigate climate change will result in an unprecedented warming with significant biodiversity loss. The mitigation potential on land is high. However, how land-based mitigation options potentially affect biodiversity is poorly understood.
Insect pollinators are becoming visible to societies. Many peer-reviewed papers evidence biophysical and ecological aspects of managed and non-managed insect pollinators. Evidence on stressors of declines yield peer-reviewed calls for action. Yet, insect pollinator declines are inherently a human issue, driven by a history of land-use trends, changes in technologies, and socio-cultural perceptions that unwittingly cause and perpetuate declines. Conservation requires integrating social and ecological understandings to reconfigure human behaviors across societies’ sectors.
Ocean health is critical for human well-being but is threatened by multiple stressors. Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity agreed to protect 10% of their waters by 2020. The scientific evidence supporting the use of marine protected areas (MPAs) to conserve biodiversity stems primarily from knowledge on fully protected areas, but most of what is being established is partially protected. Here, we assess the protection levels of the 1,062 Mediterranean MPAs.
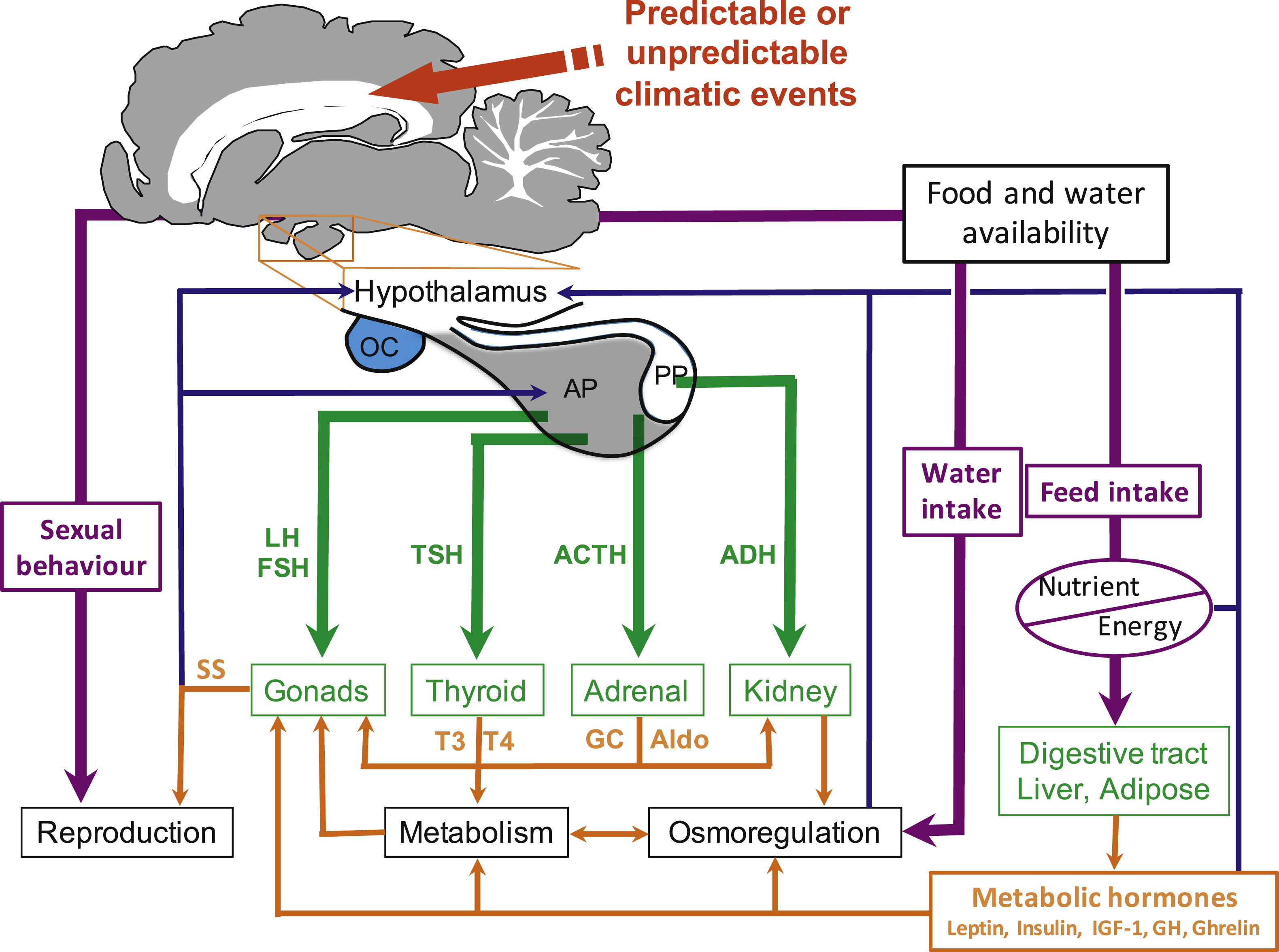
Climate change will expose mammals to an array of stressors, some new, and some with increased frequency and severity. Those stressors influence endocrine and metabolic function, with potential consequences for the survival and persistence of mammalian species. Here, we review the similar consequences of climate change on the physiological function of terrestrial mammals, including direct effects of increasing air temperatures and reduced water availability, as well as the indirect effect of reduced or unpredictable food supply.
On April 22nd 1970, 20 million Americans took to the streets, parks and auditoriums to demonstrate for a healthy, sustainable environment in massive coast-to-coast rallies. Spearhead by Senator Nelson, after witnessing the ravages of the 1969 Santa Barbara oil spill, the first Earth Day protests forced environmental protection onto the national political agenda and led to the creation of the United States Environmental Protection Agency and the passing of key environmental legislation.