Elsevier,
Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 412, 1 August 2023
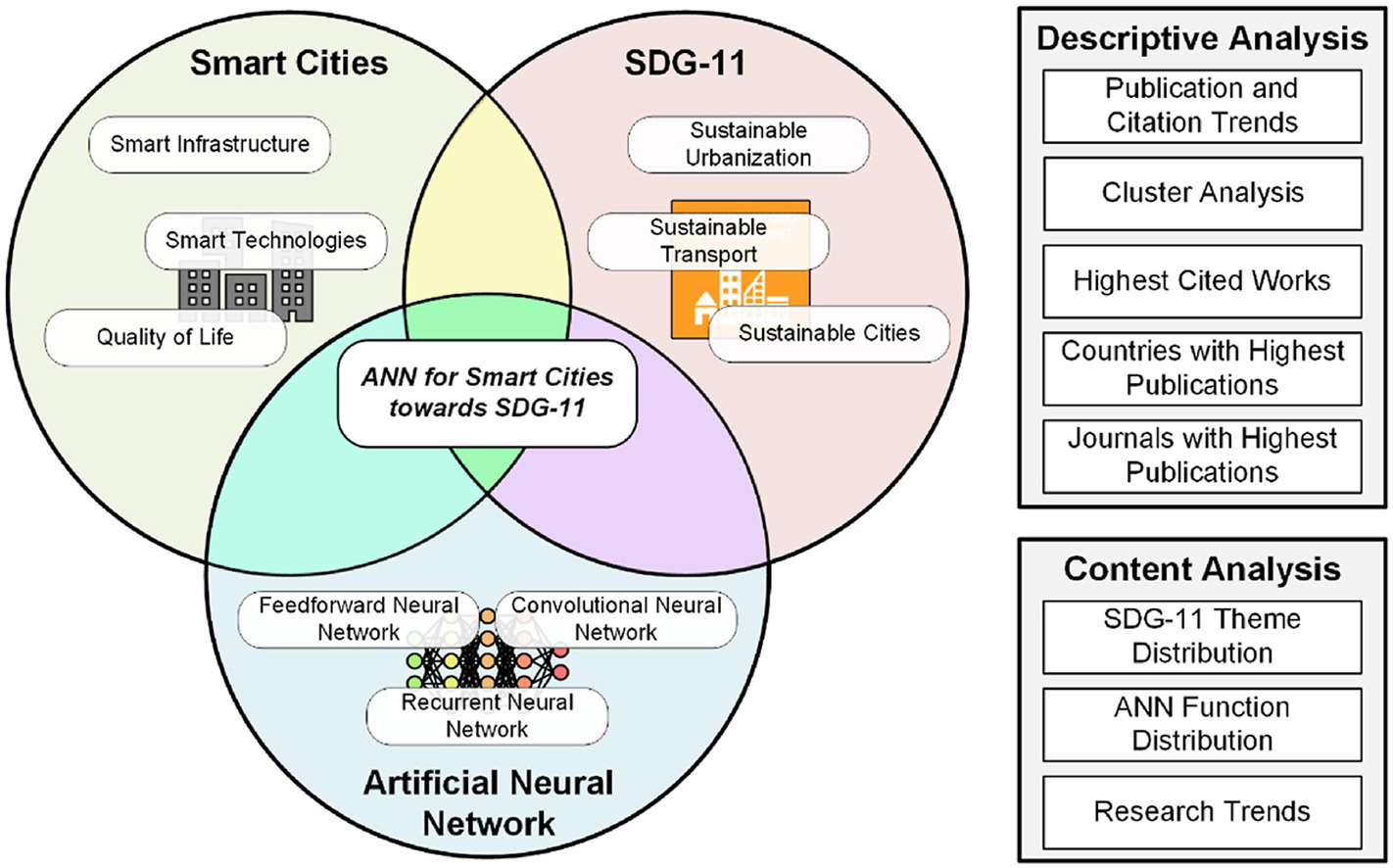
This review assessed the academic landscape on the use of ANN for Smart Cities towards SDG-11. A keyword-based methodological framework was used to retrieve the relevant documents. The documents were assessed using descriptive and content analysis. Results revealed significant research interest on the topic and is on an increasing trend. Research works on the topic are expected to increase as clusters on specific topics have formed. This review identified the SDG-11 themes Environmental Impact, Transport Systems, and Urbanization among the most prominent. Research gaps were identified in the SDG-11 themes on Green and Public Spaces, and Natural and Cultural Heritage.
Elsevier,
iScience, Volume 26, 18 August 2023
This study links multiple models for a comprehensive assessment of the economic-environmental-health co-benefits of renewable energy development in China. The results show that developing renewable energy can avoid 0.6 million premature mortalities, 151 million morbidities, and 111 million work-loss days in 2050.
Elsevier,
American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology MFM, Volume 5, August 2023
This research illustrates that an advanced oral hygiene regimen has the potential to reduce the incidence of preterm birth in socially disadvantaged obstetrical patients with higher rates of health disparities.
Elsevier,
Cell Reports Physical Science, Volume 4, 16 August 2023
The demand for solar energy as a clean way to power human lives is increasing, but solar panels are land-intensive and may compete for space with farms. In this article, the authors examine how agrivoltaics (combining farming and solar technologies) can provide synergistic benefits together rather than in isolation, showing positive benefits in climate mitigation, climate resilience, and land equivalent ratios. This contributes to SDGs 2 (ensuring the promotion of sustainable agriculture), 7 (harnessing sunlight to power society), and 13 (agrivoltaics as a way to combat climate change).