Elsevier, General and Comparative Endocrinology, Volume 303, 1 March 2021
Anthropogenic activity is a major driver of seabird injury and mortality in the 21st century. Although most seabirds perish within the natural environment as a result of human activities, some are rescued and admitted to rehabilitation centres. Despite the considerable number of admissions, little is known regarding the physiological response seabirds have to specific admission reasons and the rehabilitation process.
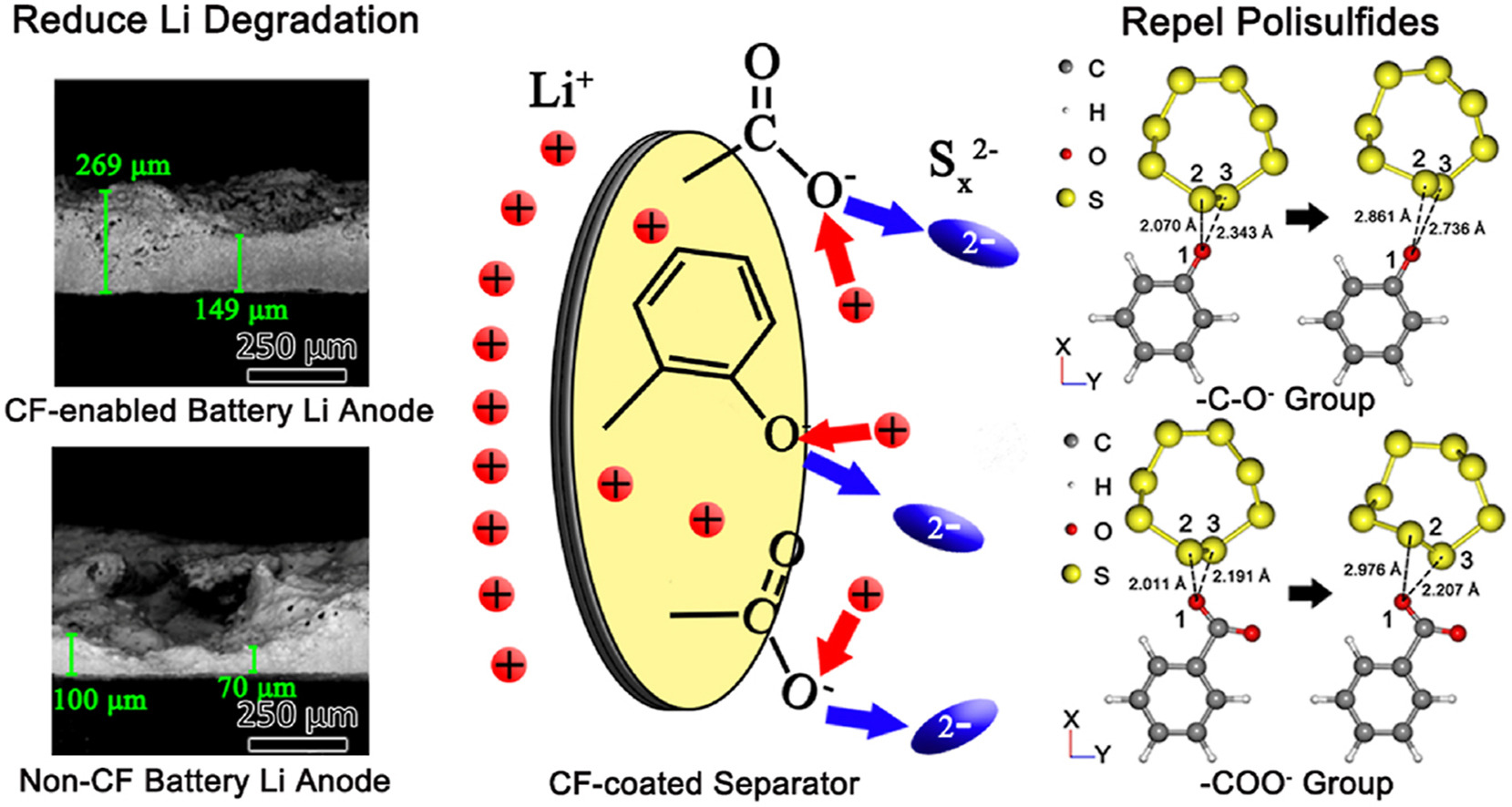
Elsevier, Materials Today Energy, Volume 19, March 2021
The fast-expanding electric vehicle market demands eco-friendly, high-performance, and low-cost energy storage systems. Lithium-sulfur battery with higher theoretical specific capacity and lower cost is regarded as a promising successor to lithium-ion battery. However, lithium-sulfur battery's polysulfide shuttling and lithium degradation have hindered its practical applications. In this study, cellulose fibers (CFs) were extracted from recycled paper hardboards by a simple alkaline treatment and then coated onto polypropylene separators by vacuum filtration.
Elsevier, Materials Today Sustainability, Volume 11-12, March 2021
Fatty alcohols (FAs) have been widely studied as typical phase-change materials for their high latent heat, low undercooling, non-toxicity, and low cost in thermal energy storage applications. The thermal properties, especially the heat capacity, play a vital role in designing-related energy storage techniques. However, there are few studies on the thermal properties of FAs systematically investigated in a wide temperature region, which greatly limit their application in thermal energy storage field.
Elsevier, Materials Today Sustainability, Volume 11-12, March 2021
With the growing global environmental awareness, the development of renewable and green materials has gained increased worldwide interest. Being at the heart of current scientific research studies, renewable polymers, include natural, semisynthetic, and microbial polymers, have a scope in vast diverse applications in packaging, agriculture, medicine, and optoelectronic technological fields.
Elsevier, Behavioural Brain Research, Volume 402, 26 March 2021
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the foremost cause of dementia among other neurodegenerative diseases, leading to memory loss and cognitive deficits. AD has gained extensive attention in research for exploring possible interventions. One promising field is natural substances and compounds that could provide a wide range of neuroprotection against AD. This study aimed to investigate the possible effects of melatonin (MEL) and resveratrol (RES) in improving memory deficits in a sporadic mouse model of AD. Memory deficit was induced using AlCl3 and d-galactose for generating an AD mouse model.
Elsevier, Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, Volume 65, March 2021
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder of the brain that ultimately results in the death of neurons and dementia. The prevalence of the disease in the world is increasing rapidly. In recent years, many studies have been done to automatically detect this disease from brain signals. Method: In this paper, the Hjorth parameters are used along with other common features to improve the AD detection accuracy from EEG signals in early stages.
Elsevier, JAAD International, Volume 2, March 2021
Introduction: Skin diseases have a significant global impact on quality of life, mental health, and loss of income. The burden of dermatologic conditions and its relationship with socioeconomic status in Asia is currently not well understood. Methods: We selected Global Burden of Disease Study datasets to analyze disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in 50 Asian countries, including Central Asia, northern Asia, eastern Asia, western Asia, southeastern Asia, and southern Asia, between 1990 and 2017.
Elsevier, Food Quality and Preference, Volume 88, March 2021
A shift to a more healthy and sustainable diet (as recommended by the EAT Lancet Commission report) is currently hampered by persistent choices for meat, which are based on stable preferences and positive feedback mechanisms at the individual, social, and economic/organizational level. This paper puts forward the view that proposals for a diet shift will fall short without broad social legitimation, aimed at a change in social norms.