This Climate Countdown paper supports SDGs 3 and 13 by summarising procress through 27 climate indicators in China from 2021 to 2022.
Study of hydrochemical and geochemical characteristics and solute fluxes in Upper Ganga Basin, India
Journal of Asian Earth Sciences: X, Volume 8, 1 December 2022
This article supports SDGs 13 and 14 because it confirmed the significant correlation observed between flux and river discharge in Bhagirathi, a turbulent Himalayan river. Himalayan rivers are considered the most sensitive of all the ecosystems to the impact of climate change.
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 13 by using credible climate and population projections to estimate future heatwave-attributable deaths under different emission scenarios and to explore the drivers underlying these patterns of changes in China.
This article supports SDG 6, 3, 9 by exploring the diversity and ecology of freshwater diatom as bioindicators of 6 major freshwater ponds of Kanyakumari district, Tamilnadu
Bay of Bengal (BoB) has immense significance with respect to ecological diversity and natural resources. Studies on microbial profiling and their functional significance at sediment level of BoB remain poorly represented. Herein, we describe the microbial diversity and metabolic potentials of BOB deep-sea sediment samples by subjecting the metagenomes to Nanopore sequencing.
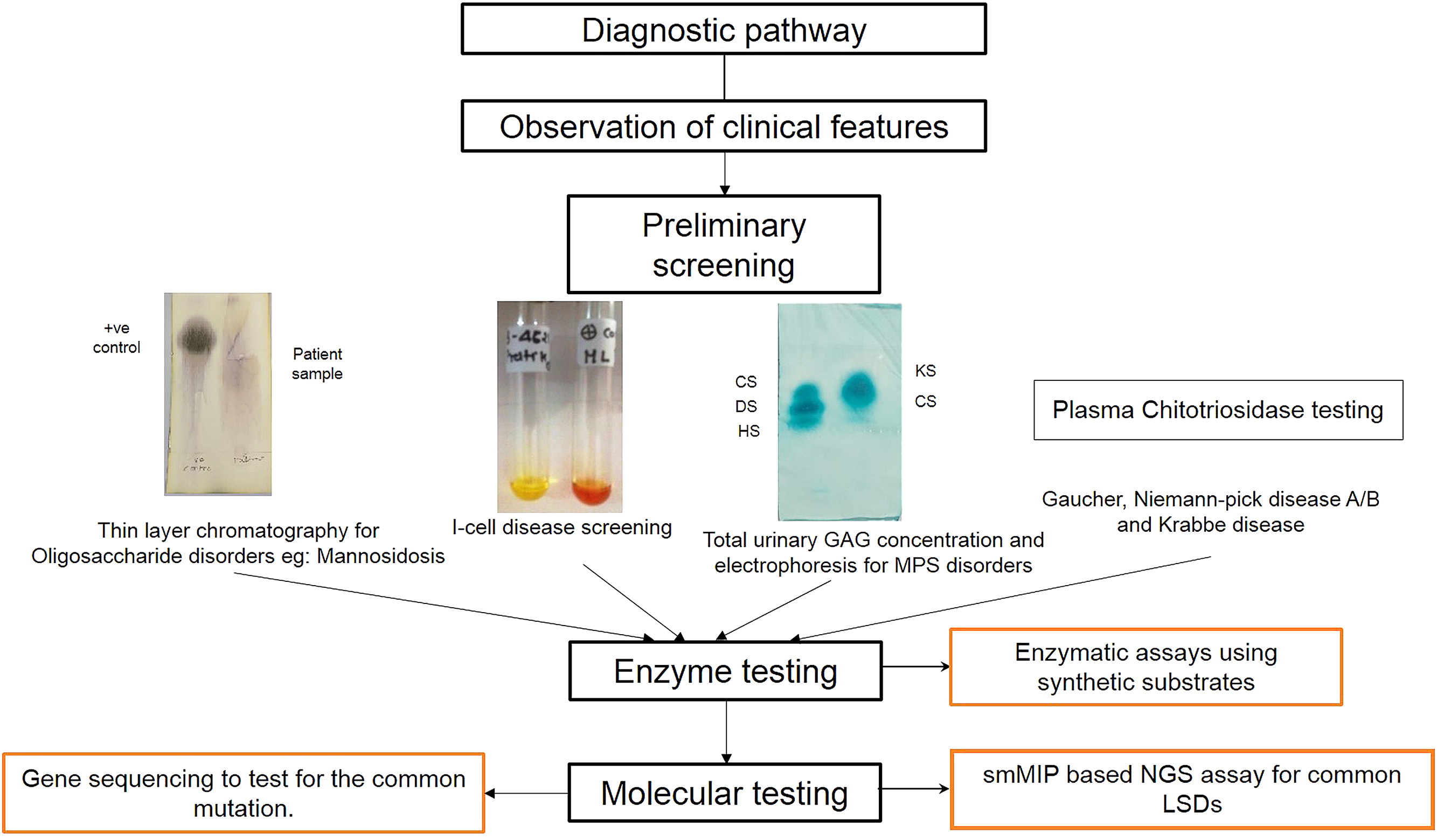
This Review supports SDG 3 by summarising the spectrum of lysosomal storage disorders (a group of rare diseases), their molecular epidemiology, and prevention efforts in India.
Turner syndrome (TS) is a rare congenital ovarian hypoplasia. This letter to the editor outlines that it is easy to misdiagnose by simply relying on conventional karyotypes. TS patients should be diagnosed as soon as possible, and the chromosomal karyotype should be determined as soon as possible as the prognosis of gonadblastoma can be further differentiated into various malignant germ cell tumors.
This article ties to SDG 3. This article investigated whether wartime stress exposures occurring during adolescence and early adulthood affect weathering in late adulthood via linear regression with data from the Vietnamese Health and Aging Study (VHAS).
This article ties to SDG 3 & 4. The present study adapted and assessed the efficacy of a brief psychological group intervention, the STAR program: Strengths, Transitions, Adjustments and Resilience for university students who are Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs).The present study adapted and assessed the efficacy of a brief psychological group intervention, the STAR program: Strengths, Transitions, Adjustments and Resilience for university students who are Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs).
It is important to learn how to manage Asian male elephant reproductive behaviour for the long-term sustainability of the species. The authors provide important information that can be directly applied to improving the well-being of elephants and other wildlife.