Elsevier,
Free Radical Biology and Medicine, Volume 162, January 2021
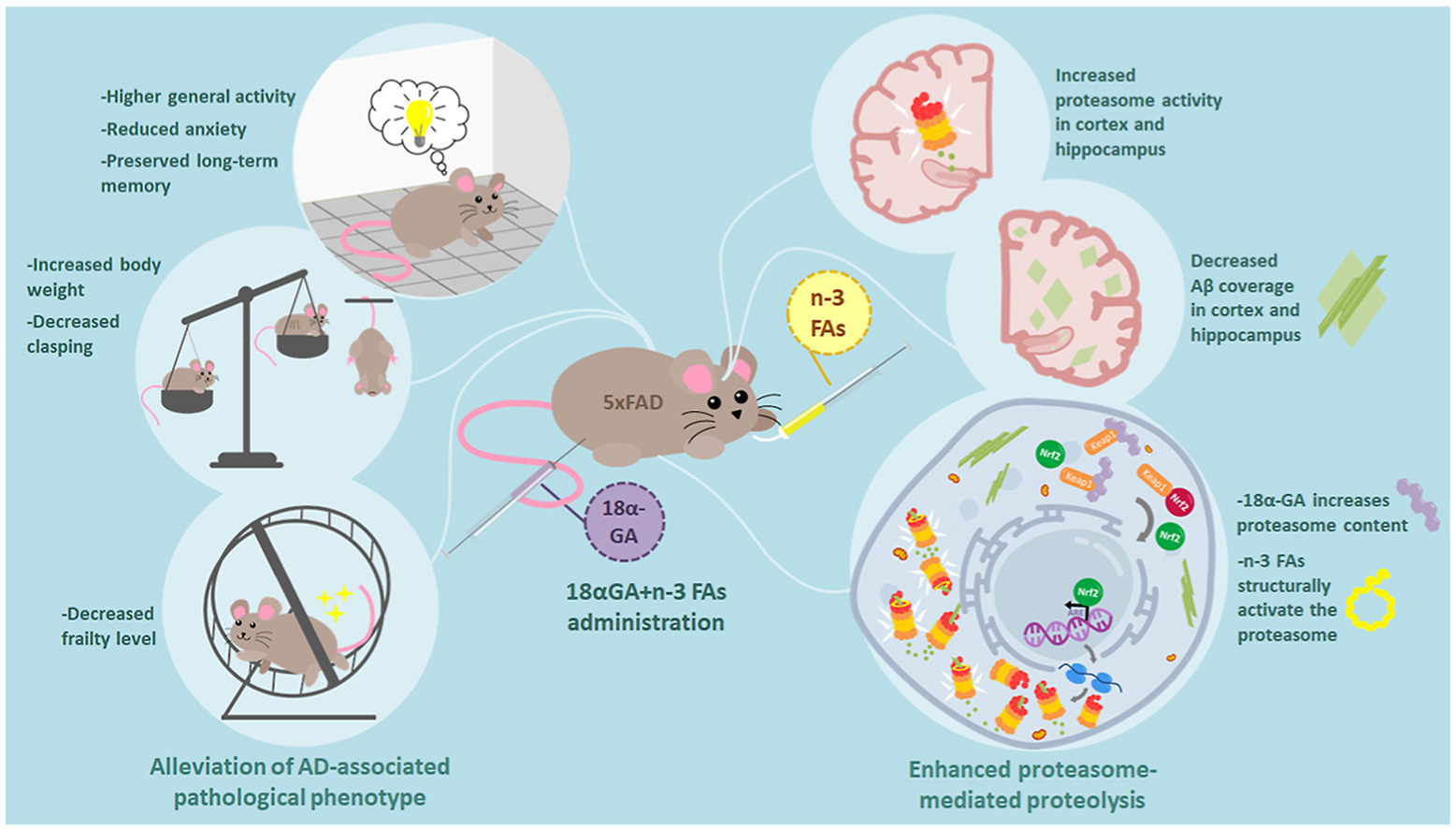
Proteasome function is impaired in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Proteasome activation is followed by a decrease in amyloid-beta (Aβ) load. A reduced amount of Aβ correlates with significantly improved behavior and frailty level. Proteasome activation represents a promising intervention for alleviating AD pathology.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, Volume 9, 2021
This Article supports SDG 3 by summarising global, regional, and national estimates of the burden of tracheal, bronchus, and lung cancer and larynx cancer and their attributable risks from 1990 to 2019, and highlighting the importance of preventive measures such as smoking control interventions, air quality management programmes focused on major air pollution sources, and widespread access to clean energy.
Elsevier, Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, Volume 60, January 2021
Women represent ⅔ of the cases of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Current research has focused on differential risks to explain higher rates of AD in women. However, factors that reduce risk for AD, like cognitive/brain reserve, are less well explored. We asked: what is known about sex and gender differences in how reserve mitigates risk for AD?
Elsevier,
Redox Biology, Volume 38, January 2021
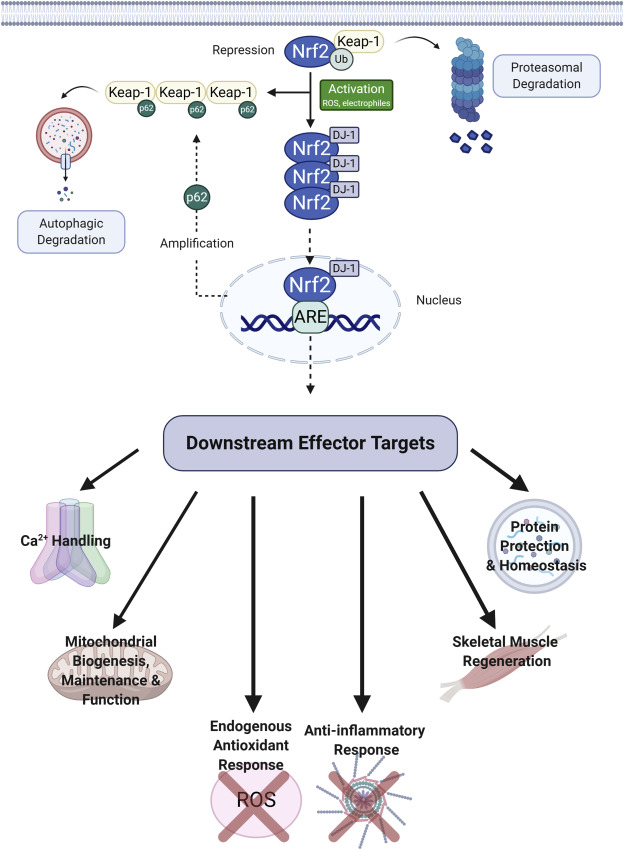
Imbalances in redox homeostasis can result in oxidative stress, which is implicated in various pathological conditions including the fatal neuromuscular disease Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). DMD is a complicated disease, with many druggable targets at the cellular and molecular level including calcium-mediated muscle degeneration; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress; inflammation; insufficient muscle regeneration and dysregulated protein and organelle maintenance. Previous investigative therapeutics tended to isolate and focus on just one of these targets and, consequently, therapeutic activity has been limited. Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a transcription factor that upregulates many cytoprotective gene products in response to oxidants and other toxic stressors. Unlike other strategies, targeted Nrf2 activation has the potential to simultaneously modulate separate pathological features of DMD to amplify therapeutic benefits. Here, we review the literature providing theoretical context for targeting Nrf2 as a disease modifying treatment against DMD.
Elsevier,
Journal of Integrative Agriculture, Volume 20, January 2021
Using China Health and Nutrition Survey data, this study employs a consistent two-step quadratic almost ideal demand system model, with addressed problems of endogeneity of total expenditure and zero shares, to estimate the food demand elasticities among adults in rural areas with regard to the different income strata.