World Hepatitis Day takes place every year on 28 July to raise awareness of the global burden of viral hepatitis. To highlight this important disease, Elsevier is proud to host this special collection of book chapters and journal articles which are freely available to download.
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 7, February 2022
A History of Vaccines and their Opponents, 2023, Pages 281-292
Two modern vaccines that have elicited significant opposition are those directed against hepatitis B and human papilloma viruses. In the case of hepatitis B, unfounded claims suggest that it can cause the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis. These claims have resulted in multiple lawsuits. In the case of human papilloma virus, that causes a sexually transmitted disease, much of the opposition has centered on the suggestion that it will promote sexual promiscuity in young children.
Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 22, June 2023
Oncogenic Viruses, Volume 1: Fundamentals of Oncoviruses, 2023, Pages 5-27
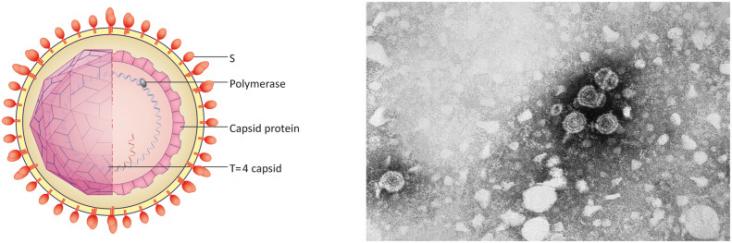
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for between 85% and 90% of primary liver cancers. It has several interesting epidemiological characteristics. Differences in distribution have been noted between geographic regions and ethnic groups but also according to sex and the presence of several risk factors linked to the environment. A variety of risk factors for HCC have been reported, including hepatitis B and C viruses, aflatoxin B1, alcohol consumption, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and hemochromatosis. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a ubiquitous virus with worldwide distribution.
Annals of Hepatology, Volume 28, Issue 1, 2023, 100764
Plotkin's Vaccines (Eighth Edition), 2023, Pages 443-450
For many years, hepatitis E was thought to be largely restricted to endemic developing countries where hepatitis E virus (HEV) genotypes 1 and 2 are transmitted by contaminated water and cause large epidemics in association with monsoon rains in Asia or during humanitarian crises in Africa. It is now estrablished that hepatitis E is endemic in many developed countries where it is a porcine zoonosis caused by HEV genotypes 3 and 4. HEV is responsible of life-theatening illness in vulnerable populations including pregnant women in developing countries.
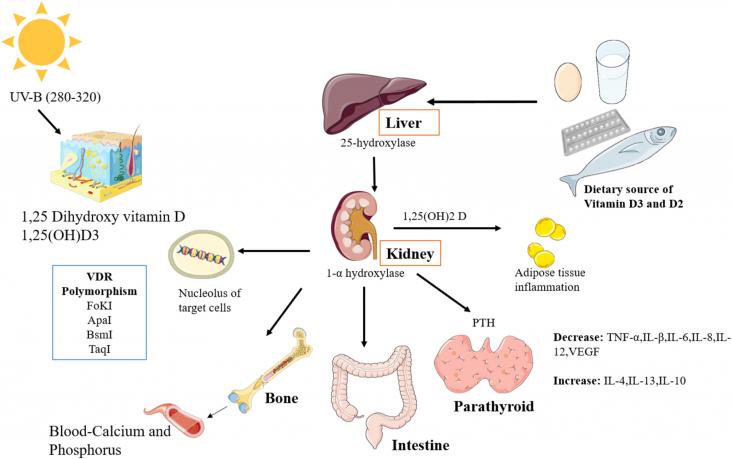
Cardio-Hepatology: Connections Between Hepatic and Cardiovascular Disease, 2023, Pages 123-132
Chronic right-sided heart failure has deleterious effects on many organ systems, and the liver is no exception. Passive hepatic congestion not only can precipitate impaired hepatic synthetic function and hepatic fibrosis, but it can also predispose the liver to more severe acute injury in the setting of circulatory compromise, an entity known as hypoxic hepatitis.
Oncogenic Viruses, Volume 2: Medical Applications of Viral Oncology Research 2023, Pages 173-189
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a hepatotropic virus capable of evading immune defense, usually leading to chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. The death rate in case of patients suffering from liver cancer associated with hepatitis B oncovirus is on the rise. Thus to effectively reduce the incidence of this disease, vaccination with preventive HBV vaccines is essential, and continuous development of therapeutic vaccines is needed to treat patients with preexisting infection.
Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis Advances
2023, Pages 137-152
Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis Advances
2023, Pages 429-441
Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 22, June 2023
Fate of Biological Contaminants During Recycling of Organic Wastes
2023, Pages 279-295
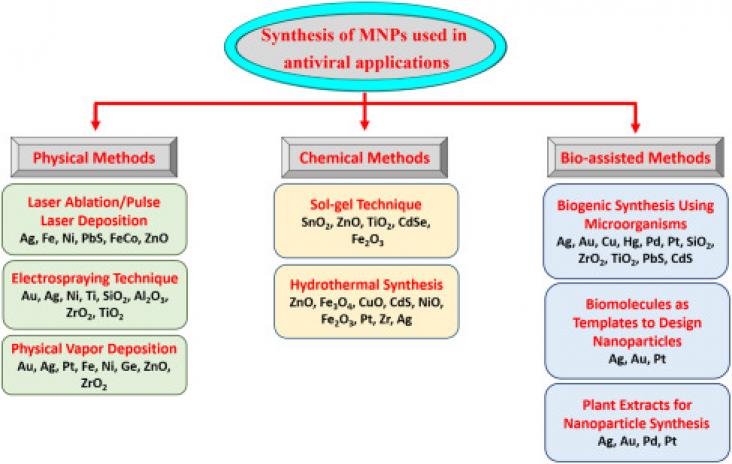
Smart Nanomaterials to Combat the Spread of Viral Infections
Advanced Strategies for the Prevention of Viral Infections
2023, Pages 97-123
Viruses (Second Edition)
From Understanding to Investigation
2023, Pages 401-407
Viral Infections and Antiviral Therapies
2023, Pages 85-98
Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis Advances
2023, Pages 429-441
Comprehensive Guide to Hepatitis Advances
2023, Pages 137-152
Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases (Sixth Edition)
2023, Pages 1237-1243.e3
Oncogenic Viruses
Volume 1: Fundamentals of Oncoviruses
2023, Pages 243-262
eClinicalMedicine, Volume 56, February 2023
Annals of Hepatology, Volume 27, 1 November 2022
Annals of Hepatology, Volume 28, 1 January 2023
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, Volume 19, August 2022
The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Volume 7, Issue 8, 2022, Pages 724-735
Transplantation and Cellular Therapy, Volume 28, July 2022
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, Volume 16, November 2021
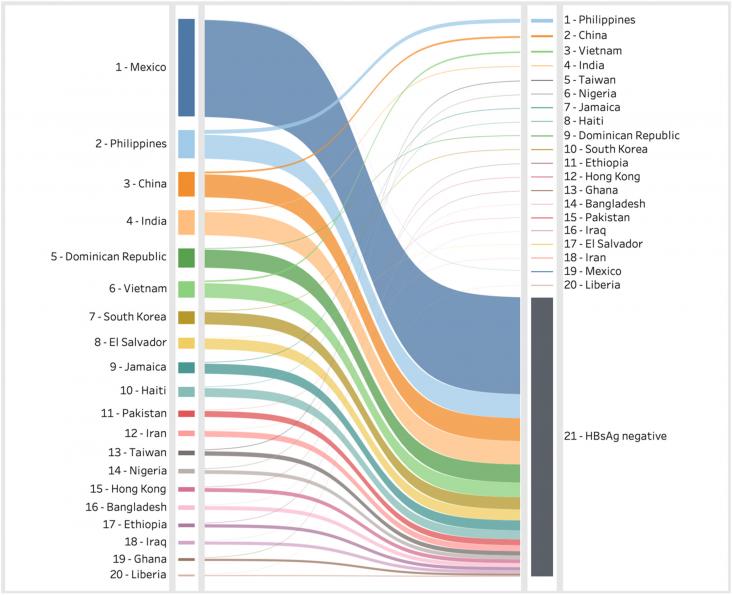
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 10, April 2022
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 9, November 2021
eBioMedicine, Volume 79, May 2022
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, Volume , 2023
The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Volume 8, July 2023
The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Volume 8, June 2023
The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Volume 8, March 2023
The Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Volume 7, October 2022
Heliyon, Volume 4, March 2018
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 7, February 2022
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 7, July 2022
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 8, April 2023
eClinicalMedicine, Volume 58, April 2023
eBioMedicine, Volume 80, June 2022
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, Volume 30, January 2023
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, Volume 24, July 2022
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 11, May 2023
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific, Volume 16, November 2021
iLIVER, Volume 1, Issue 2, June 2022, Pages 117-121
iLIVER, Volume 1, Issue 2, June 2022, Pages 139-140
iLIVER, Volume 1, Issue 3, September 2022, Pages 141-144
iLIVER, Volume 1, Issue 3, September 2022, Pages 145-153
iLIVER, Volume 1, Issue 4, December 2022, Pages 235-236