This study aims to analyse catastrophic floods and severe droughts affected by climate change from paleo studies to studies that focus on future projections.
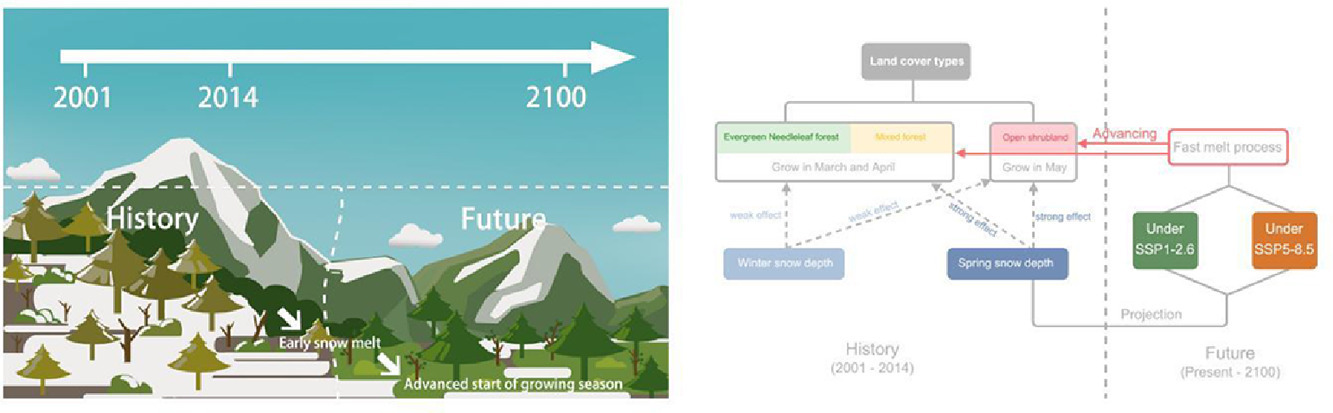
Under global warming, seasonal snow takes faster melting rate than before, which greatly changes the hydrological cycle. This study offer insights into understanding the effect from seasonal snow on vegetation and promote the sustainable utilization of regional vegetation in the Northern Hemisphere.
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health and Wellbeing as well as Goal 10: Reducing Inequalities by presenting early evidence on what it meant to be a frail older individual in the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of three different settings: community, hospitals, and nursing homes. Lessons learned provide opportunities to improve health outcomes, community and health services, and how we want to live as aging societies.
Elsevier,
Adolescent Mental Health
Towards Technological Advances and Service Innovations
2023, Pages 111-144
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health and Wellbeing as well as Goal 10: Reducing Inequalities by presenting available evidence of the effects of acute COVID-19 illness on children and young people, the impact on at-risk groups, and access to mental health services and education during the pandemic, as well as discussing the implications and recommendations for research, practice, and policy.
This content links with Goal 3: Good health and well-being and Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities by providing important insights informing basic mechanisms underlying febrile seizures.
This chapter aligns with Goal 14: Life Below Water and Goal 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure by acknowledging increased rates of Arctic transit resulting from declines in sea ice, recognizing the associated risk of increasingly frequent oil spills, and proposing methods to efficiently and effectively respond to such events.
With the aging global population, the relationship between older people and their residential environments is increasingly important. This relationship is based on the match between the individual characteristics of a person, their needs and expectations, and the characteristics of their environment. By creating access to various health improvement factors and exposure to various risk factors, the conditions under which an individual ages can be modified. This helps to accelerate or decelerate the process of incapacitation that individuals undergo as they age. This can also reduce or reinforce socio-spatial inequalities, which underlie the preponderant role of territory and spatial policies in the prevention and promotion of healthy aging. This chapters supports the process for developing the Decade of Healthy Ageing (2020 – 2030) aligned to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG3).
Elsevier,
Shaping the Future of Child and Adolescent Mental Health: Towards Technological Advances and Service Innovations, 2023, pp 3-31
This content aligns with Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being, Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure, and Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities by discussing the mental health threats and potential benefits of digital technology use by children and adolescents, with a focus on sex and age-related differences.
This content aligns with Goal 10: Reduced Inequalities by focusing on the impact and importance of building community for under-represented students in STEM.
This Comment supports SDG 3 by highlighting the environmental and endocrine healths harms from plastics and the need to reduce production and use of plastics. It describes the launch of negotiations to produce a global treaty aimed at achieving this goal.