The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 11 aims to "Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable." This goal acknowledges the growing importance of urban areas, as it's projected that by 2050, nearly 70% of the world's population will live in cities. Consequently, cities bear significant implications for sustainability, economic growth, and societal wellbeing.
Inclusivity is a key feature of sustainable cities. This refers to equitable access to opportunities, public services, and amenities, regardless of a person's background or circumstances. It implies the availability of affordable and adequate housing, thus addressing issues of homelessness and substandard living conditions.
Safety in cities means ensuring urban environments that protect their inhabitants from both physical harm and psychological distress. This involves addressing crime rates, traffic accidents, and potential hazards from poor infrastructure, while also considering the impacts of noise, pollution, and overcrowdedness on mental health.
Resilience is another important aspect, particularly in the face of climate change. Resilient cities can withstand and quickly recover from shocks such as natural disasters or economic crises. This involves aspects such as resilient infrastructure, disaster risk reduction strategies, and adaptive capacities at the community level.
Sustainability, finally, requires cities to function in a way that doesn't compromise future generations' ability to meet their own needs. This includes sustainable urban planning to reduce environmental impact, promote energy efficiency, and conserve resources. It also considers the importance of green spaces for biodiversity and the wellbeing of urban residents.
SDG 11 is interconnected with many other SDGs. For example, sustainable urban transport systems contribute to SDG 13 (Climate Action) by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Meanwhile, ensuring access to green and public spaces supports SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being).
Achieving sustainable cities and human settlements requires cooperation and participation from various stakeholders, including government authorities, urban planners, businesses, and citizens. Through their collective efforts, cities can be transformed into hubs of sustainability, resilience, and inclusivity, contributing significantly towards the realization of the SDGs.
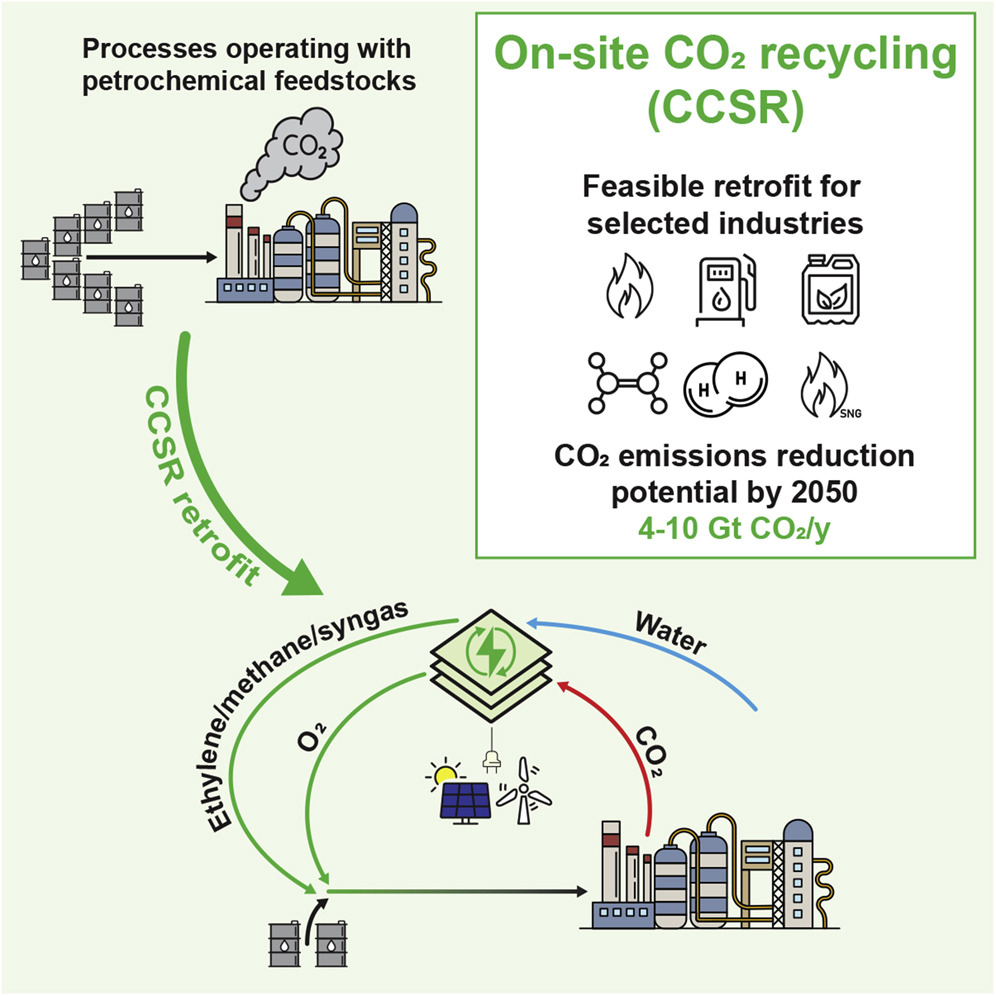
The chemical industry needs to significantly decrease carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in order to meet the 2050 carbon neutrality goal. Utilization of CO2 as a chemical feedstock for bulk products is a promising way to mitigate industrial emissions; however, CO2-based manufacturing is currently not competitive with the established petrochemical methods and its deployment requires creation of a new value chain.
Disaster Resilience and Sustainability, Adaptation for Sustainable Development, 2021, Pages 1-20