Background: Increasing access to hepatitis C virus (HCV) care and treatment will require simplified service delivery models. We aimed to evaluate the effects of decentralisation and integration of testing, care, and treatment with harm-reduction and other services, and task-shifting to non-specialists on outcomes across the HCV care continuum.
This chapter supports SDGs 3, 16 by exploring the challenges confronting internally displaced persons and refugee children.
Compared to other climate regions of the world, Mediterranean regions are likely to experience more severe effects of climate change as rainfall decreases and temperatures increase. Global climate change models predict a reduction in rainfall and rise in the temperature of rivers in South Africa's Cape Fold Ecoregion (CFE) – a Mediterranean region in the south-west corner of the country.
This study identified, for the first time, determinants of low Symphysis–Fundal Height (SFH) in the context of multiple infections, nutrient deficiencies, and inflammation in a marginalized community of pregnant indigenous women and recommends the use of low SFH as a screening tool in remote settings for the identification of high-risk pregnancies is a first step to improve maternal and fetal health
Earth Day is widely recognised as the largest secular observance in the world, marked by more than a billion people every year as a day of action to change human behaviour and provoke policy changes. This day recognises and celebrates the Earth and its ecosystems as our home and highlights the need to protect earth to enhance people’s livelihoods, counteract climate change, and stop the collapse of biodiversity. To raise awareness of Earth Day 2021, Elsevier presents a curated list of free access journal articles and book chapters in support of this year's theme - Restore our Earth.
This chapter reviews the concept of happiness and how it is defined.
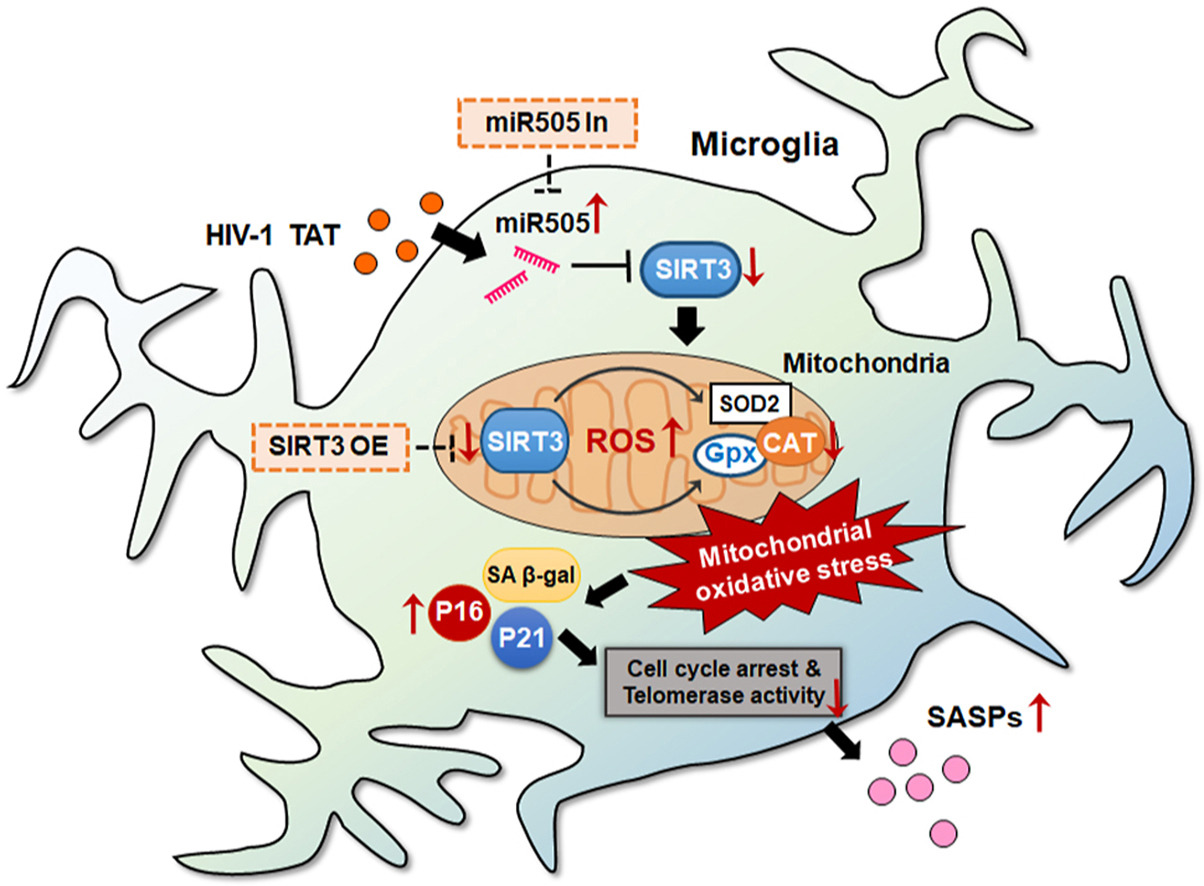
The introduction of combined antiretroviral treatment (cART) for HIV-1 has significantly reduced peripherary viral levels and extended the lives of patients. However, longer lifespans have led to more age-related health issues, like HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). This study investigates how the HIV TAT protein mediates microglial mitochondrial oxidative stress, leading to neuroinflammation and microglial aging.
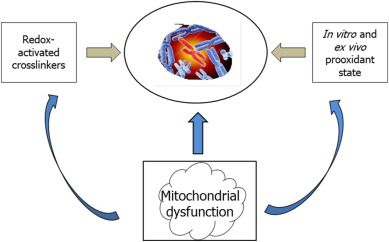
Fanconi anemia (FA) has been investigated since early studies based on two definitions, namely defective DNA repair and proinflammatory condition. The former definition has built up the grounds for FA diagnosis as excess sensitivity of patients’ cells to xenobiotics as diepoxybutane and mitomycin C, resulting in typical chromosomal abnormalities. Another line of studies has related FA phenotype to a prooxidant state, as detected by both in vitro and ex vivo studies. The discovery that the FA group G (FANCG) protein is found in mitochondria (Mukhopadhyay et al., 2006) has been followed by an extensive line of studies providing evidence for multiple links between other FA gene products and mitochondrial dysfunction. The fact that FA proteins are encoded by nuclear, not mitochondrial DNA does not prevent these proteins to hamper mitochondrial function, as it is recognized that most mitochondrial proteins are of nuclear origin. This body of evidence supporting a central role of mitochondrial dysfunction, along with redox imbalance in FA, should lead to the re-definition of FA as a mitochondrial disease.
This paper briefly reviews different debates about approaches for paths out of poverty, considering several views, from the analysis of specific policies to more general or systemic considerations.
Elsevier,
Reciprocal Translation Between Pathophysiology and Practice in Health and Disease, 2021, Pages 93-107
This chapter aligns with the SDG goal 3 of good health and wellbeing by showing the role of the gut microbiota on liver function, disease, and inflammation.