Elsevier,
Sai Karthik Cheemalamarry, Vinayak Sharma, Yaddanapudi Varun, I. Sreedhar, Satyapaul A. Singh,
10 - Recent advances of nanotechnology in water remediation,
Editor(s): Noel Jacob Kaleekkal, Prasanna Kumar S. Mural, Saravanamuthu Vigneswaran,
In Micro and Nano Technologies,
Nano-Enabled Technologies for Water Remediation,
Elsevier,
2022,
Pages 311-333,
ISBN 9780323854450
This chapter contributes to SDG 6 by providing up-to-date information on nanomaterial potential application in water remediation.
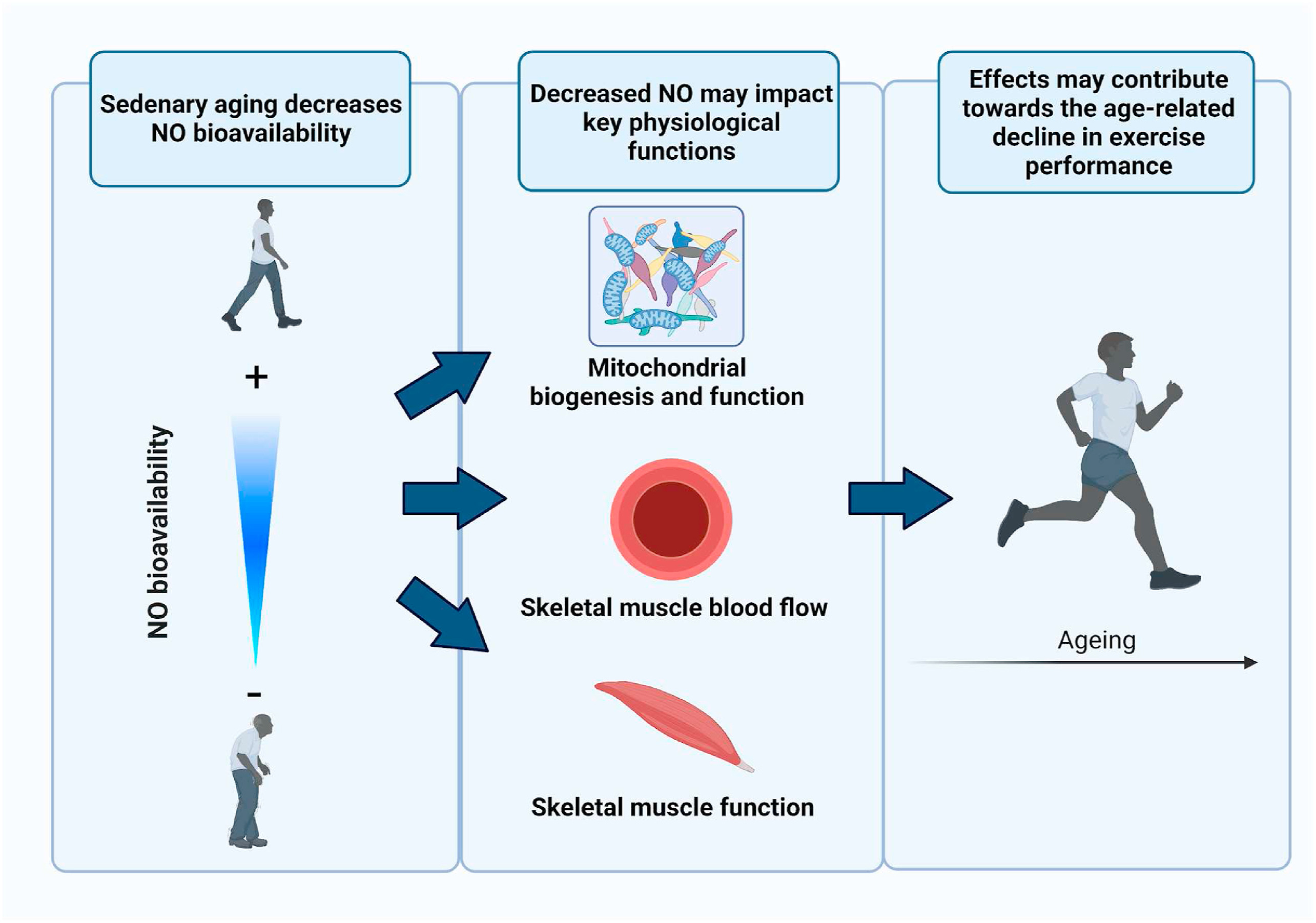
Worldwide, individuals are living longer. This population aging is associated with an anticipated increase in the burden of the leading causes of death in modern societies — chronic, degenerative diseases such as cardiovascular, kidney and Alzheimer's disease — which is largely driven by age-related declines in physiological function. Engaging in healthy lifestyle practices that preserve physiological function with age has important implications for reducing the risk of morbidity and mortality and preserving healthspan — the period of an individual's life when one is generally healthy and devoid of serious chronic disorders. In this regard, regular exercise and physical activity are considered key “first line” strategies for healthy aging.
A literature quantitative research analysis carried out via Scopus, researching publications on food dyes and their related health relationship. Consumers are becoming increasingly interested in the link between additives such as food dyes and overall food quality.
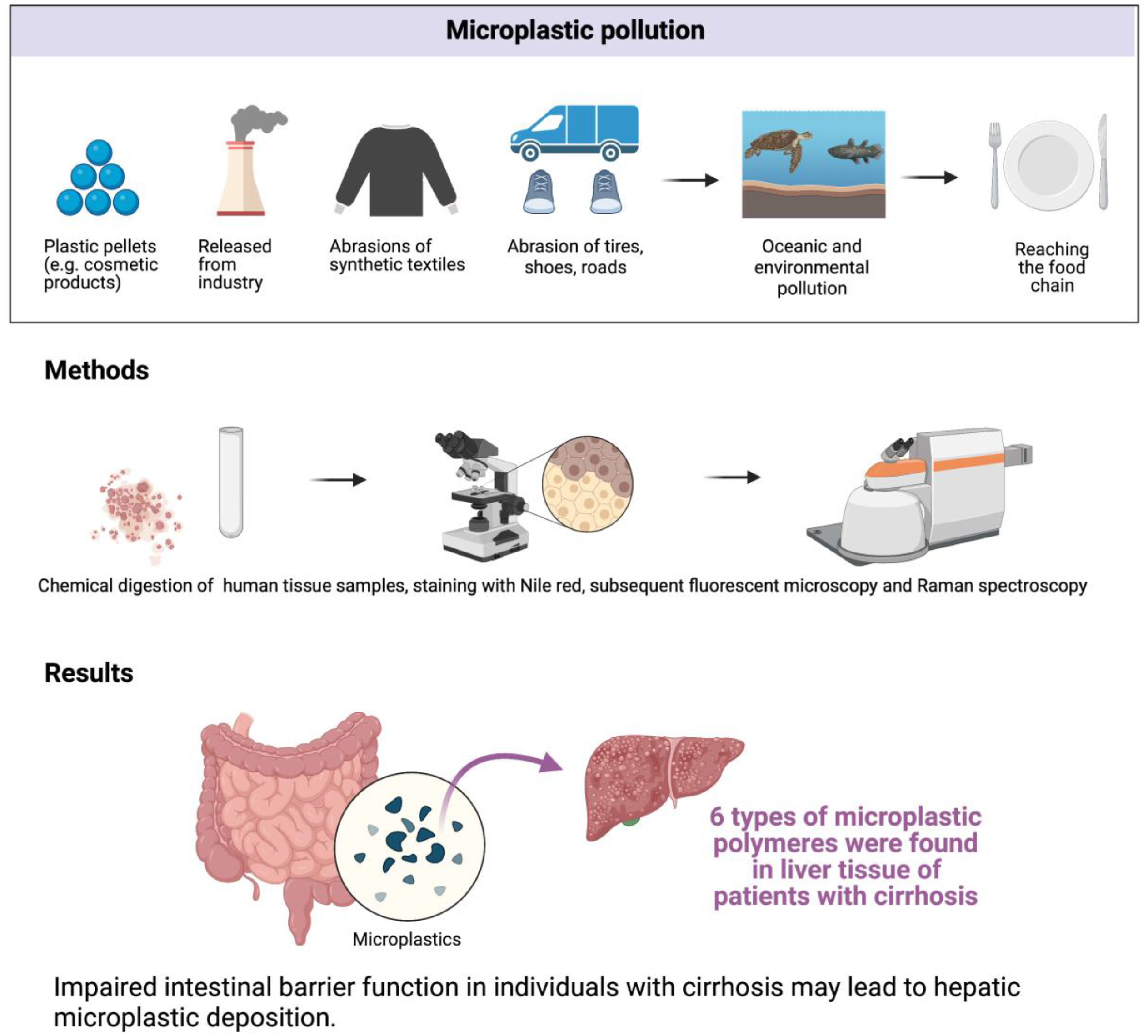
This Article supports SDG 3 by assessing the presence of microplastics in human liver tissue and identifying six different microplastic polymers in the liver of individuals with liver cirrhosis.
The United Nations General Assembly decided that International Day of the World’s Indigenous Peoples would be observed every year on 9th August. On this day, people from around the world are encouraged to help spread the UN’s message on the protection and promotion of the rights of indigenous peoples. Elsevier is pleased to share this special collection of freely available articles to help spread awareness about this important topic. Please feel free to download and share these papers.
Systematic review of mental health consequences of traffic accidents - large study on a major phenomenon.
Climate adaptation and mitigation strategies aim at strengthening existing food systems and infrastructure of agro-ecosystems, to make them more resilient to the effects of climate-led adversities.
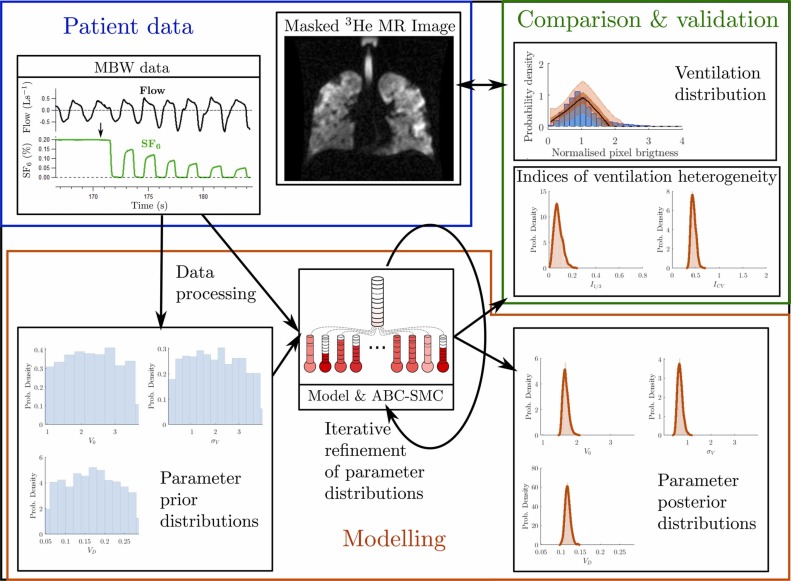
Background: Indices of ventilation heterogeneity (VH) from multiple breath washout (MBW) have been shown to correlate well with VH indices derived from hyperpolarised gas ventilation MRI. Here we report the prediction of ventilation distributions from MBW data using a mathematical model, and the comparison of these predictions with imaging data. Methods: We developed computer simulations of the ventilation distribution in the lungs to model MBW measurement with 3 parameters: σV, determining the extent of VH; V0, the lung volume; and VD, the dead-space volume. These were inferred for each individual from supine MBW data recorded from 25 patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) using approximate Bayesian computation. The fitted models were used to predict the distribution of gas imaged by 3He ventilation MRI measurements collected from the same visit. Results: The MRI indices measured (I1/3, the fraction of pixels below one-third of the mean intensity and ICV, the coefficient of variation of pixel intensity) correlated strongly with those predicted by the MBW model fits (r=0.93,0.88 respectively). There was also good agreement between predicted and measured MRI indices (mean bias ± limits of agreement: I1/3:−0.003±0.118 and ICV:−0.004±0.298). Fitted model parameters were robust to truncation of MBW data. Conclusion: We have shown that the ventilation distribution in the lung can be inferred from an MBW signal, and verified this using ventilation MRI. The Bayesian method employed extracts this information with fewer breath cycles than required for LCI, reducing acquisition time required, and gives uncertainty bounds, which are important for clinical decision making.
Elemental selenium, a new type of selenium supplement, can be biosynthesized via microorganisms. This study is to characterize a patent probiotic bacteria Enterococcus durans A8–1, capable of reducing selenite (Se6+ or Se4+) to elemental selenium (Se0) with the formation of Se nanoparticles (SeNPs).