Translational Oncology, Volume 16, February 2022
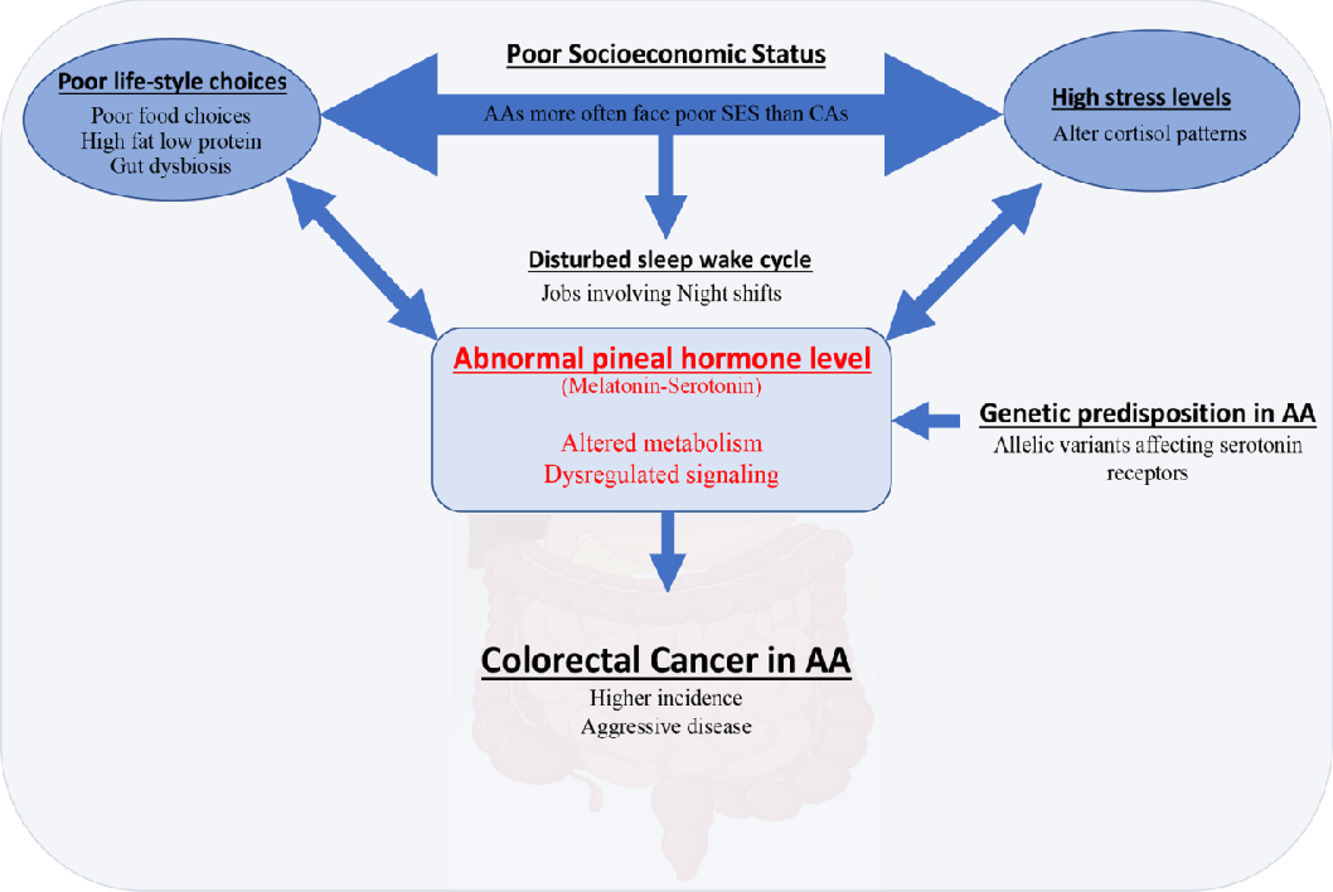
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States. Despite increased screening options and state-of-art treatments offered in clinics, racial differences remain in CRC. African Americans (AAs) are disproportionately affected by the disease; the incidence and mortality are higher in AAs than Caucasian Americans (CAs). At the time of diagnosis, AAs more often present with advanced stages and aggressive CRCs, primarily accounting for the racial differences in therapeutic outcomes and mortality.
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe, Volume 13, February 2022
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 7, February 2022
The Lancet Public Health, Volume 7, February 2022
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 6, February 2022
Social Sciences & Humanities Open, Volume 3, Issue 1, 2021, 100112