This study shows that TB progression risk is higher in native Peruvians, and the conclusions support including more diverse populations in genomic studies to provide better targeted healthcare in indigenous populations.
The Growing Resilience action-research project as detailed in this paper, aims to help support the health and food sovereignty of Wind River Indian Reservation (WRIR) communities by providing families with information for monitoring their individual health and by supporting families in improving their health by growing home food gardens.
The results of this study show that children of the USAP region as a whole would benefit from an increase in their overall intake of fruit and vegetables and developing strategies to promote a greater frequency of consumption of all F&Vs, in particular traditional fruits and vegetables prepared by traditional practices, should benefit the health of people in the Pacific.
Recognising that "sexting" is a form of violence and is not innocent.
This chapter contributes to SDG 6 by introducing the impact of COVID-19 on water and sanitation, explaining Sustainable Development Goal-6 (clean water and sanitation) in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, and highlighting lessons learned regarding the water and COVID-19.
This chapter advances the UN SDG Goal 3: Good Health by discussing the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic on achieving SDG 3 targets—with a special focus on SDG 3.4 (NCDs) and SDG 3.8 (UHC).
A discussion of the use of law to protect women against violence.
Calculated emissions reductions possible through ecosystem restoration and shows they are insufficient to rely upon.
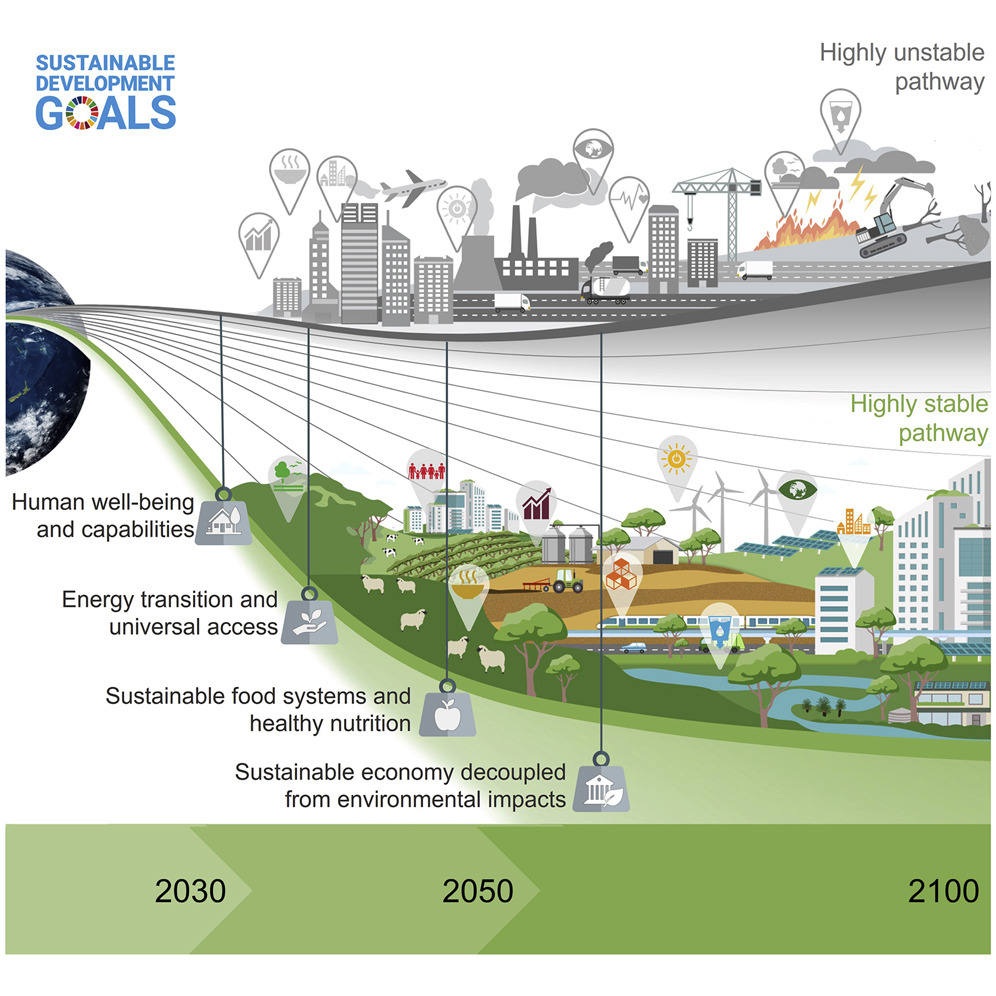
Indicate the importance of adopting longer-term timeframes and pathways to ensure that the necessary pre-conditions are in place for sustainability (including climate action) beyond the current 2030 Agenda.
Understanding the complexity in which Farmer-Based Organizations' (FBO) participation, empowerment, nutritional status, and food security are linked is critical in designing interventions that promote gender equality and improved nutrition.