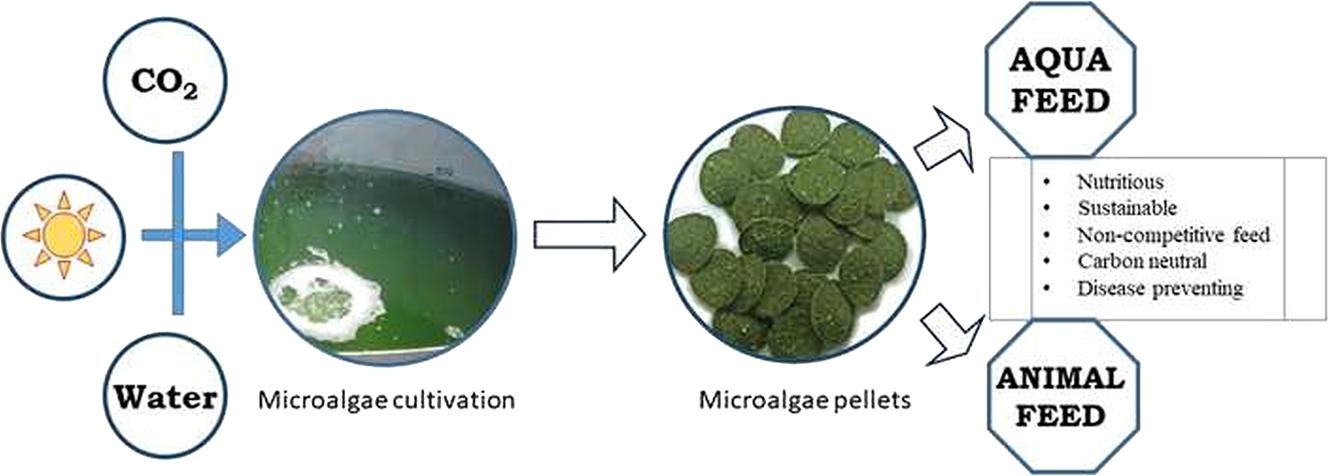
SSM - Population Health, Volume 9, December 2019
Psychological abuse within intimate relationships is linked to negative health outcomes among women and is frequently identified as more wounding than physical or sexual violence. There is little agreement, however, on how to conceptualize or measure the phenomenon, despite measurement being necessary to estimate the prevalence of psychological abuse, establish its interaction with physical and sexual violence, assess its health impacts, and monitor progress towards global Sustainable Development Goals.
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, Volume 116, December 2019
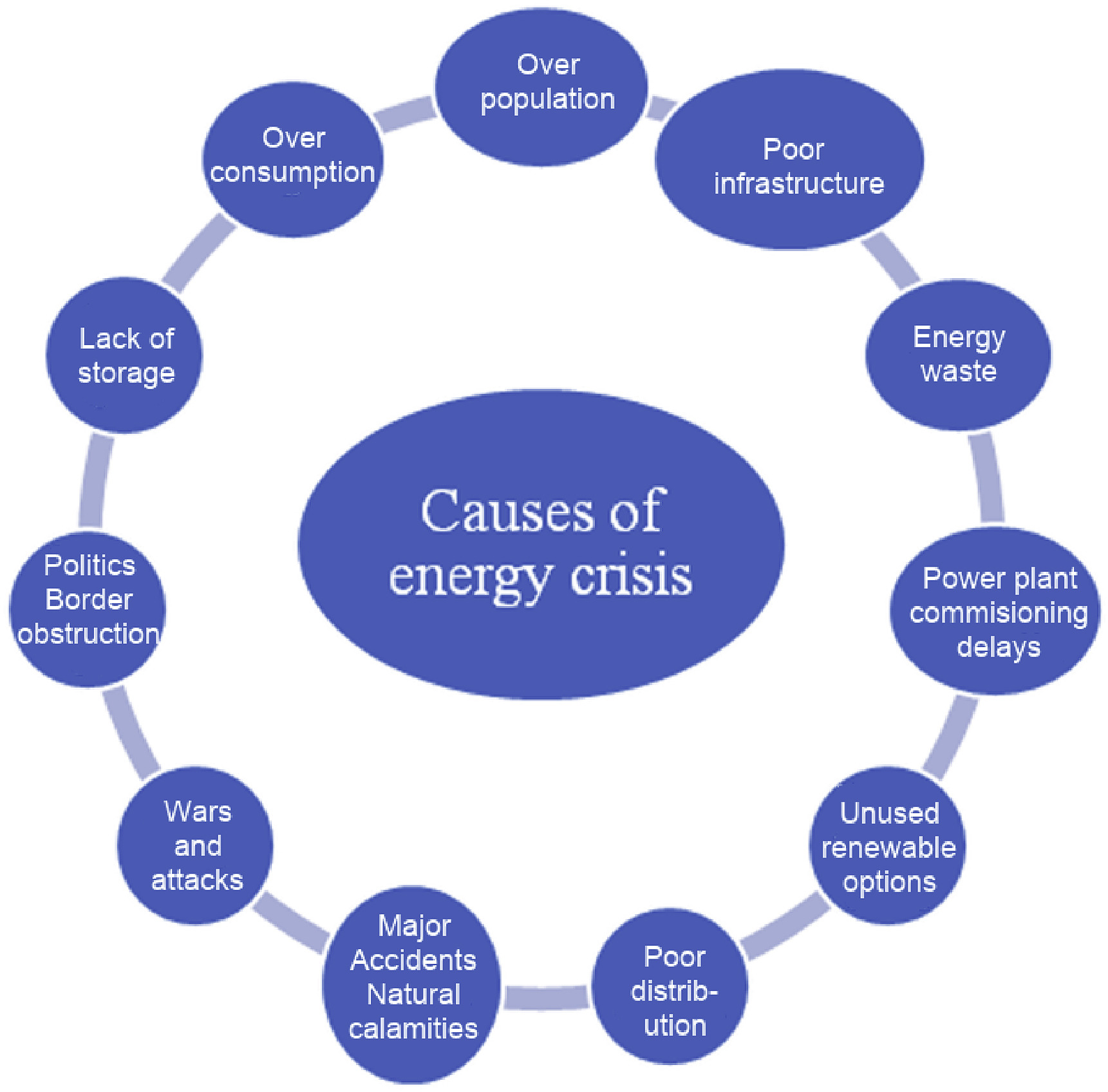
Nepal has been suffering from a serious energy crisis for decades. It has severely affected its economic, social and political developments. Owing to the continuously evolving energy situation in Nepal, and the recent progress in renewable energy technologies, this study aims to provide an up to date perspective on the current energy crisis in Nepal. In particular, the current energy production and consumption profiles are reviewed, and the main factors contributing to a widening gap between the energy supply and demand are identified.
Current Opinion in Food Science, Volume 30, December 2019
Enteric viruses are an important food safety concern and have been associated with many foodborne disease outbreaks. Norovirus and Hepatitis A virus have been implicated in majority of outbreaks; however, other foodborne viruses such as Hepatitis E virus, Sapovirus and Rotavirus can also present a risk to humans. Viral foodborne disease outbreaks have typically been associated with foods served raw including shellfish, fruits and vegetables. The contamination of food by viruses can occur anywhere in the supply chain.
Journal of the Energy Institute, Volume 92, December 2019
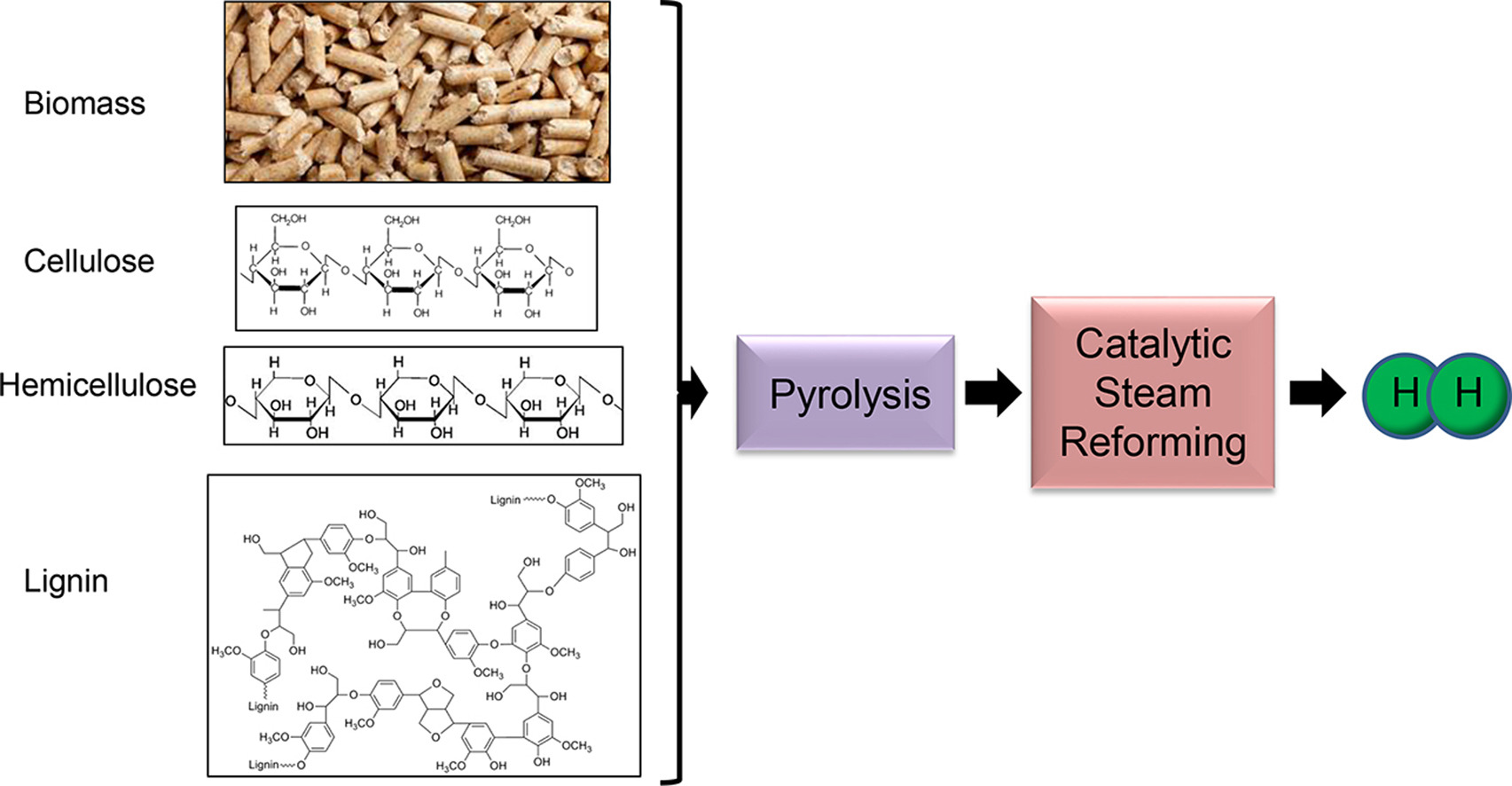
The pyrolysis-catalytic steam reforming of six agricultural biomass waste samples as well as the three main components of biomass was investigated in a two stage fixed bed reactor. Pyrolysis of the biomass took place in the first stage followed by catalytic steam reforming of the evolved pyrolysis gases in the second stage catalytic reactor. The waste biomass samples were, rice husk, coconut shell, sugarcane bagasse, palm kernel shell, cotton stalk and wheat straw and the biomass components were, cellulose, hemicellulose (xylan) and lignin.
Heliyon, Volume 5, December 2019
The Lancet Child and Adolescent Health, Volume 3, December 2019
Biomarkers in Neuropsychiatry, Volume 1, December 2019