Elsevier,
Fuel Communications
Volume 10, March 2022, 100045
This paper looks into the issues around renewable energy with a view to identify the opportunities for Nigeria and critically review the nation's renewable energy policy vis-à-vis the efforts and achievement of governments and indigenous practitioners.
Elsevier,
IBRO Neuroscience Reports, Volume 11, December 2021
Depression is a serious mental and mood disorder with global health and economic burden. Nutrition through the application of necessary food classes or herbs as well as their phytochemicals, may go a long way to effectively manage depression. This nutritional strategy should be given more attention in research, assessment and treatment for those with depression and other mental illness in low income countries, especially in Africa.
Elsevier,
Redox Biology, Volume 48, December 2021
MiRNA mouse models are emerging tools to study the protective and/or deleterious effects of miRNAs in human diseases. In the current study, miR-455-3p TG and KO models were successfully generated by using pronuclear injection of miR-455-3p transgene to mouse embryo and CRISPER/Cas9 knockout techniques.
Elsevier,
SLAS Discovery, Volume 26, December 2021
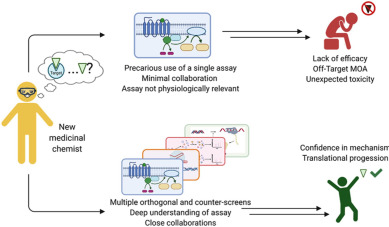
"A diverse range of biochemical and cellular assays are used by medicinal chemists to guide compound optimization. The data collected from these assays influence decisions taken on structure-activity relationship (SAR) campaigns. Therefore, it is paramount that medicinal chemists have a solid understanding of the strengths and limitations of each assay being used to characterize synthesized analogs.
This Perspective Article takes a look at assays relevant to Gaucher, Pompei, Wolman, and Fabry disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and Cystic Fibrosis."
Elsevier, Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 5, 1 December 2021
This study explores the pathways from a nutrition-sensitive agriculture intervention to improved diets of women and young children. It also tests theoretical agriculture-to-nutrition pathways by comparing the authors' documented pathways with the pathways from the widely used TANDI (Tackling the Agriculture–Nutrition Disconnect in India) framework.
Elsevier,
Current Research in Microbial Sciences, Volume 2, December 2021
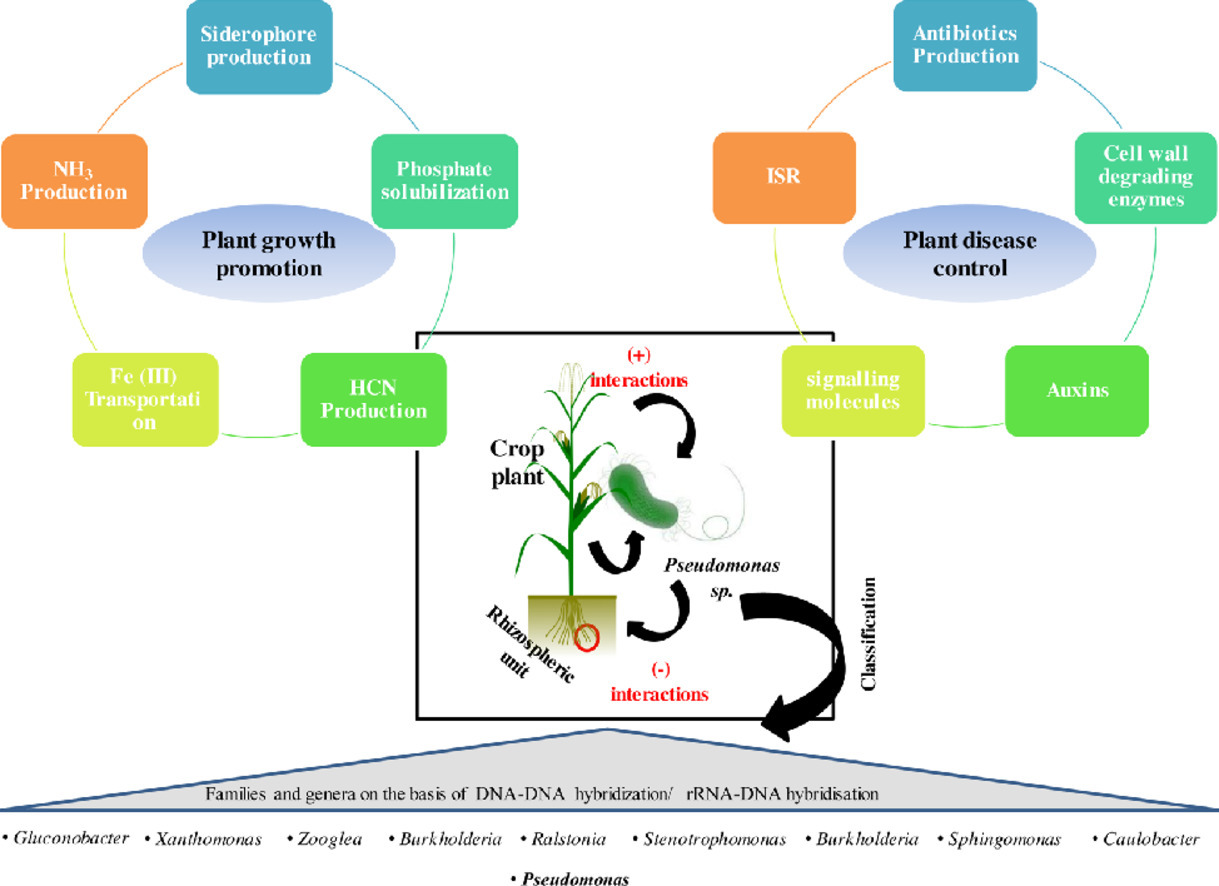
Fluorescent and non-fluorescent species of Pseudomonas are important for plant growth promotion, phytopathogenic control and plant disease management. Ecologically significant applications of Pseudomonas in biocontrol and bioaugmentation are crucial for maintaining food security.
Elsevier,
Current Research in Microbial Sciences, Volume 2, December 2021
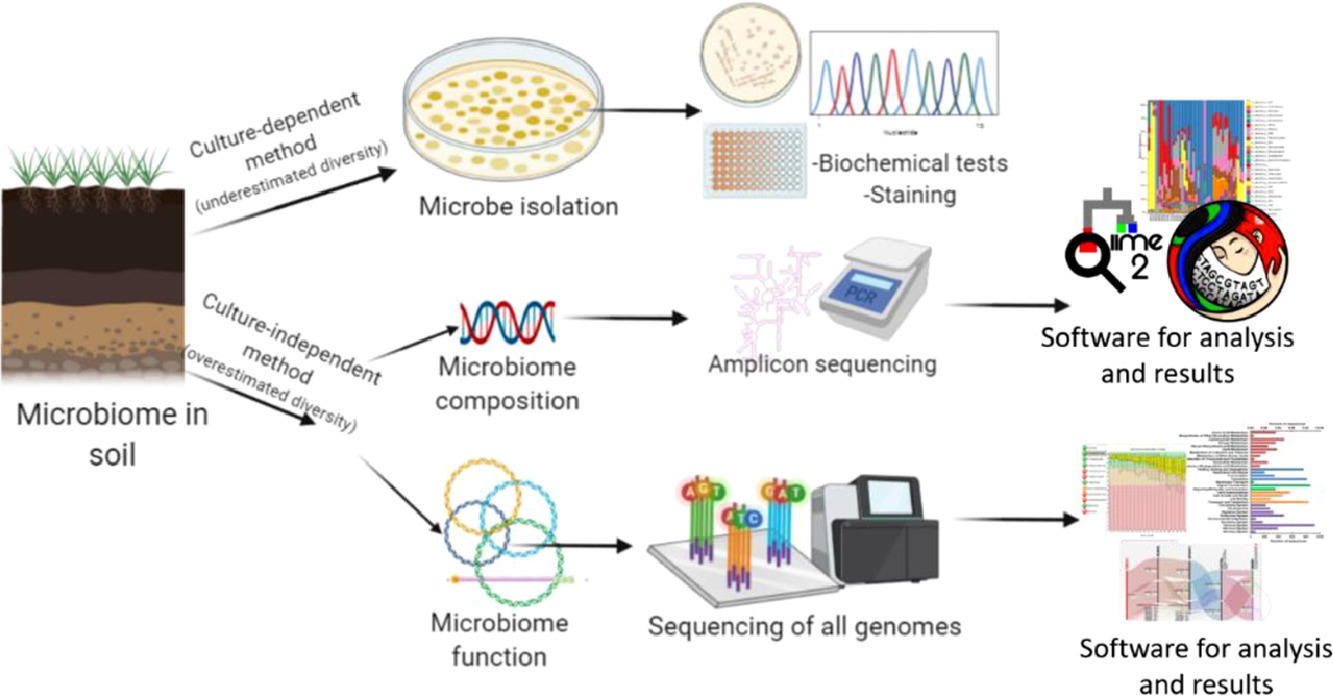
In this review, we explore how agriculture is implementing the use of microbial inoculants (single species or consortia) to improve crop yields, and discuss current strategies to study plant-associated microorganisms and how their diversity varies under unconventional agriculture.
Elsevier,
Current Research in Microbial Sciences, Volume 2, December 2021
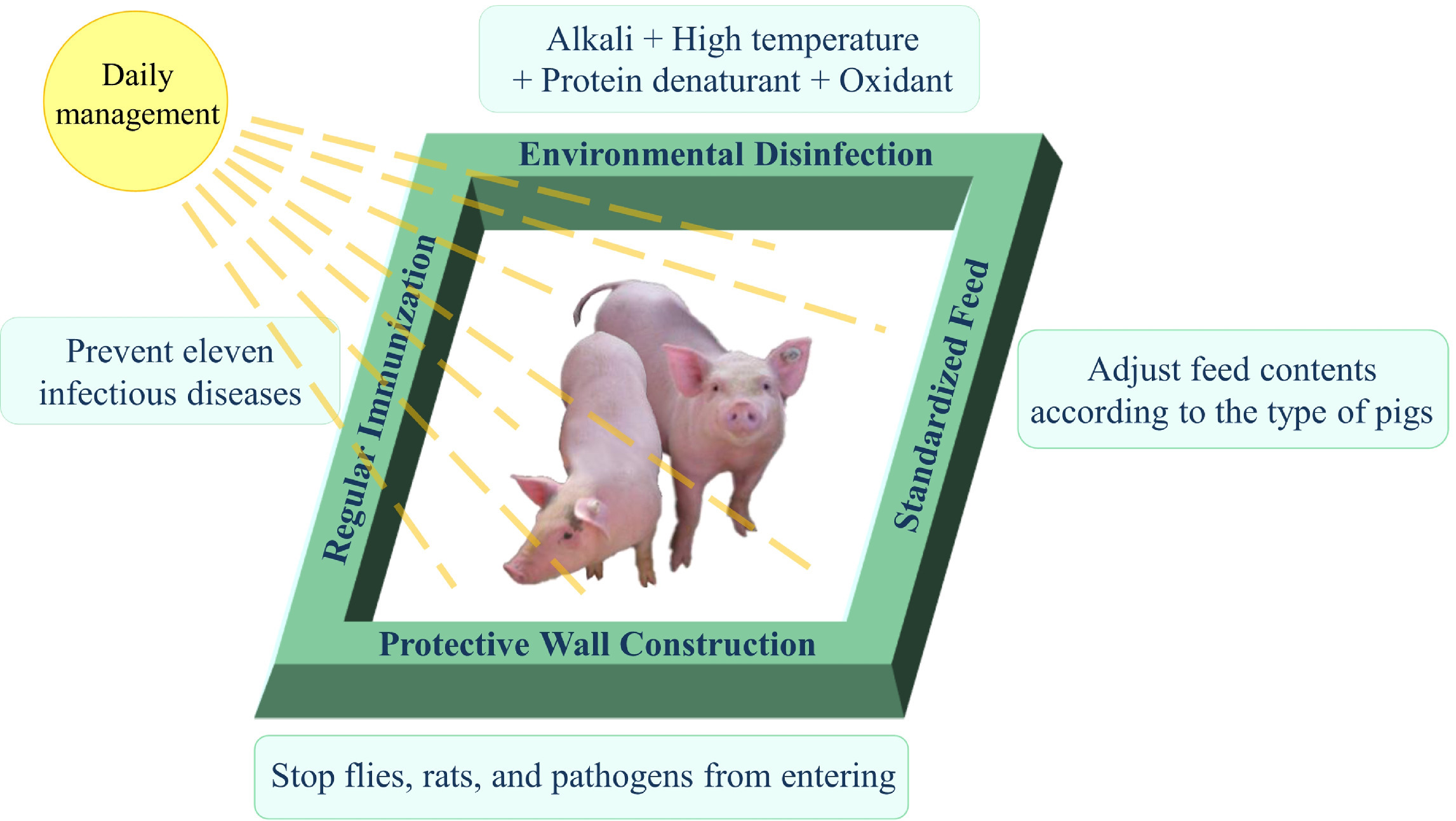
African swine fever outbreak has caused serious economic losses in China. Consequently, pork supply faces huge demand. An effective biosafety procedure was developed for production of pigs in small-scale farms in China.