Elsevier,
Geoderma, Volume 443, March 2024
Artificial grassland restoration can be an effective method when applied to severely degraded grassland in alpine areas, however, their effects on slope runoff and sediment yield are still unclear. Qian et al., 2024 studied the effects of artificial restoration and degradation on the runoff sediment process in three areas and found that artificial grassland can significantly reduce runoff and sediment yield compared to alpine meadows and severely degraded alpine meadows. The study underscores the importance of plant and soil characteristics in erosion processes, highlighting the effectiveness of artificial grassland in mitigating soil erosion through improved soil conditions and enhanced vegetation coverage, with implications for restoration efforts in alpine regions.
Elsevier,
One Earth, Volume 7, 16 February 2024
This research highlights the potential environmental and social impacts of scaling renewable energy technologies that rely on transition minerals, emphasizing the need to study resource frontiers to understand the local consequences of global climate policies. This topic is relevant to the International Day of Indigenous Peoples as it underscores the importance of considering the impacts on indigenous communities and their lands in the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions.
Elsevier,
One Earth, Volume 7, 16 February 2024
This study emphasizes the importance of adopting nexus approaches in Arctic governance to address the complex interactions between climate change, biodiversity loss, land use pressures, and local livelihoods. While Arctic policies often incorporate nexus elements, there is a need to better recognize the agency and impact of local communities and traditional livelihoods in decision-making processes. This aligns with the goals of the International Day of Indigenous Peoples by highlighting the significance of involving indigenous communities in environmental governance and promoting cross-sectoral policies that consider their perspectives and contributions.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Child and Adolescent Health, Volume 8, February 2024
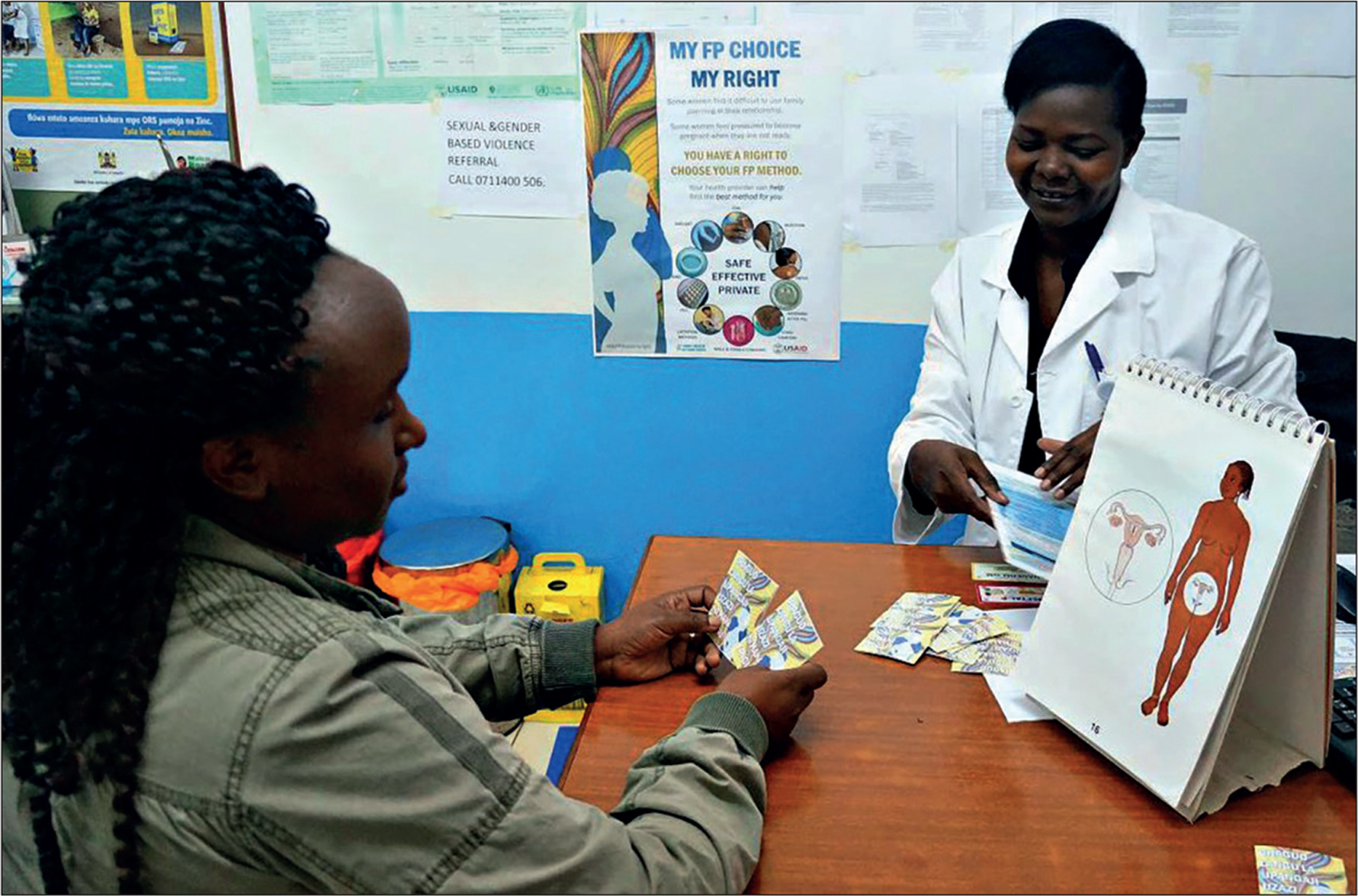
As a type of violence in intimate relationships, reproductive coercion encompasses a range of behaviours that exert external control over reproductive autonomy, from threats to coerce pregnancy to sabotaging contraception and controlling outcomes of a pregnancy, such as coerced abortion or forced continuation of a pregnancy. At a time when reproductive rights and bodily autonomy are under attack in many countries, and when adolescents (especially transgender and gender-diverse youth) are experiencing large barriers to health care, elucidating core characteristics of reproductive coercion, identifying harm reduction strategies, and preventing relationship abuse and reproductive coercion are of paramount importance.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Global Health, Volume 12, February 2024
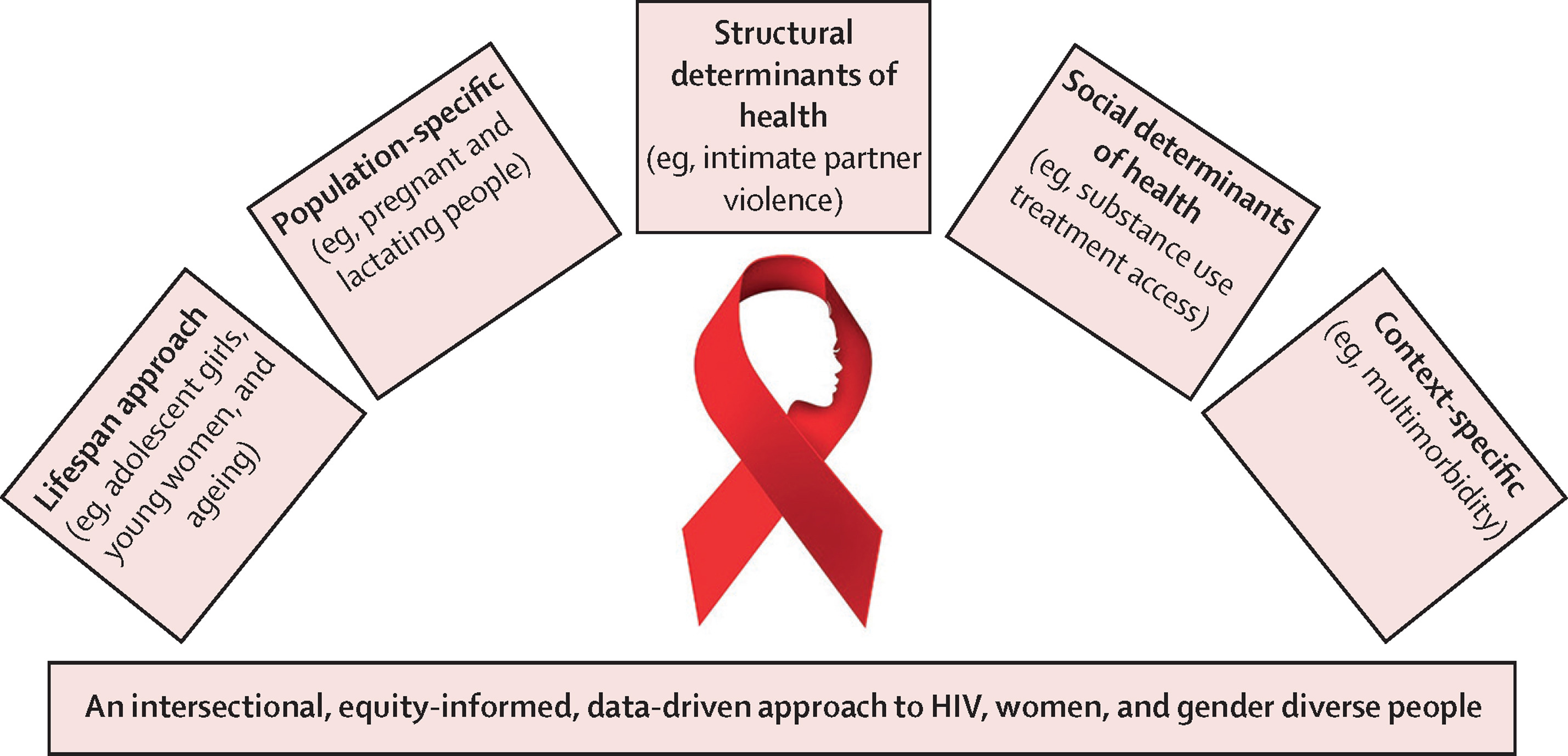
This Series paper supports SDGs 3 and 5 by examining the determinants of maternal health and mortality and how these could be addressed to improve outcomes. The causes of maternal mortality, and efforts to improve maternal health, require a multipronged and multidisciplinary approach.