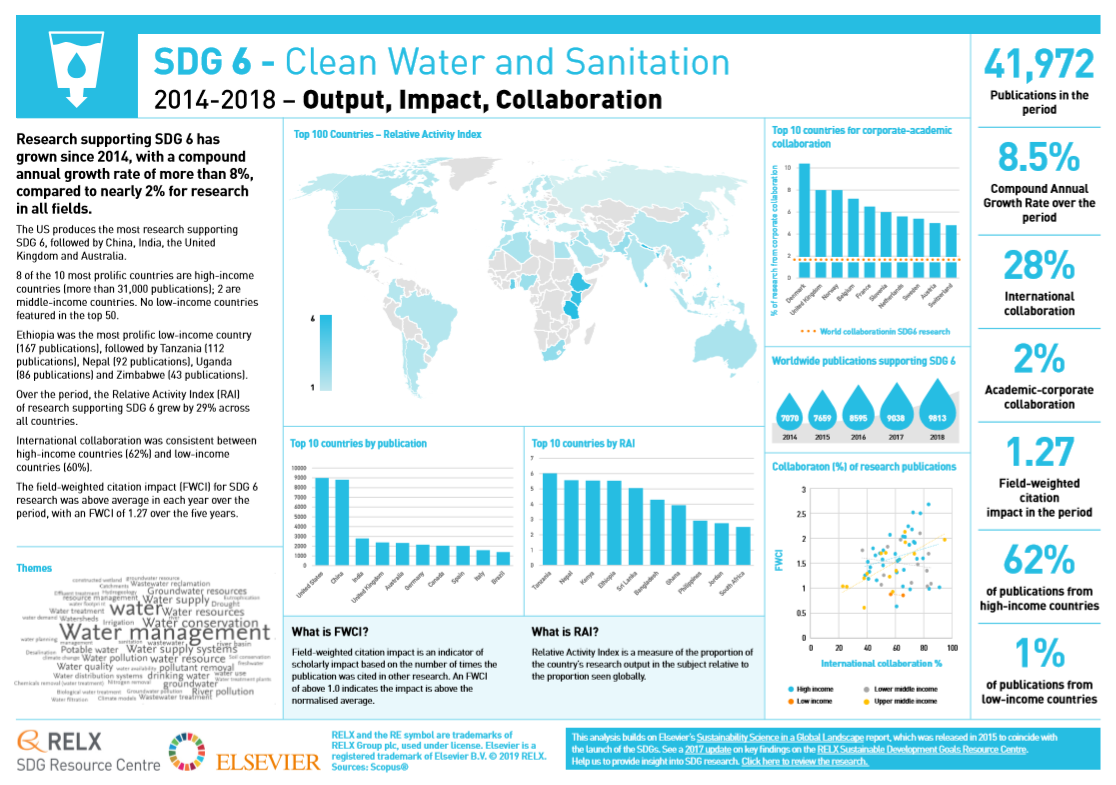
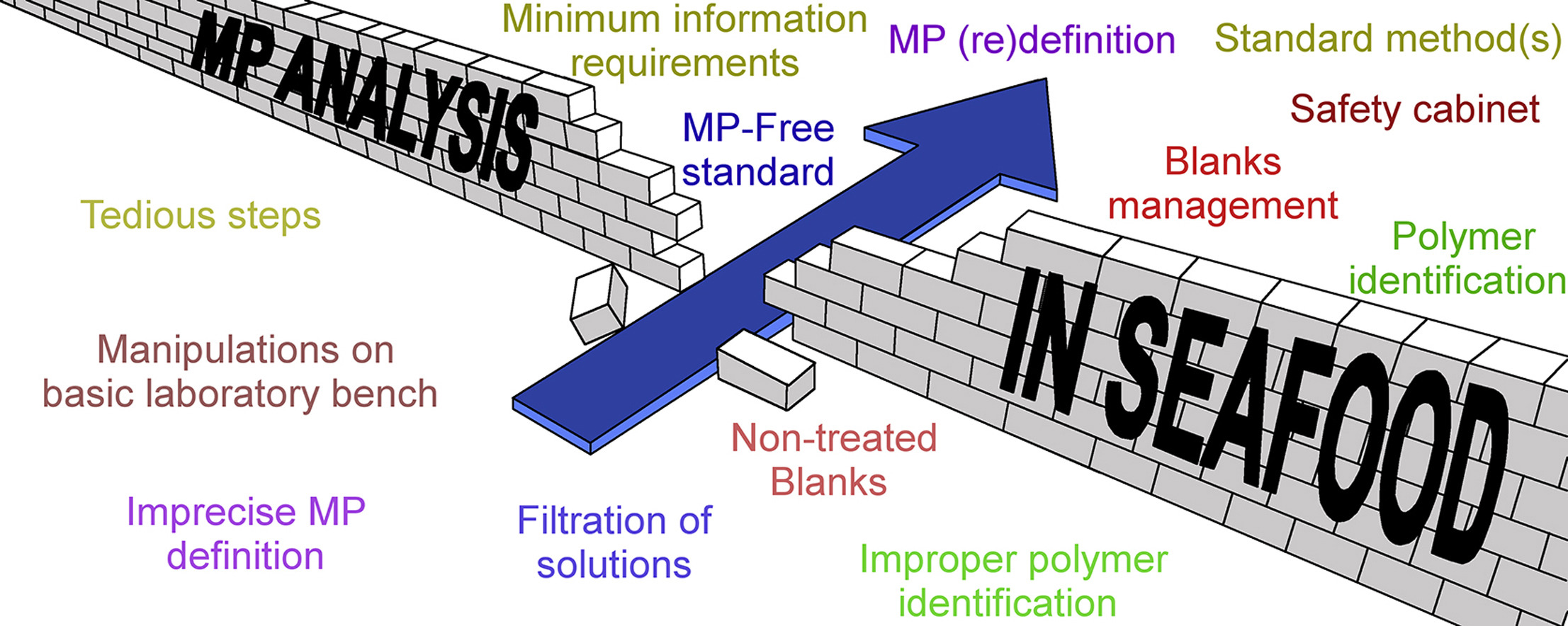
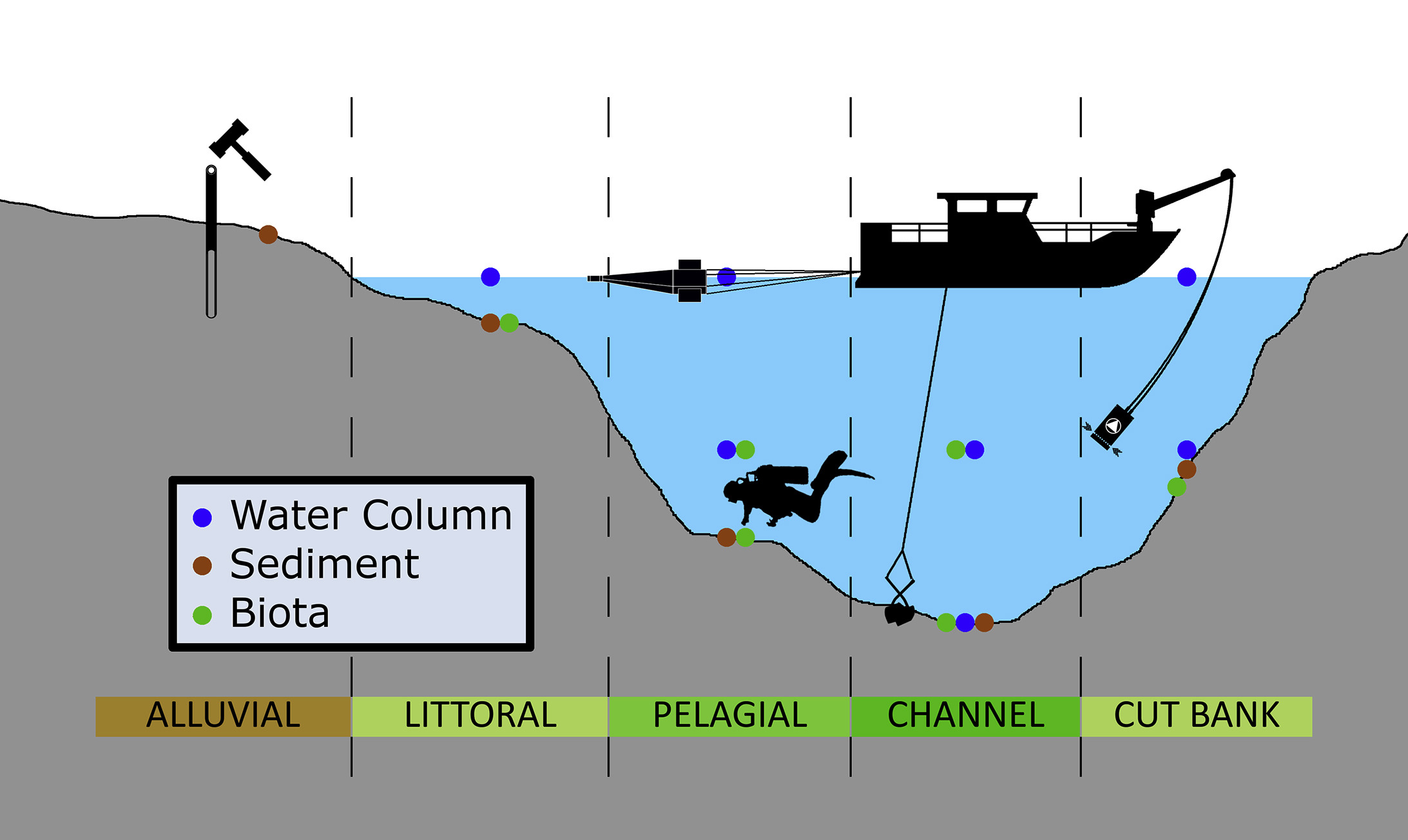
Data and analytics are increasingly recognized as fundamental elements in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These 17 goals, adopted by the United Nations in 2015, aim to address global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace, and justice. Each goal is interconnected, requiring a holistic approach to achieve sustainable development by 2030. Within this framework, SDG 17, "Partnerships for the Goals," is particularly crucial as it highlights the need for high-quality, timely, and reliable data to drive progress across all goals.
The importance of data and analytics in realizing the SDGs cannot be overstated. Accurate and insightful data is necessary for several key aspects: assessing current progress, identifying existing gaps, informing policy-making, and guiding the allocation of resources. For instance, in addressing SDG 1, "No Poverty," data helps in understanding the demographics of poverty, allowing for targeted interventions. Similarly, for SDG 3, "Good Health and Well-being," data analytics play a crucial role in tracking disease outbreaks, understanding health trends, and improving healthcare delivery.
In the education sector, under SDG 4, "Quality Education," data can inform about areas where educational resources are lacking or where dropout rates are high, guiding efforts to enhance education systems. Additionally, for SDG 13, "Climate Action," data is indispensable for understanding climate patterns, predicting future scenarios, and formulating strategies to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
Advancements in data collection and analytics methods have opened up new possibilities. Mobile technology, for example, has revolutionized data collection, enabling real-time gathering and dissemination of information even in remote areas. Remote sensing technologies, such as satellite imagery, provide critical data on environmental changes, agricultural patterns, and urban development. These methods not only expand the scope of data collection but also enhance its accuracy and timeliness.
However, challenges remain in harnessing the full potential of data for the SDGs. These include issues related to data availability, quality, accessibility, and interoperability. In many parts of the world, especially in developing countries, there is a significant data deficit. This gap hinders the ability to make informed decisions and effectively address the SDGs. Moreover, data collected must be reliable and relevant to be useful in policy formulation and implementation.
To overcome these challenges, partnerships between governments, private sector, academia, and civil society are vital. These collaborations can foster innovation in data collection and analytics, ensure data sharing, and build capacities for data analysis. Furthermore, there is a need for a global framework to standardize data collection and reporting methods, which will facilitate comparison and aggregation of data across regions and countries.