12th October 2020
Clinical Breast Cancer, Volume 20, October 2020
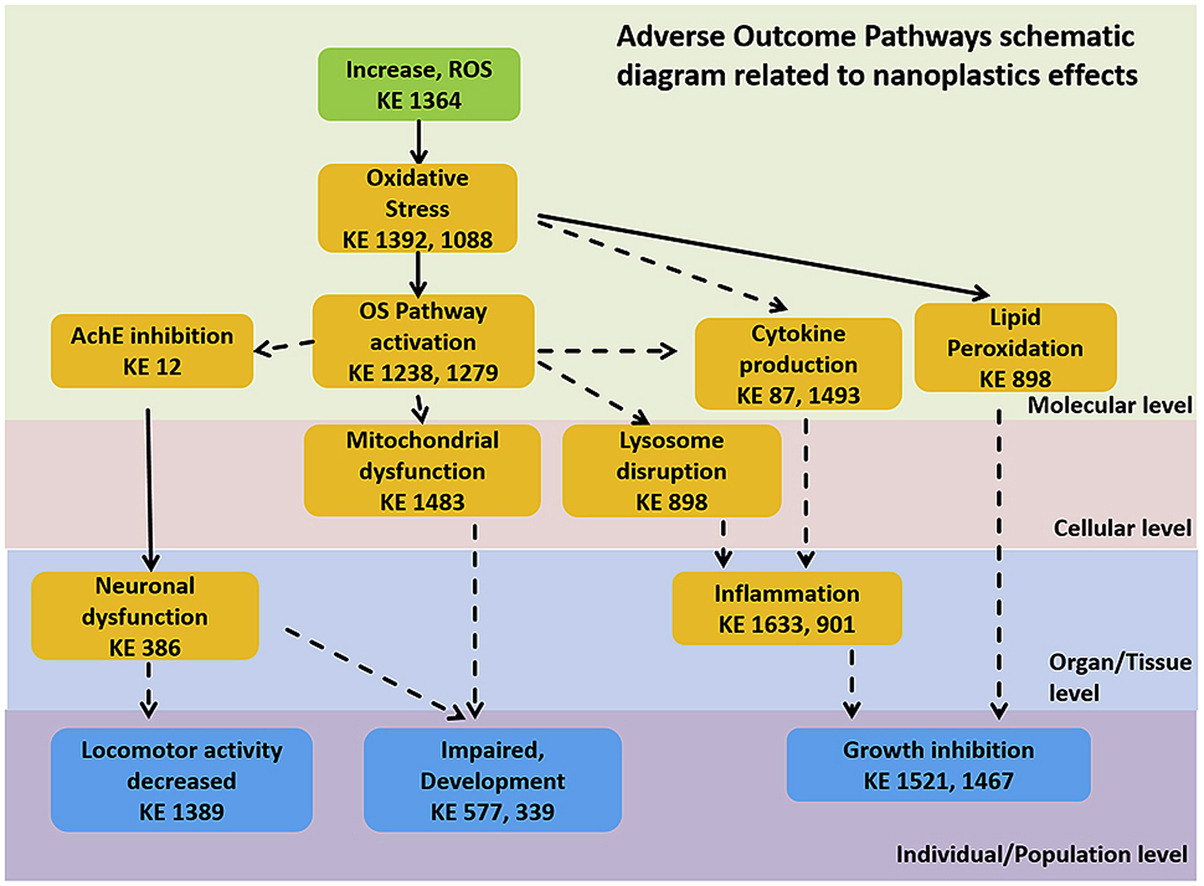
Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part - C: Toxicology and Pharmacology, Volume 235, September 2020
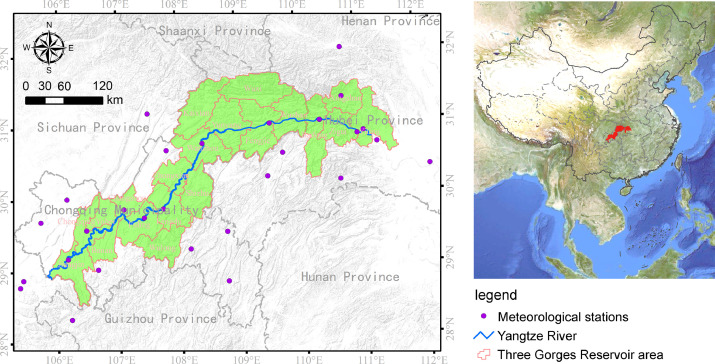
Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, September 2020
Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, September 2020
Climate, land use and land cover (LULC) changes are among the primary driving forces of soil loss. Decoupling their effects can help in understanding the magnitude and trend of soil loss in response to human activities and ecosystem management. Here, the RUSLE model was applied to estimate the spatial-temporal variations of soil loss rate in the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) area during 2001–2015, followed by a scenario design to decouple the effects of climate and LULC changes. The results showed that increasing rainfall generated as much as 2.90 × 107 t soil loss in the TGR area.