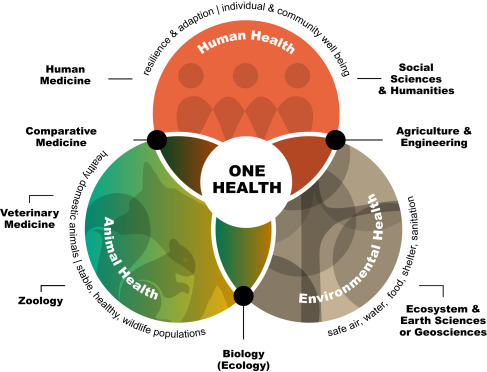
One Health and the Exposome embrace a broad view of human health and its environmental drivers as well as provide various tools and modes of operation to systematically uncover pathways linking poor health outcomes with their root causes to inform interventions supporting the WHO SDG3.
The study shows that resource variables are relevant for understanding the situation of cancer patients. Clinicians who notice low levels of sense of coherence, resilience, or optimisms in their patients will be better prepared for identifying patients in need for interventions. Especially younger patients deserve special attention.
This study produces a large dataset of pesticide concentrations in Italian women.
Instresting paper on Mediterranean river microplastic pollution
This article supports SDGs 7 and 13 by achieving the efficient CO2 capture via connecting a packed bubble column (S-PBC) contactor in series, combined with machine learning and multi-objective optimization based on Enhanced Weathering (EW) technology.
Background: The current investigation aimed to assess the mental health burden on healthcare workers during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Methods: A link to an online survey was sent to an estimate of 18,100 employees of Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (STH) who had access to email. The survey was completed between 2nd and June 12, 2020.1390 healthcare workers (medical, nursing, administrative and other professions) participated in the first survey. Data from a general population sample (n = 2025) was used for comparison.
Elsevier,
Translational Surgery
Handbook for Designing and Conducting Clinical and Translational Research
2023, Pages 591-597
The extensive history of abuse and ongoing mistreatment of Black Americans continues to foster apprehension and distrust of healthcare providers. This has resulted in substantial barriers for modern healthcare to appropriately address the needs of Black patients. These concerns have been visibly manifested during the COVID-19 pandemic. This article supports WHO SDG 3 Good Health and Wellbeing and SDG10 Reduced Inequalities.
Elsevier,
The Thinking Healthcare System
Artificial Intelligence and Human Equity
2023, Pages 99-129
Highlights the 21st century's fundamental “global health” reformulation of PubHealth and anticolonial resistance (to a perceived cultural imperialism of the West including in PubHealth) supporting SDG 3.
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 10 by evaluating home telemonitoring of women with complicated pregnancies, finding that it might be a safe alternative to hospital admission. If implemented, it is possible that this alternative could reduce costs and increase patient access to care and monitoring
Digital health programs are urgently needed to accelerate the adoption of Artificial Intelligence and Clinical Decision Support Systems (AI-CDSS) in clinical settings. However, such programs are still lacking for undergraduate medical students, and new approaches are required to prepare them for the arrival of new and unknown technologies.