Elsevier, Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 31, October 2021
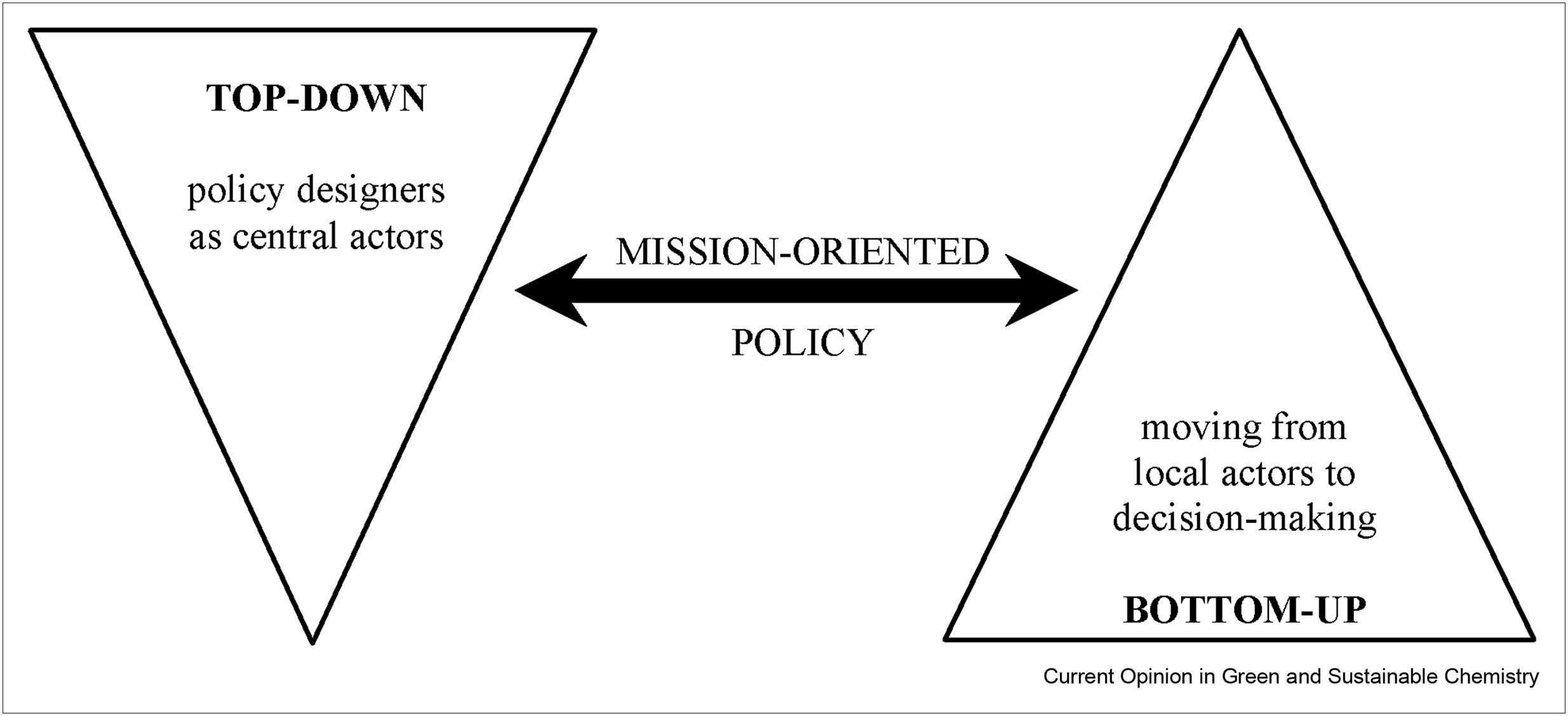
Global warming and climate change caused by an ever-increasing accumulation of atmospheric CO2 are reaching alarming levels. In order to address this issue, significant research effort has been dedicated to the development of carbon capture processes for sequestration or utilization of CO2. Current technologies rely on energy-intensive temperature- or pressure-swing of CO2 sorbents, limiting the economic feasibility of the process. Herein, we review recent advances in electrochemically mediated CO2 capture and release.
Elsevier, Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, Volume 31, October 2021
Hydrogen as a clean, reliable and potentially sustainable energy vector has attracted growing interest for promoting the sustainable development of both industry and society worldwide. Hydrogen is a rising enabler for a multisectorial transition toward a low-carbon economy based on renewable energy sources. Nevertheless, there is a lack of literature scientifically scrutinizing the relationships between a hydrogen economy and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Elsevier, Prostaglandins and Other Lipid Mediators, Volume 156, October 2021
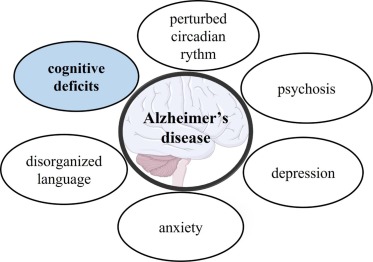
Millions of people are affected by neurodegenerative diseases worldwide. They occur due to the loss of brain functions or peripheral nervous system dysfunction. If untreated, prolonged condition ultimately leads to death. Mostly they are associated with stress, altered cholesterol metabolism, inflammation and organelle dysfunction. Endogenous cholesterol and phospholipids in brain undergo auto-oxidation by enzymatic as well as non-enzymatic modes leading to the formation of by-products such as 4-hydroxynonenal and oxysterols.
Elsevier, Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, Volume 49, 1 October 2021
Despite the better understanding of the mechanisms underlying Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and launched clinical trials, no AD-modifying treatment based on a synthetic drug has been introduced for almost twenty years. The serotonin 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors turned out to be promising biological targets for modulation of central nervous system dysfunctions including cognitive impairment. Within this paper, we evaluate the pharmacological potency of both, 5-HT6R and 5-HT7R, agents in search for novel AD treatment.
Elsevier, Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, Volume 64, October 2021
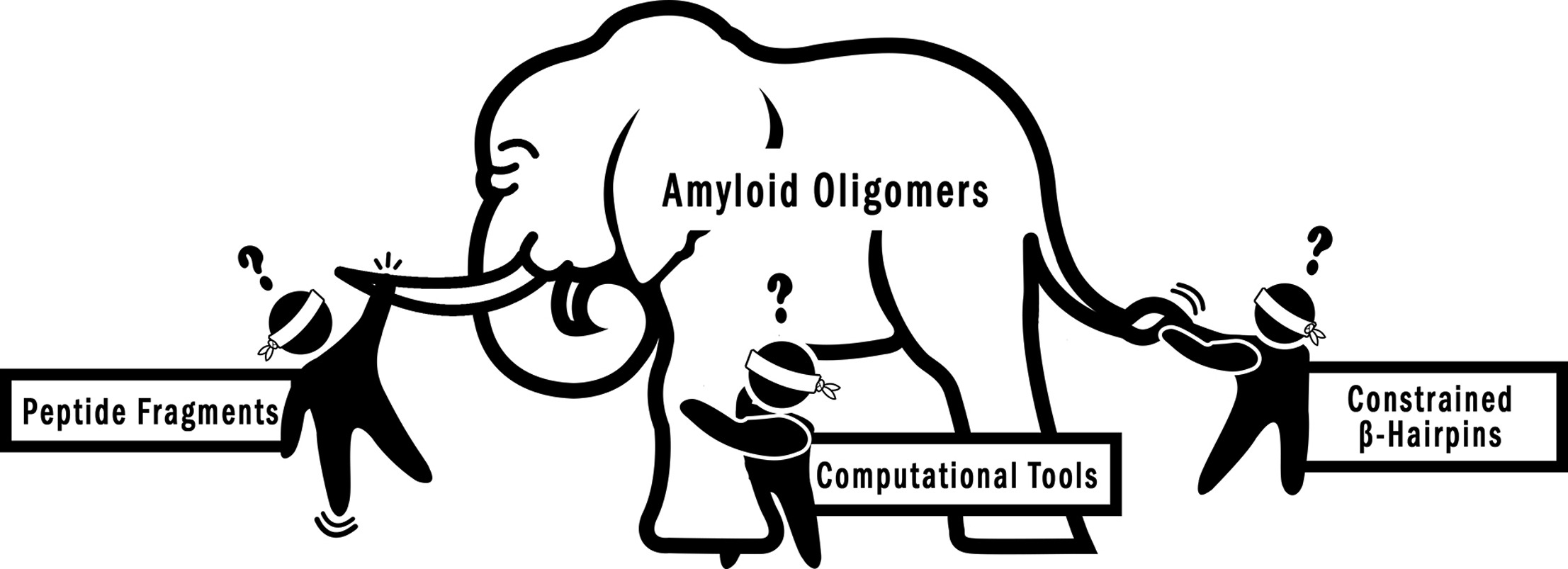
The assembly of amyloidogenic peptides and proteins, such as the β-amyloid peptide, α-synuclein, huntingtin, tau, and islet amyloid polypeptide, into amyloid fibrils and oligomers is directly linked to amyloid diseases, such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's diseases, frontotemporal dementias, and type II diabetes. Although amyloid oligomers have emerged as especially important in amyloid diseases, high-resolution structures of the oligomers formed by full-length amyloidogenic peptides and proteins have remained elusive.
Elsevier, Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, Volume 64, October 2021
More than a century has passed since pathological protein aggregates were first identified in the brains of patients with neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). Yet, we still do not have effective therapies to treat or slow the progression of these devastating diseases or diagnostics for early detection and monitoring disease progression.
Elsevier, Food Quality and Preference, Volume 93, October 2021
Cultured meat is a potentially successful future alternative to conventional meat if consumers perceive it as similar enough to conventional meat. This paper aimed to investigate how consumers categorize cultured meat after receiving information about it being similar to meat or meat substitutes. The first study (N = 130) showed that similarity information between cultured meat and meat resulted in the categorization of cultured meat as meat. This effect was not found for similarity information between cultured meat and meat substitutes.
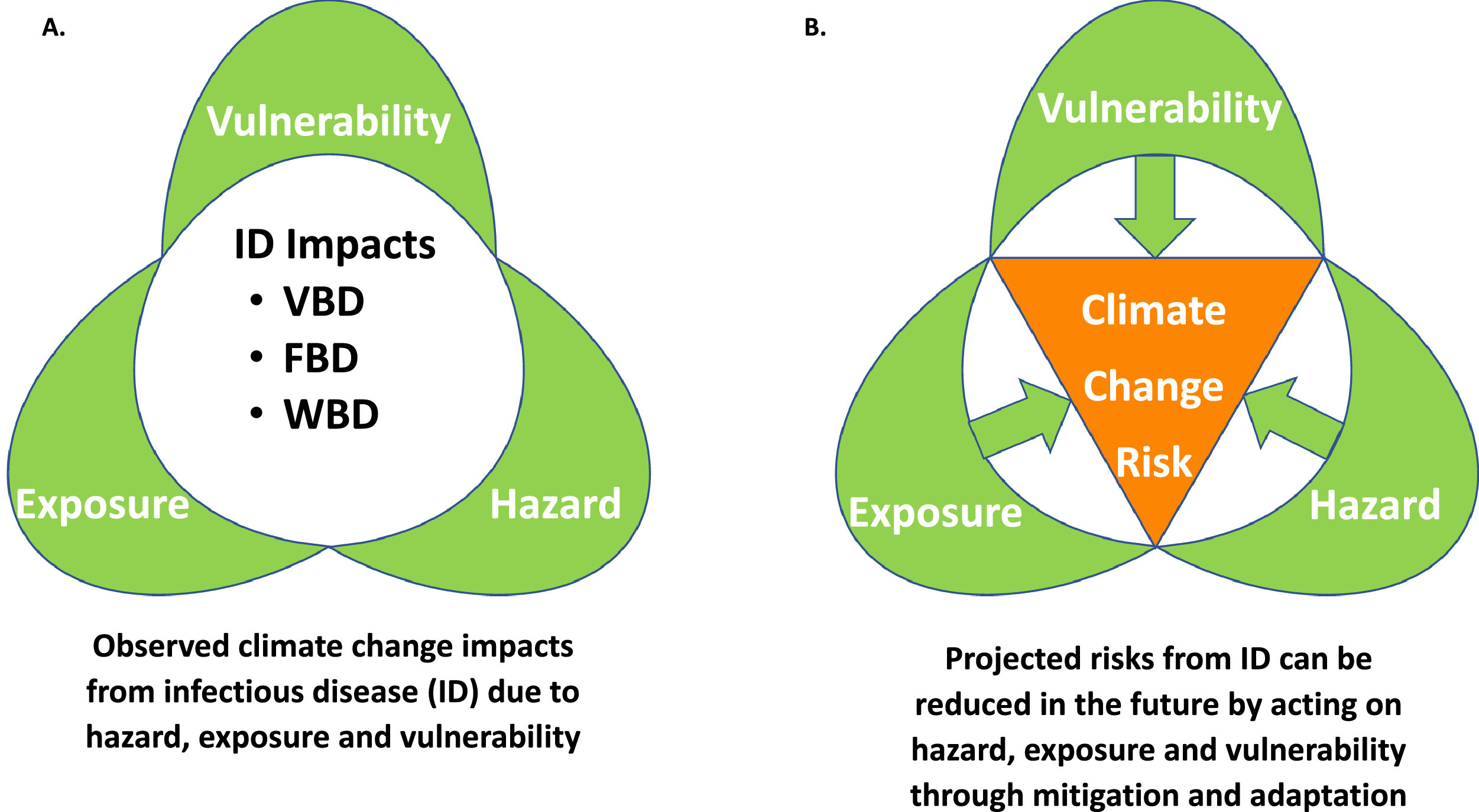
Elsevier, The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, Volume 9, October 2021
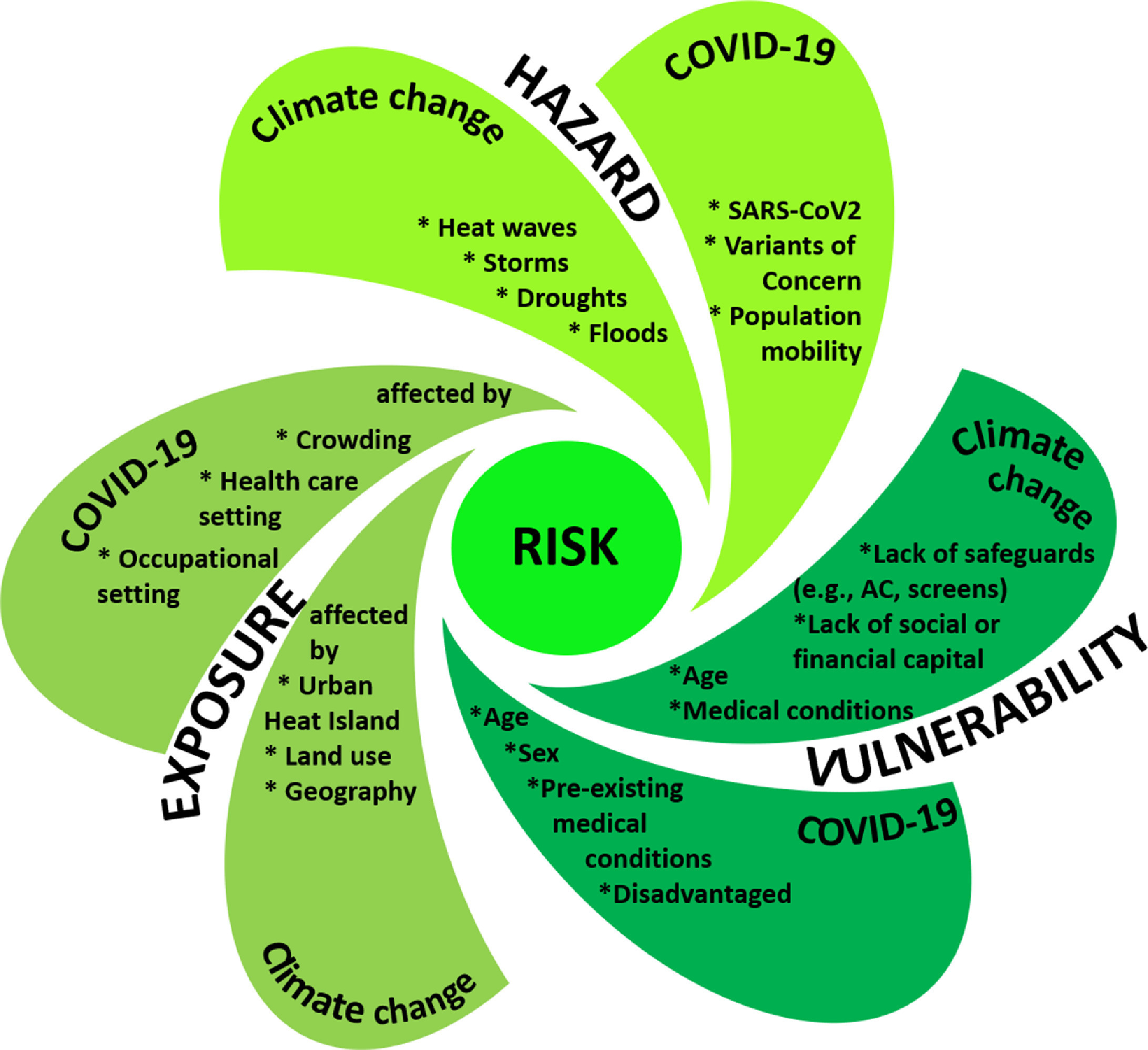
Europeans are not only exposed to direct effects from climate change, but also vulnerable to indirect effects from infectious disease, many of which are climate sensitive, which is of concern because of their epidemic potential. Climatic conditions have facilitated vector-borne disease outbreaks like chikungunya, dengue, and West Nile fever and have contributed to a geographic range expansion of tick vectors that transmit Lyme disease and tick-borne encephalitis.