Elsevier,
EClinicalMedicine, Volume 33, March 2021
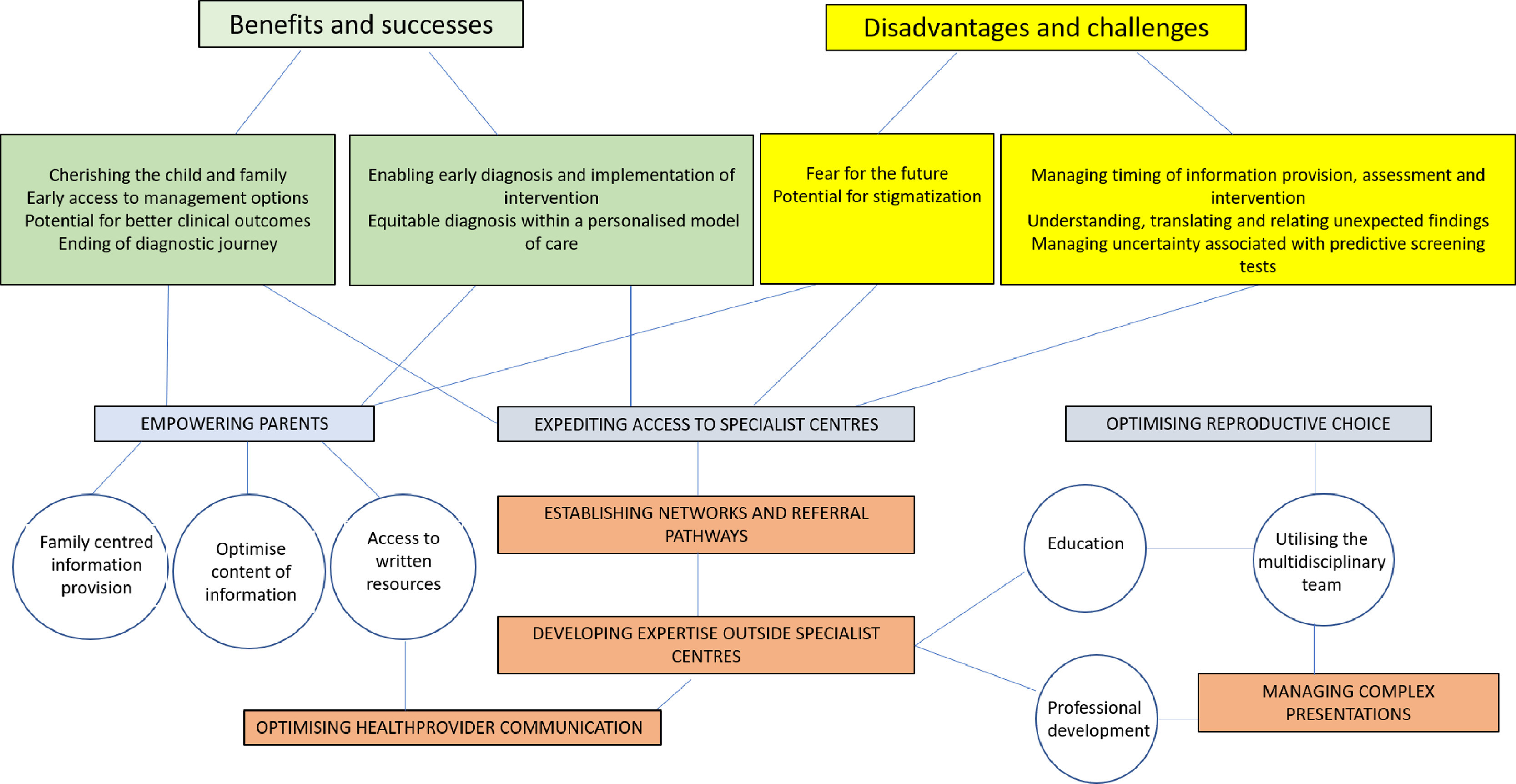
This Article supports SDG 3 by highlighting the benefits of equipping a wider (non-specialist) workforce to deal with the demands of population screening for rare diseases such as spinal muscular atrophy through education programmes and access to expert opinions.
Elsevier, The Lancet, Volume 397, 6 February 2021
The nature of armed conflict throughout the world is intensely dynamic. Consequently, the protection of non-combatants and the provision of humanitarian services must continually adapt to this changing conflict environment. Complex political affiliations, the systematic use of explosive weapons and sexual violence, and the use of new communication technology, including social media, have created new challenges for humanitarian actors in negotiating access to affected populations and security for their own personnel.
Elsevier,
Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 5, 1 February 2021
Complementary Feeding (CF) involves an array of behaviors ranging from producing or purchasing food to preparing and feeding it to the child. Nutrition-specific and nutrition-sensitive interventions support different dimensions of improved CF, including dietary diversity, adequate frequency and daily intake, food hygiene, responsive feeding, and parenting practices. Beyond messages specific to what to feed young children, interventions to improve CF could address norms related to early child development; family dynamics; water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH)
Elsevier,
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 9, February 2021
An Article in support of SDGs 3 and 17, analysing the extent to which the budgets of The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria support health security, highlighting the importance of disease-specific global health initiatives to support health security efforts and to respond to current and future pandemics.
Elsevier, The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 5, February 2021
Background: nationally determined contributions (NDCs) serve to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement of staying “well below 2°C”, which could also yield substantial health co-benefits in the process. However, existing NDC commitments are inadequate to achieve this goal. Placing health as a key focus of the NDCs could present an opportunity to increase ambition and realise health co-benefits.