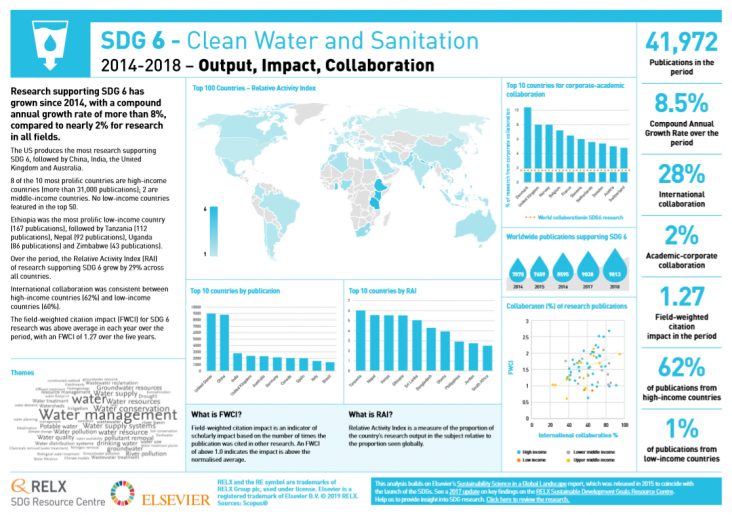
The latest analysis of SDG-supporting research focusses on SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation. This graphic shows key metrics for research into clean water and sanitation.

RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers, has announced the winners of the 2019 RELX Environmental Challenge. The Challenge supports innovative solutions to improve SDG 6 (clean water and sanitation).
Linking to SDGs 6 (clean water and sanitation), 12 (responsible consumption and production) and 17 (partnerships for the goals), this website catalogues and facilitates water stewardship projects in river basins and regions around the world.
This chapters focuses on the consequences mining on river contamination in Bolivia. An unintended consequence of mining has been widespread contamination of riverine environments by toxic trace metals and metalloids. (e.g., arsenic, antimony, cadmium, mercury, lead, and zinc). The type, magnitude, and extent of contamination differ significantly between the humid to hyperhumid tropical rainforests in the north and the semiarid, heavily impacted, rivers in the south.
In the last couple of years, deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have been raising a lot of attention mainly due to their versatility and their easy and speedy preparation without the need of further purifi
The number of countries with a national development plan has more than doubled, from about 62 in 2006 to 134 in 2018.
This paper relates to remote sensing of water use and water stress in the African savanna ecosystem at a local scale, as well as the development and validation of a monitoring tool.

This article selection displays a sample of research that Elsevier publishes in its microbiology and medical journals, highlighting Elsevier's contribution to the efforts of battling the huge problem of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Research within this selection supports SDGs 3 (good health and well-being), 6 (clean water and sanitation), 12 (responsible production and consumption) and 17 (partnerships for the goals).
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development is ambitious and inclusive, but how well are these global aspirations likely to result in implementable policy change for water and sanitation?

Water–Sanitation–Hygiene (WASH) remains vital for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, yet many countries have not localised the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDG 6, which
