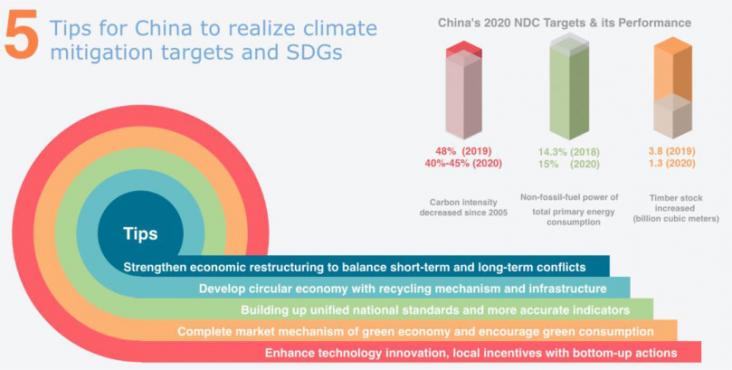
This paper summarized China's integrated actions (2015 onwards) that benefit both climate change mitigation and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).

Viral diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, known as arboviruses, pose a significant threat to human life and are a major burden on many health systems around the world.
Purpose: Given incomplete data reporting by race, we used data on COVID-19 cases and deaths in U.S. counties to describe racial disparities in COVID-19 disease and death and associated determinants.
To be socially accepted widely, the emerging circular bioeconomy needs to rely increasingly on residual bio-based feedstock and waste, hence reducing its dependency on crops which are in competition w
In 2016, the World Health Organization declared that ‘Health is one of the most effective markers of any city's successful sustainable development’ (World Health Organisation, 2016).
Purpose and setting: Infrastructure is a global multi-trillion dollar market presenting many opportunities and risks for sustainable development.
Few public health interventions can match the immense achievements of immunization in terms of mortality and morbidity reduction.

This articles highlights one of the winning proposals of the Elsevier Foundation Green & Sustainable Chemistry Challenge, “Butterfly attractant for pollination and ecosystem health.” The project, which combines ecology and chemistry, involved field observations and lab-based experiments to protect biodiversity in the Western Ghats of India by increasing butterfly pollination, contributing to SDGs 13, 15 and 17.
This study suggests that climate and anthropogenic factors play critical roles in controlling the spatial and seasonal distribution of China's ecosystem fire disturbances.
This study indicates that croplands have a large potential to sequester Carbon through implementing better land use management practices, which may partially offset soil organic carbon loss caused by climate change.
