Elsevier,
The Lancet Healthy Longevity, Volume 4, January 2023
This Article supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by examining whether psychological intervention for anxiety disorders is associated with a lower incidence of dementia. The results suggest that improvement in anxiety from these therapies was associated with reduced incidence of future dementia.
Elsevier,
Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 17, January 2023
This Article supports Sustainable Development Goal 3 by developing a methodology for discriminating between and classifying Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia according to demographic, clinical, and cognitive data, across centres in Latin America. The approach provided high accuracy with the combination of classical statistical and machine learning procedures.
Elsevier,
Sustainable Production and Consumption, Volume 35, January 2023
This research aimed to determine how interested people are in bio-based bottles. We also compared bio-based options to the fossil-based industry standard and determined consumer reactions to both. We measured consumer demand for bio-based plastic bottles as an alternative to a conventional (fossil-based) plastic bottle and investigated what conditions underlie this preference (e.g., bottle appearance).
Elsevier,
Journal of Responsible Technology, Volume , 2023
The authors seek to create a framework that can inform the research agenda of the emerging literature of responsible digital transformation (DT). Through the research, two core questions are examined: '(1) when we can consider a DT process responsible (i.e., responsibility in DT), and (2) when we can consider DT outcomes responsible (i.e., the responsibility of DT)'. The authors point to the UN's sustainable development goals and its Universal Declaration of Human Rights as reference points for responsible DT.
Elsevier,
Energy and AI, Volume 11, January 2023
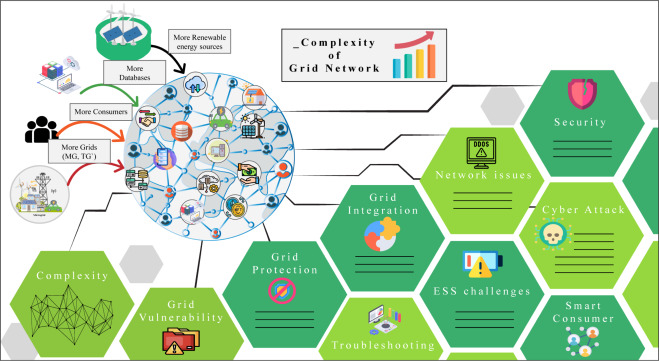
This article supports SDGs 7,9 and 11 by proposing that the real-time online analysis, data integration, and prediction of future status, monitoring, decision-making, and self-healing of the power grid can be achieved, providing high security, reducing the risk of power grid accidents, and serving multiple fields of producers, consumers, and the entire country.
Elsevier,
Trends in Immunology, Volume 44, January 2023
Due to multiple cellular blocks in transcription, HIV-1 latency can only be reversed in a minor fraction of infected but potentially virus-producing CD4+ T cells from infected patients. New insights into the regulation of transcription elongation factor P-TEFb as a crucial rate-limiting step in the emergence of HIV-1 from latency may help design more effective latency reversal agents during HIV-1 infection.
Elsevier,
Antiviral Research, Volume 209, January 2023
This review supports SDG3 by detailing the current fundamental knowledge of HDV lifecycle and review antiviral treatments under development against this virus, outlining their respective mechanisms-of-action. Finally, it describes the antiviral effect these compounds are showing in ongoing clinical trials, discussing their promise and potential pitfalls for managing HDV infected patients.