The internal combustion engine (ICE) does not efficiently convert chemical energy into mechanical energy. A majority of this energy is dissipated as heat in the exhaust and coolant.
Healthy-food procurement: Using the public plate to reduce food insecurity and diet-related diseases
Sustainability transitions have been studied as complex multi-level processes, but we still know relatively little about how they can be effectively governed, especially in transnational domains.

This article highlights the winning proposals of the first edition of the Elsevier Foundation Green & Sustainable Chemistry Challenge. The winning proposals were chosen for their innovative green chemistry aspects and their large positive impact on the environment, contributing to SDGs 6, 12 and 15.
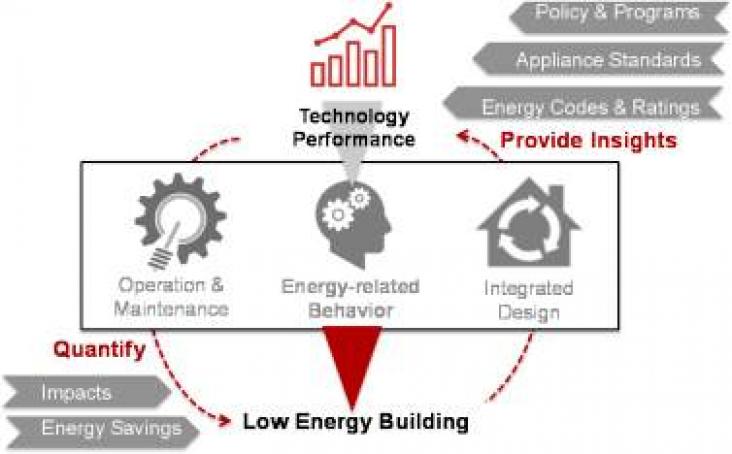
Occupant behavior is one of the major factors influencing building energy consumption and contributing to uncertainty in building energy use prediction and simulation.
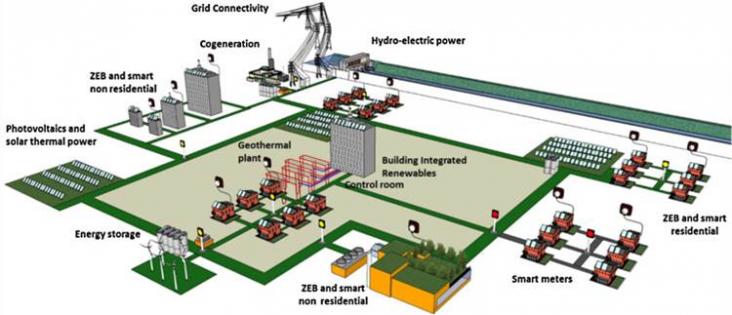
The smart grids are modern electric power grid infrastructure for enhanced efficiency and reliability through automated control, high-power converters, modern communications infrastructure, sensing
The discussion links Principle 5 of the Women’s Empowerment Principles (WEPs), which encourages companies to expand on their business connections with women-owned enterprises, to advance Goal 5
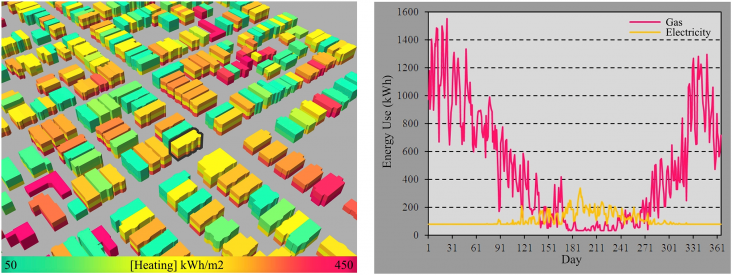
Over the past decades, detailed individual building energy models (BEM) on the one side and regional and country-level building stock models on the other side have become established modes of analysis
Recent research on CO2 capture is focusing on the optimization of CO2 absorption using amines (mainly monoethanolamine-MEA) in order to minimize the energy consumption of this very energy-intensive pr
Ecological impacts of industrial agriculture include significant greenhouse gas emissions, loss of biodiversity, widespread pollution by fertilizers and pesticides, soil loss and degradation, declinin
