One Earth, Volume 4, 22 January 2021
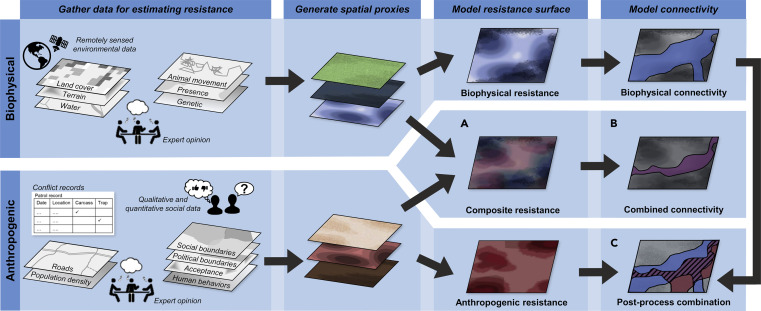
Maintaining or restoring connectivity among wildlife populations is a primary strategy to overcome the negative impacts of habitat fragmentation. Yet, current connectivity planning efforts typically assess landscape resistance, the ability of organisms to cross various biophysical elements in a landscape, while overlooking the various ways in which human behaviors influence connectivity. Here, we introduce the concept of “anthropogenic resistance” to capture the impacts of human behaviors on species' movement through a landscape.
Advances in Ecological Research, Volume 64, January 2021
Global social and economic changes, alongside climate change, are affecting the operating environment for agriculture, leading to efforts to increase production and yields, typically through the use of agrochemicals like pesticides and fertilizers, expanded irrigation, and changes in seed varieties. Intensification, alongside the expansion of agriculture into new areas, has increased harvest, but has also had numerous well-known impacts on the environment, ultimately resulting in a loss of resilience and lack of sustainability in agro-ecosystems.
Climate Risk Management, Volume 34, January 2021
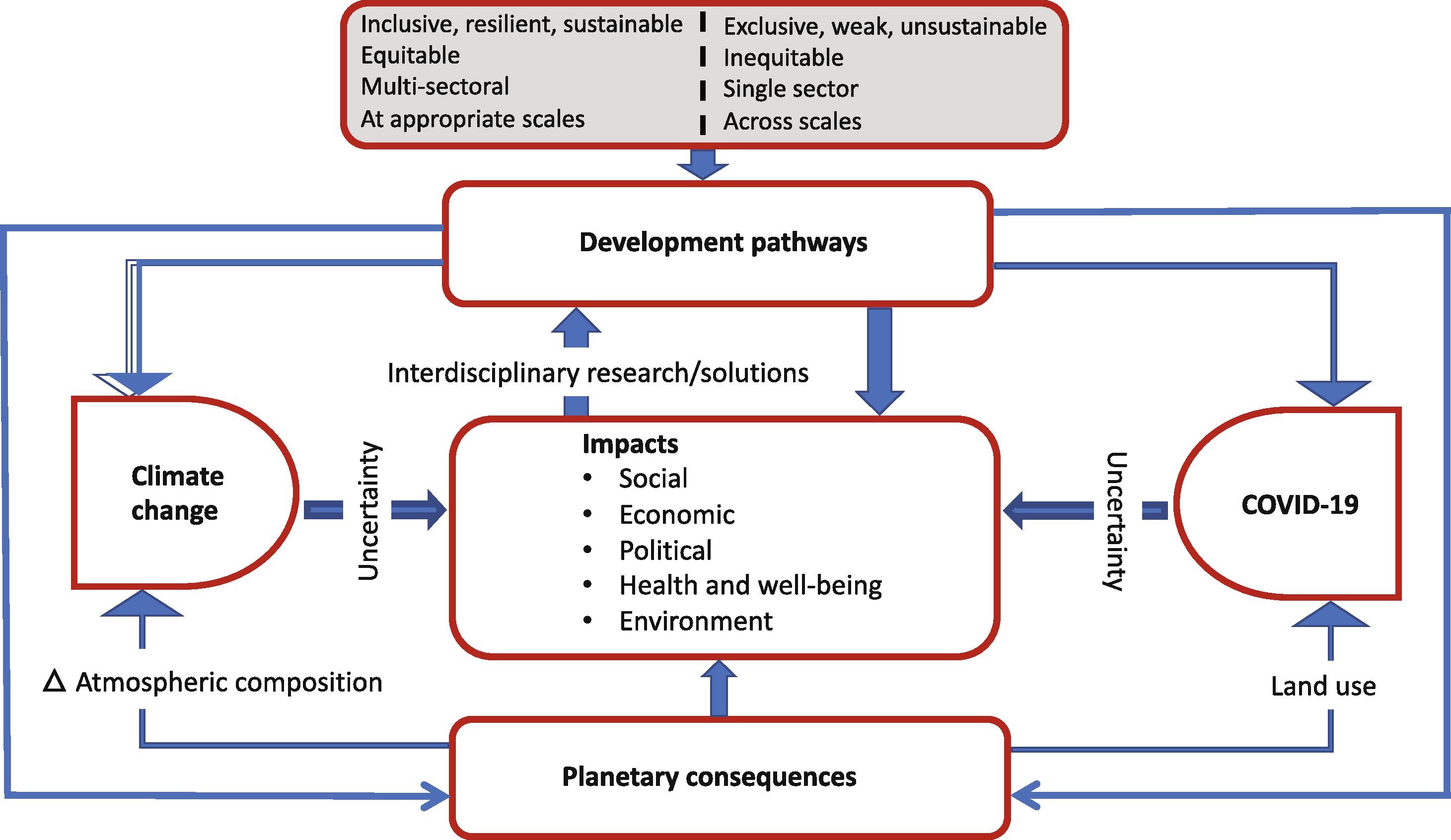
The COVID-19 pandemic and climate change are complex existential threats, unpredictable in many ways and unprecedented in modern times. There are parallels between the scale and scope of their impacts and responses. Understanding shared drivers, coupled vulnerabilities, and criteria for effective responses will help societies worldwide prepare for the simultaneous threats of climate change and future pandemics. We summarize some shared characteristics of COVID-19 and climate change impacts and interventions and discuss key policy implications and recommendations.
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, Volume 519, 1 January 2021
The ability to maintain a (relatively) stable body temperature in a wide range of thermal environments by use of endogenous heat production is a unique feature of endotherms such as birds. Endothermy is acquired and regulated via various endocrine and molecular pathways, and ultimately allows wide aerial, aquatic, and terrestrial distribution in variable environments. However, due to our changing climate, birds are faced with potential new challenges for thermoregulation, such as more frequent extreme weather events, lower predictability of climate, and increasing mean temperature.
Journal for Nurse Practitioners, Volume , 2021
Climate change is the most critical public health crisis of the 21st century. Physical and medical sequelae of climate and weather-related events are well documented and may be addressed in clinical practice. Mental health impacts of climate change are increasingly addressed in the literature but remain underrecognized by clinicians. This report focuses on mental health impacts of climate change through the theoretical framework of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.