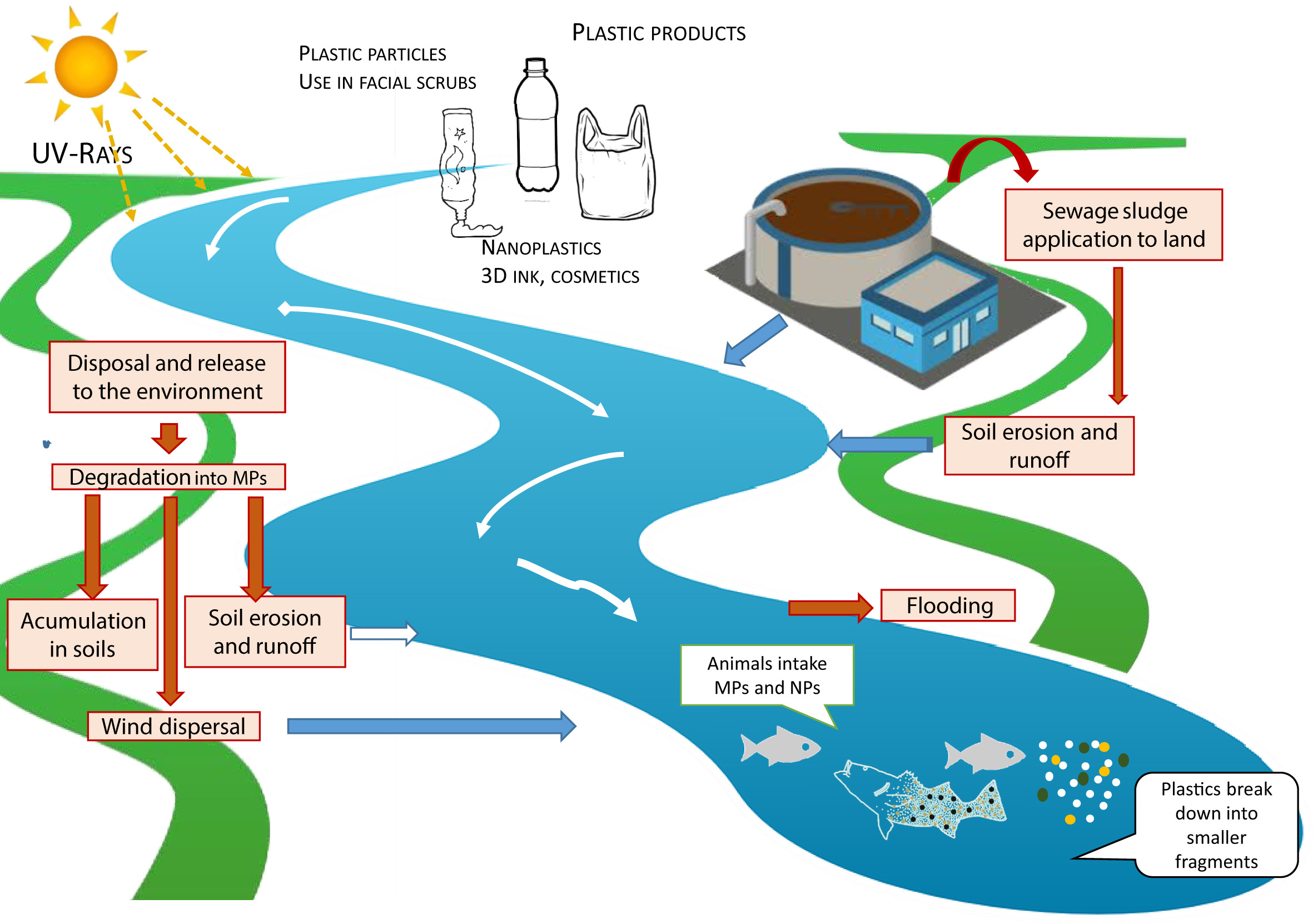
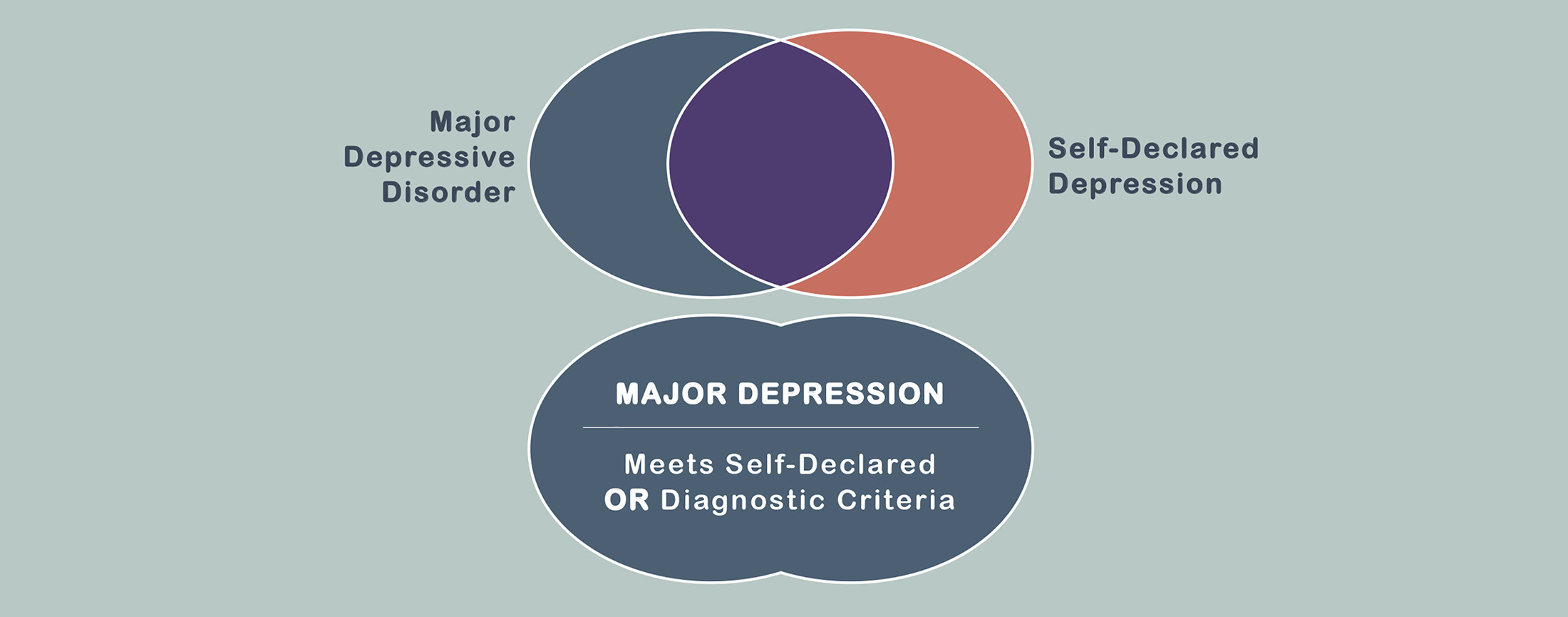
Perinatal depression (PND) is a heterogeneous disorder with differences in timing of onset of depression, which influences symptomology, severity, and treatment efficacy. Researchers must embrace the heterogeneity to bring fruition to a precision medicine approach for women in reproductive mental health care. Galea and Frokjaer discuss the heterogeneity of perinatal depression based on timing onset, which influences symptoms and has implications for etiology and treatment efficacy.
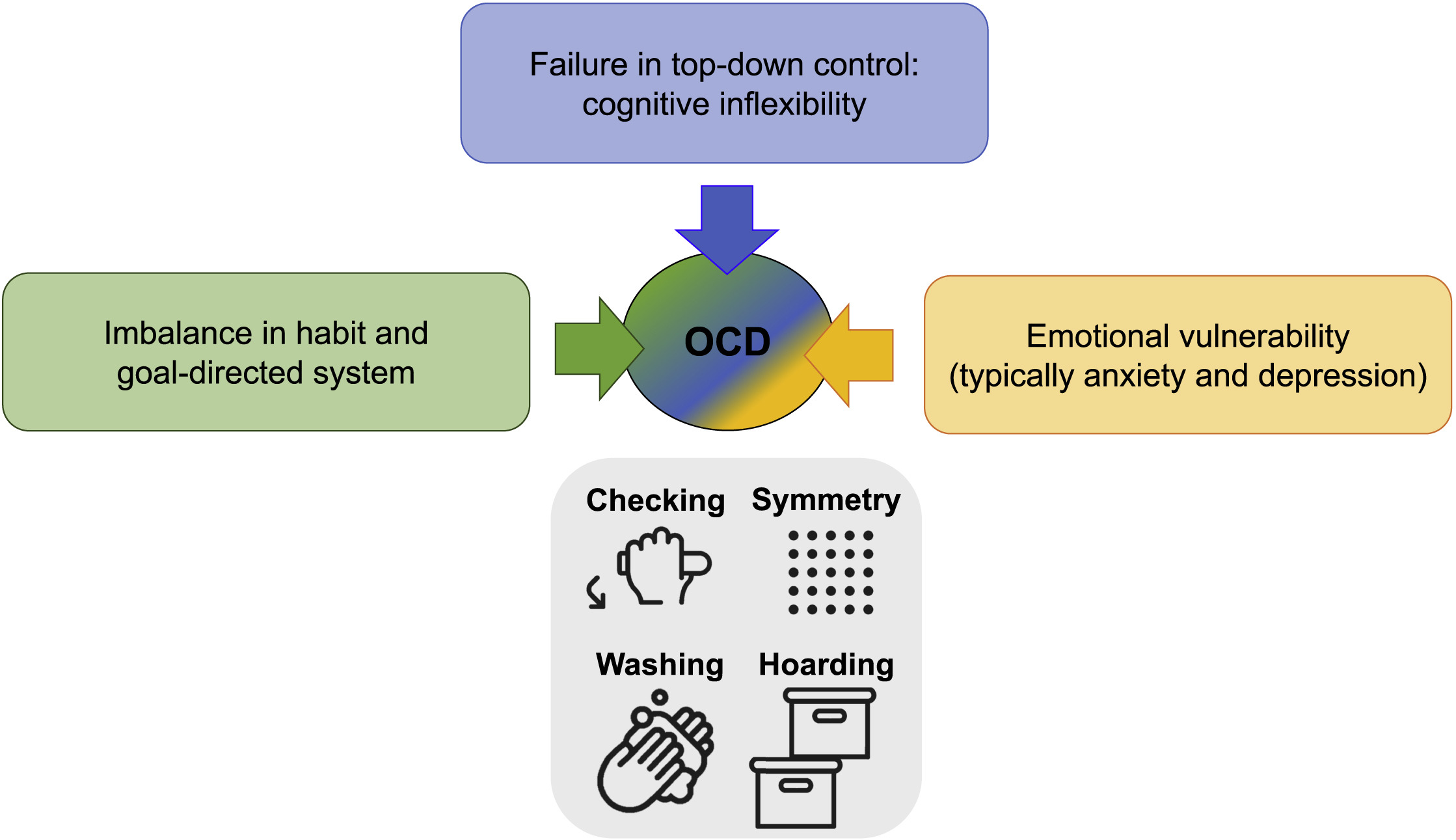
There have been several recent studies addressing the genetic architecture of depression. This review serves to take stock of what is known now about the genetics of depression, how it has increased our knowledge and understanding of its mechanisms, and how the information and knowledge can be leveraged to improve the care of people affected.
Pyrolysis converts biomass into liquid, gaseous and solid fuels. This work reviews the existing models for biomass pyrolysis, including kinetic, network and mechanistic models. The kinetic models are based on the global reaction mechanisms and have been extensively used for a wide range of biomass under various operating conditions. Major emphases have been on the network models as these models predict the structural changes during biomass pyrolysis. Key aspects of various network models include reaction schemes, structural characteristics and applications to CFD simulations.