The demand-supply balance of electricity systems is fundamentally linked to climate conditions.
This article supports SDG 15 by demonstrating overall rangelands greening has a complex impacts on biodiversity under high environmental heterogeneity and societal dynamics.

Rivers and estuaries transport vast amounts of carbon from land to oceans and play an important role in the global carbon cycle through their high rates of carbon respiration and sequestration.
Background: Various retrospective studies have reported on the increase of mortality risk due to higher diurnal temperature range (DTR).
The principal motivations for the worldwide trend towards reducing meat consumption are health, the environment and animal welfare.

This paper assesses the influence of land development patterns on intra-urban thermal variation in a densely-developed subtropical city, considering joint effect from greenspace pattern and built-up g

Meat consumption has been increasing since the 1960s, but especially from the 1980s decade to today.

This article highlights the winning proposals of the fifth edition of the Elsevier Foundation Green & Sustainable Chemistry Challenge. The winning proposals were chosen for their innovative green chemistry aspects and their large positive impact on the environment, contributing to SDGs 7, 8, 10, 12, 13, 14 and 15.
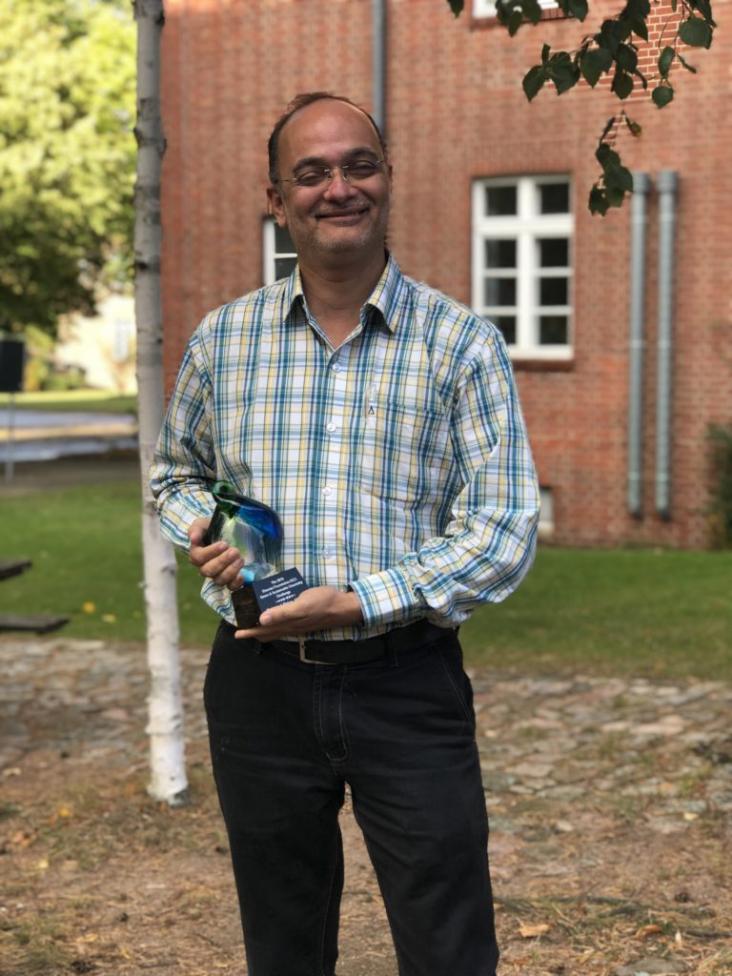

In 2019, Dr. Ankur Patwardhan, Head of the Biodiversity Department at Maharashtra Education Society’s Abasaheb Garware College, Pune, India, was awarded the second prize in the Elsevier Foundation Green and Sustainable Chemistry Challenge. Contributing to SDGs 13 and 15, his project, “Butterfly attractant for pollination and ecosystem health”, focused on the plant-pollinator interactions that play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem balance and aimed at enhancing floral visits by butterflies through the development of natural attractant formulations. One year later, we interviewed Dr. Patwardhan about his experience at the Challenge, as well as the upcoming steps for his project.
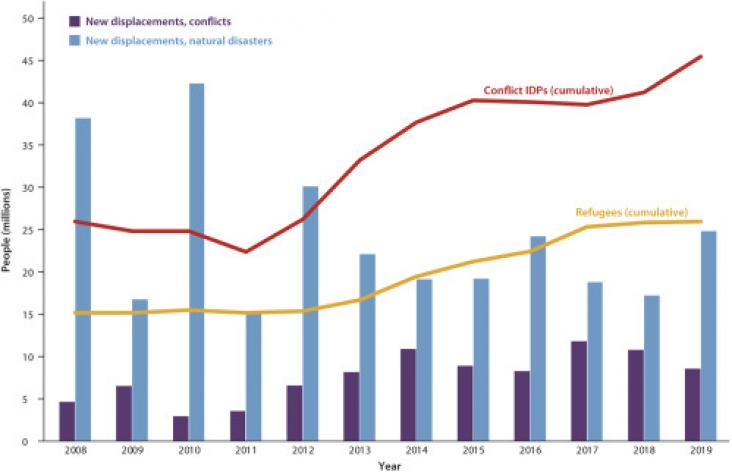
Climate change is reshaping the comparative advantage of regions and hence driving migration flows, principally toward urban areas.
