Addressing efficient management of energy has become a central objective due to the scarcity of traditional energy sources and global warming. To cope with this overarching issue, some technological solutions such as Smart Grids, Internet of Things or Demand response are proposed. However, the majority of them overlooks the role of human beings in the equation.
Most of the terrestrial world is experiencing high rates of land conversion despite growth of the global protected area (PA) network. There is a need to assess whether the current global protection targets are achievable across all major ecosystem types and to identify those that need urgent protection. Using recent rates of habitat conversion and protection and the latest terrestrial ecoregion map, we show that if the same approach to PA establishment that has been undertaken over the past three decades continues, 558 of 748 ecoregions (ca.
If moral concern for nonhuman nature underpins conservation, it is essential to understand how individuals populate their “moral communities,” a core concept from environmental ethics, with various elements of biodiversity. Using data from an online survey of the United States public (N = 1331), we investigated the extent to which respondents' moral communities align with four worldviews discussed in the environmental ethics literature: anthropocentrism, zoocentrism, biocentrism, and ecocentrism. Each worldview provides a vision for how the moral community should be constituted.
Refuges and refugia are important to conservation management because of their potential to protect species from difficult-to-manage threats such as changing climate, extreme events (e.g., drought, fire) and biotic threats (e.g., disease, invasive species). To provide conservation managers with an evidence-based approach to identifying refuges and refugia, we ask: which places have been observed to function as refuges/refugia, with results reported in the scientific literature? We systematically reviewed the past 20 years of research into refuges/refugia.
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and is a serious health problem. The disease is expected to increase further in the upcoming years with the increase of the elderly population. Developing new treatments and diagnostic methods is getting more important. In this study, we focused on the early diagnosis of dementia in Alzheimer's disease via analysis of neuroimages. We analyzed the data diagnosed by the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) protocol.
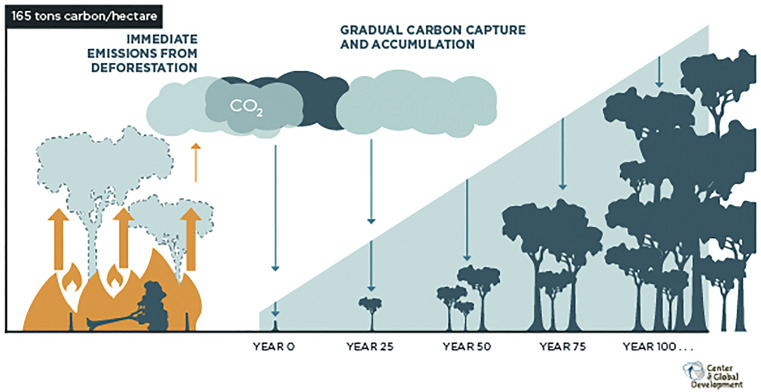
Largely driven by the corporate sector, the recent surge of interest in trees as a solution to climate change has a distinct emphasis on planting trees. Realizing anticipated benefits will require managing the risks and trade-offs of land-use interventions and embracing the imperative of protecting existing forests.
Forests are key components of the global carbon cycle and dominate mitigation strategies for climate change and biodiversity loss. In contrast, the importance of and threats facing ocean forests—kelp forests—are comparatively underappreciated. Yet, increasing the global area of kelp forests would enhance biodiversity and drawdown CO2, mitigating climate change.
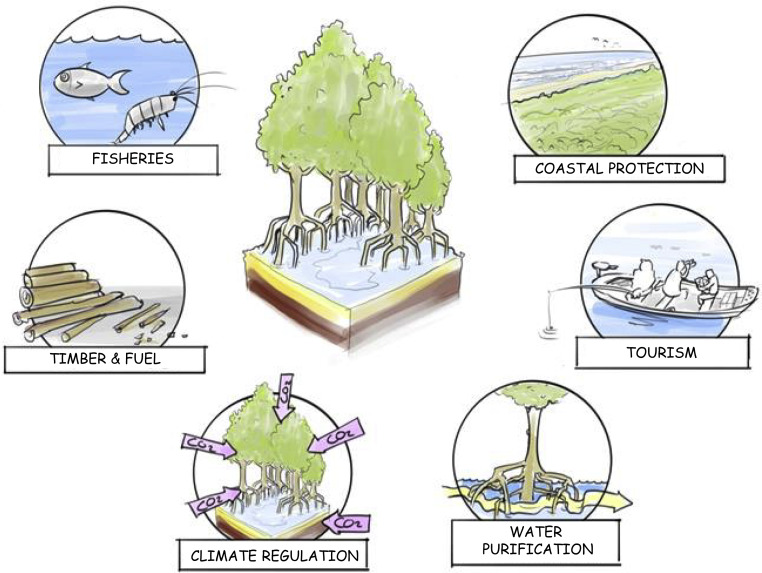
Mangrove forests are found on sheltered coastlines in tropical, subtropical, and some warm temperate regions. These forests support unique biodiversity and provide a range of benefits to coastal communities, but as a result of large-scale conversion for aquaculture, agriculture, and urbanization, mangroves are considered increasingly threatened ecosystems.
The SDG Impact of COVID-19 podcast series gathers expert opinion exploring the impact of COVID-19 on the Sustainable Development Goals. In this segment, we get the view of Dr Christian Toennesen, Senior Partner at Carnstone and Chair of the Responsible Media Forum.
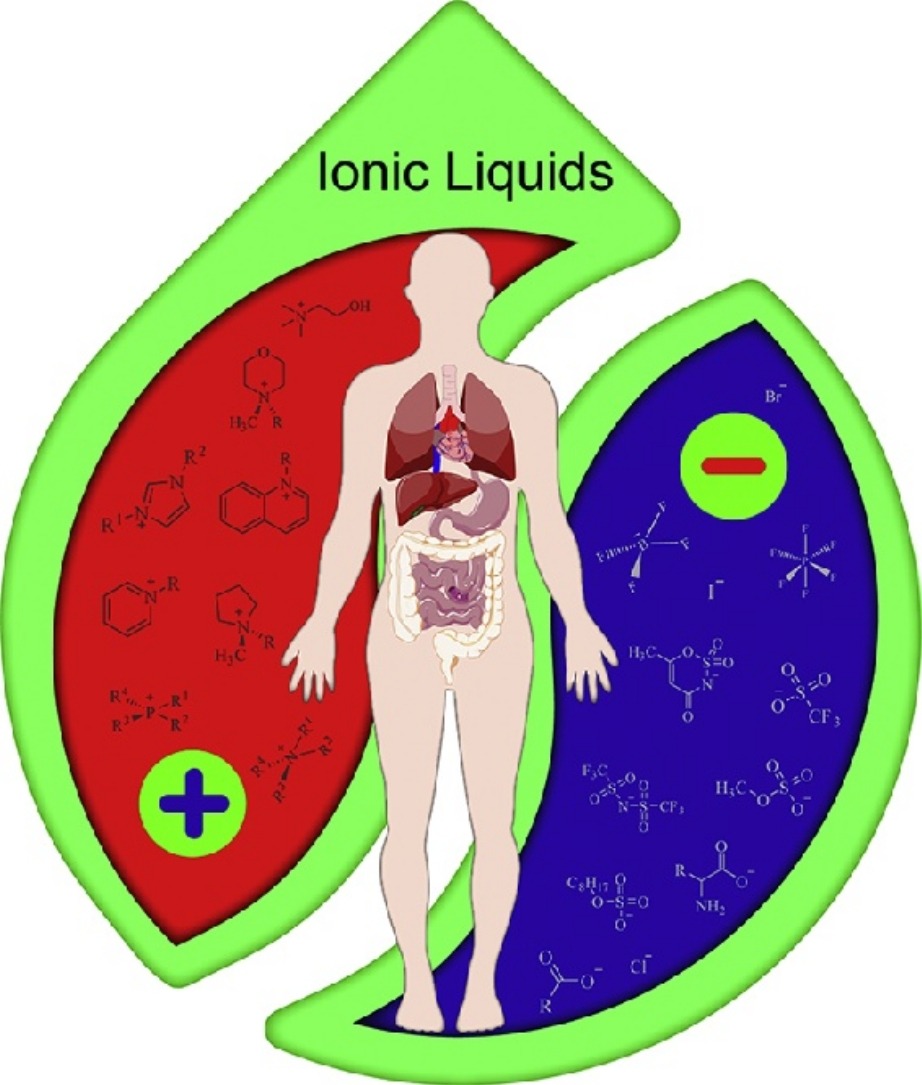
Beyond their traditional use as green solvents, new applications have become available for ionic liquids (ILs) in drug delivery. Their flexible tunability enables task-specific optimization of ILs at molecular level. Thus, ILs have been exploited to improve the solubility and permeability of drugs and relieve the polymorphic problems associated with crystalline active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Controlled preparation of drug nanocarriers are also achieved by using ILs either as media or as functional agents.