This study empirically examines the effects of school toilet provision on the primary-school attendance rate in Kenya. Using over 4200 school-level observations between 2013 and 2015, the results consistently show that an increase in the school toilet availability per student significantly raises the primary school attendance rate among both boys and girls. Moreover, the effects are larger for girls than for boys, and especially for pubescent girls.
Background: Globally, about 30% of women have experienced physical or sexual violence, or both, from an intimate partner during their lifetime. Associations between poverty and women's increased risk of intimate partner violence have been observed. We therefore aimed to assess the effect of a violence prevention intervention delivered to women participating in a group-based microfinance scheme in Tanzania. Methods: We did a cluster randomised controlled trial among women taking part in a microfinance loan scheme in Mwanza city, Tanzania.
The Africa Regional Data Cube (ARDC), based on the Open Data Cube infrastructure, is a technological innovation that layers 17 years of satellite imagery and Earth observation data for five African countries. This report identifies the key enabling environment, data management and sharing factors that affect the operationalization of the ARDC and makes recommendations to inform the scale-up of the technology, furthering SDGs 9 and 17.
This report showcases the latest transaction patterns, trends and cybercrime threats in Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA). It is essential reading for anyone involved in cybersecurity, financial crime, digital identity, fraud management and threat detection, advancing SDGs 8 (decent work and economic growth) and 16 (peace, justice and strong institutions).
This paper relates to remote sensing of water use and water stress in the African savanna ecosystem at a local scale, as well as the development and validation of a monitoring tool.
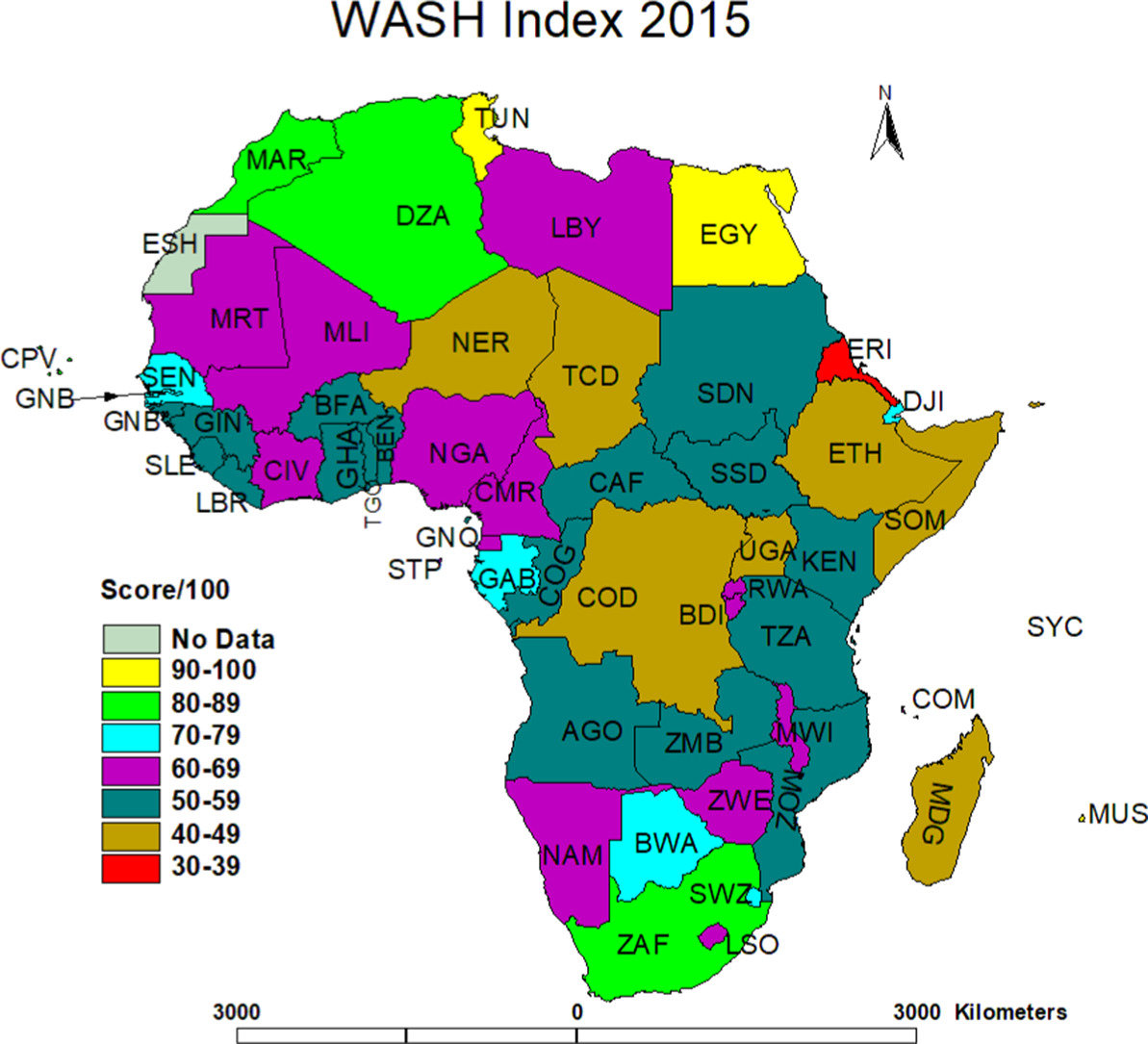
Water–Sanitation–Hygiene (WASH) remains vital for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, yet many countries have not localised the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including SDG 6, which focuses on ensuring the availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. Even in leading African economies such as South Africa, many communities still use the bucket system for sanitation.
Elsevier,
Contemporary Psychodynamic Psychotherapy: Evolving Clinical Practice, Volume , 18 June 2019
This book chapter advances SDG 3 and 10 by reviewing most relevant psychodynamic and developmental theories and empirical analyses for LGBT communities.
In May 2019, GIZ partnered with the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development Data and the Governments of Kenya and Ghana to organize a joint peer learning workshop for partners engaged in SDG implementation and monitoring from both countries. The aim of the workshop was to share and learn from each others experiences in the area of SDG monitoring and engage in a technical cross-country exchange, furthering SDG 17.
The Government of Ghana has instituted a National Poverty Reduction Program with an initiative known as the Community-based Health Planning and Services (CHPS) as its core health development strategy.
Background: Genetic diversity is a characteristic trait of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and has been associated with different clinical outcomes. In South Africa, HBV infection is a major public health concern. Most HBV infections are caused by genotype A strains. However rare cases of infection with HBV genotype D have been reported. The purpose of this study was to investigate the molecular characteristics of a rare HBV subgenotype D4 isolate. Methods: The full-length genome of isolate ZADGM6964 was amplified in a one-step polymerase chain reaction.