Elsevier, Women's Studies International Forum, Volume 79, March - April 2020
Objectives: Limited studies have investigated detailed insights into the experiences of women in transitioning countries such as Iran as active agents in their lives and their societies. This study explores how young Iranian women build and use their social capital to make a social change and improve their status. Methods: This study is the qualitative component of a larger mixed-method study exploring social capital and wellbeing in young Iranian women. Semi-structured, in-depth interviews were conducted with 17 young Iranian women aged 18–35.
Elsevier, Remote Sensing of Environment, Volume 239, 15 March 2020
In the face of the growing challenges brought about by human activities, effective planning and decision-making in biodiversity and ecosystem conservation, restoration, and sustainable development are urgently needed. Ecological models can play a key role in supporting this need and helping to safeguard the natural assets that underpin human wellbeing and support life on land and below water (United Nations Sustainable Development Goals; SDG 15 & 14).
Elsevier, Remote Sensing of Environment, Volume 239, 15 March 2020
The natural world has multiple, sometimes conflicting, sometimes synergistic, values to society when viewed through the lens of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Spatial mapping of nature's contributions to the SDGs has the potential to support the implementation of SDG strategies through sustainable land management and conservation of ecosystem services. Such mapping requires a range of spatial data.
Elsevier, Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, March 2020
Soil organic carbon (SOC) in croplands is a key property of soil quality for ensuring food security and agricultural sustainability, and also plays a central role in the global carbon (C) budget. When managed sustainably, soils may play a critical role in mitigating climate change by sequestering C and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. However, the magnitude and spatio-temporal patterns of global cropland SOC are far from well constrained due to high land surface heterogeneity, complicated mechanisms, and multiple influencing factors.
Elsevier, Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, March 2020
Agricultural landscapes cultivated in hilly and mountainous areas, often with terracing practice, could represent for some regions historical heritages and cultural ecosystem services. For this reason, they deserve to be protected. The complex morphology that characterises them, however, makes these areas intrinsically susceptible to hydrogeological instability, such as soil loss due to surface erosion or more severe mass movements. We can identify three major critical factors for such landscapes.
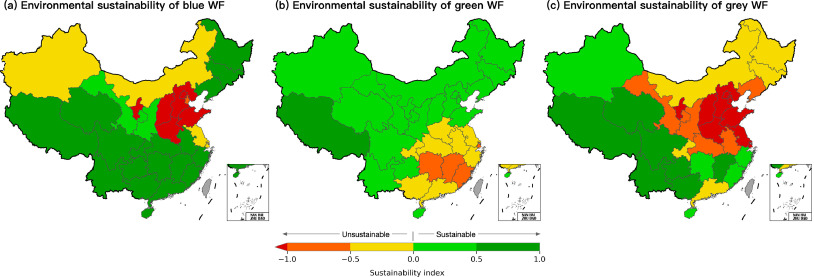
Elsevier, Geography and Sustainability, Volume 1, March 2020
Water footprint (WF) measures human appropriation of water resources for consumptive use of surface and ground water (blue WF) and soil water (green WF) and for assimilating polluted water (grey WF). Questions have been often asked about the exact meaning behind the numbers from WF accounting. However, to date environmental sustainability of WF has never been assessed at the sub-national level over time. This study evaluated the environmental sustainability of blue, green and grey WF for China's 31 mainland provinces in 2002, 2007 and 2012, and identified the unsustainable hotspots.
Elsevier, Journal for Nurse Practitioners, Volume 16, March 2020
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder and a leading cause of dementia in the elderly. AD initially presents as mild cognitive impairment (MCI); later, as AD progresses, memory and cognition are destroyed, preventing the ability to carry out activities of daily living. The primary care provider may be the first to suspect MCI, and screening tests can help with diagnosis. Development of drugs for cognitive decline in AD has been slow; however new therapies are in the pipeline and discovery of biomarkers make early diagnosis and future treatment of AD hopeful.
Elsevier, Peptides, Volume 125, March 2020
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) is a peptide hormone of the incretin family. It has growth factor properties and can re-activate energy utilization. In progressive neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, energy utilization is much reduced, and GIP has the potential to reverse this. Furthermore, GIP can reduce the inflammation response in the brain and reduce levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Tests in animal models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease show good neuroprotective effects.