Metastatic colorectal cancer outcomes continue to improve, but they vary significantly by race and ethnicity.
This book chapter addresses SDGs 3 and 10 by explaining how stakeholders can ensure the most accurate data about food security for policymakers.
Elsevier,
Mental and Behavioral Health of Immigrants in the United States, Cultural, Environmental, and Structural Factors, 2020, Pages 157-178
This chapter advances SDGs 3 and 10 by exploring how to achieve a culturally competent practice while continuing efforts are needed across various race and ethnicities as well as age groups to provide a more holistic approach to mental health treatment as well as promote protective factors such as a positive cultural identity of immigrants in the United States and worldwide.
Elsevier,
Mental and Behavioral Health of Immigrants in the United States, Cultural, Environmental, and Structural Factors, 2020, Pages 219-252
This chapter advances SDGs 3 and 10 by addressing the prevalence of mental disorders among the ethnic minority groups (African American, Latinx, and Asian American) in the United States according to immigration status.
This book chapter advances SDG 3 and 10 by providing information on various culturally sensitive methods to assess and treat mental health conditions onset by factors contributing to the immigration process for adolescents, adults, and older adults.
Findings from multiple studies link acculturation processes to the psychological and behavioral health of Latino immigrant population in the United States. A critical factor impacting this relation is the context of reception where immigrants settle. Several studies of acculturation have been conducted in traditional receiving contexts, and less attention has been paid to Latino immigrants in emerging contexts. In this chapter, we have discussed how traditional and emerging contexts of reception can confer very different experiences to Latino immigrants, and their significant implications for Latino immigrant health. Further, given the recent influx of crisis migrants from Central America, we have discussed receiving contexts for these newest Latino immigrants to the United States and demonstrated how such contexts might impact their psychological and behavioral health. We concluded with a discussion of implications for the development of policy, as well as culturally specific prevention and intervention programs for Latino immigrants.
Elsevier,
Three Facets of Public Health and Paths to Improvements: Behavior, Culture, and Environment, 2020, Pages 261-294
This book chapter advances SDG 5, 8 and 10 by explaining how the outsized role of women caregivers is attributed to historical, cultural, and social perspectives on gender and caregiving that perpetuate the gender inequalities in unpaid care work. In this chapter, the authors analyze women in unpaid work considering two regions: The United States and the Middle East and North Africa (MENA).
The suffocation death of George Floyd at the hands of police gripped the nation, and employers cannot afford to be silent. Featuring a discussion with a pair of leading diversity experts, this podcast examines constructive steps employers can take. Topics covered support SDG 10 (reduced inequalities).
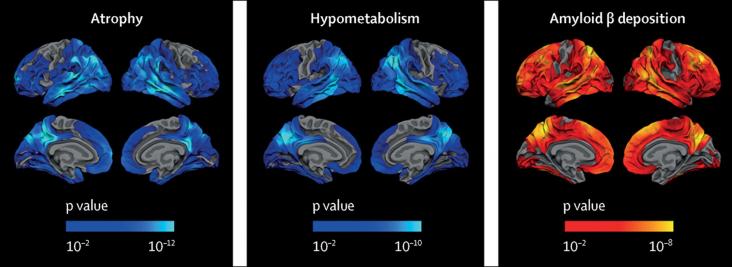
An article on the natural history of Alzheimer's disease in adults with Down syndrome, in the context of SDGs 3 and 10, focusing specifically on the order and timing of biomarker changes in this population.

Even though many workplaces remain 100% or mostly remote due to the COVID-19 pandemic, employers should not miss this opportunity to boost morale and provide support to the LGBTQ community. Employers can create new and innovative ways to celebrate Pride and promote diversity, equality and acceptance, and in so doing promote SDGs 8 and 10.
