Elsevier,
Virus Research, Volume 311, 2 April 2022
Viral metagenomics is widely applied to characterize emerging viral pathogens but it can also reveal the virome composition in health and disease. The evaluation of the virome in healthy blood donors can provide important knowledge on possible transfusion threats.
Elsevier, Free Radical Biology and Medicine, Volume 183, April 2022
Genistein is a phytoestrogen that, due to its structural similarity with estrogen, can both mimic and antagonize estrogen effects. Early analysis proved that at high concentrations, genistein inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation, thereby suggesting an anticancer activity. Since then, many discoveries have identified the genistein mechanism of action, including cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction, as well as angiogenesis, and metastasis inhibition.
Elsevier,
Applied Geochemistry, Volume 139, April 2022
The predicted future climate change can be expected to have an impact on the biogeochemical conditions in pit lakes that must be considered when modelling pit lake water quality. Climate change might e.g., affect temperature and precipitation patterns, which can influence other factors such as water balance, hydrology, limnology, and biogeochemical prediction
Elsevier,
Energy Storage Materials, Volume 46, April 2022
The impact of climate change and increasing demand for energy requires the development of more sustainable energy technologies. Hence, thermal energy storage (TES) methods can contribute to more appropriate thermal energy production-consumption through bridging the heat demand-supply gap. In addition, TES is capable of taking over all elements of the energy nexus including mechanical, electricity, fuel, and light modules by means of decreasing heat losses, waste recovery, and energy-saving approaches to improving the system's performance.
Elsevier, Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 6, 1 April 2022
This paper concludes that effective local implementation of MSN (Multisectoral Nutrition) policy requires country-level commitment together with local leadership and capacity building, and community engagement to ensure efforts fit program contexts.
Elsevier
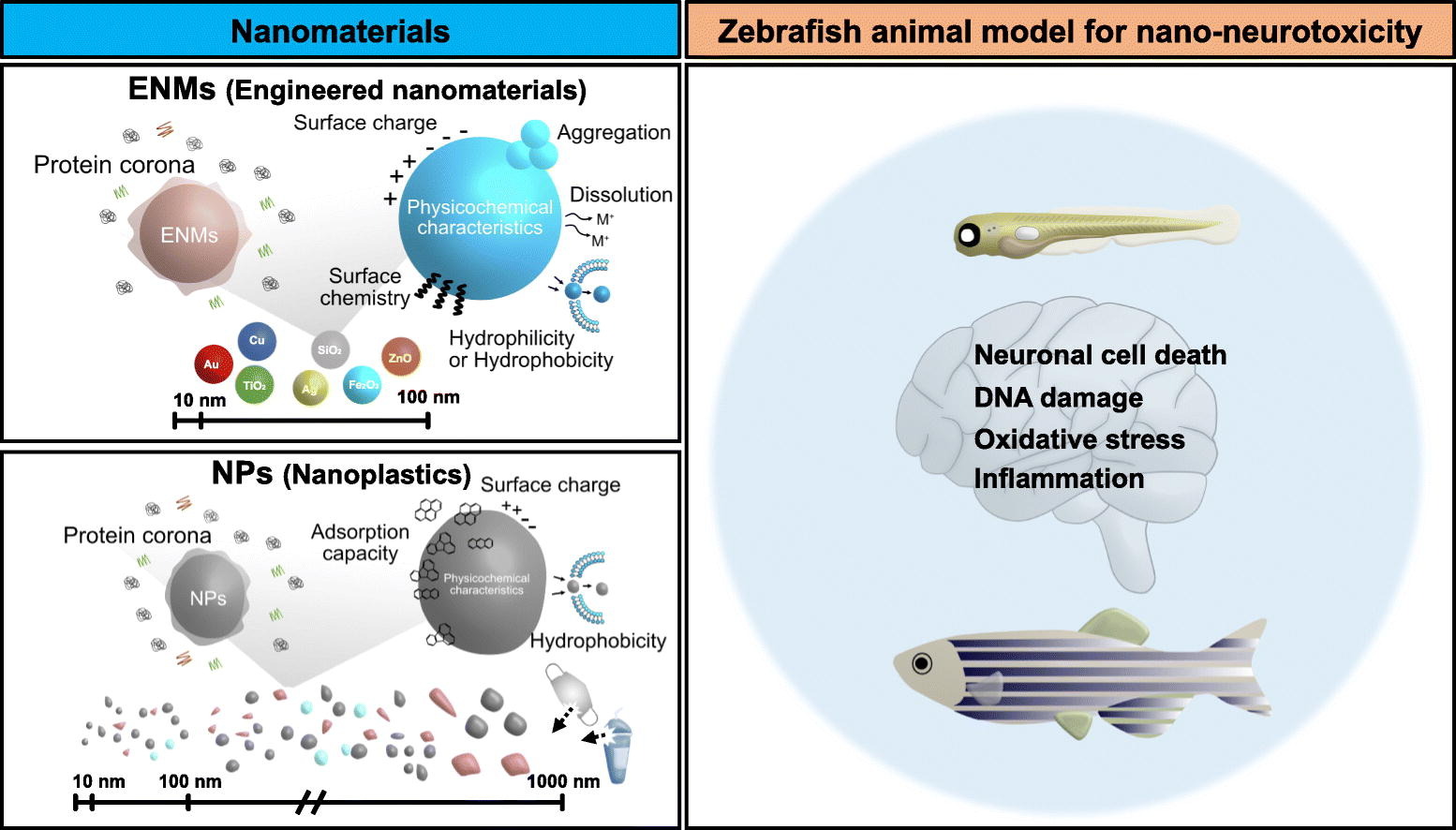
Nanomaterials including engineered nanomaterials and nanoplastics emerge as new pollutants to the ecosystem. In particular, studies on the adverse effects of nanomaterials on the brain are limited.
Various animal models offer opportunities to evaluate neurological effects of nanomaterials. We summarize recent studies and key findings on neurotoxicological effects of nanomaterials, focusing on zebrafish.