Elsevier,
The Lancet Planetary Health, Volume 6, April 2022
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 6 by developing estimates of regulated metals in community water systems, which can be used in future studies, and by showing that there are significant sociodemographic inequalities in public water uranium concentrations.
Elsevier, Heliyon, Volume 8, April 2022
In the past decade, mental health is embedded in the concept of health and teachers’ mental health has become the focus of surveys. In this study we examined the mental health of special educator-students compared to their lecturers and inspectors at the University Semmelweis Pető András Faculty. We used the validated Hungarian language Mental Health Test (MHT) to assess the mental health. The MHT is linked to the concept of physical and mental wellbeing, it is ability-based approach, and examines 5 areas: wellbeing, savoring, creative-executive efficiency self-regulation resilience.
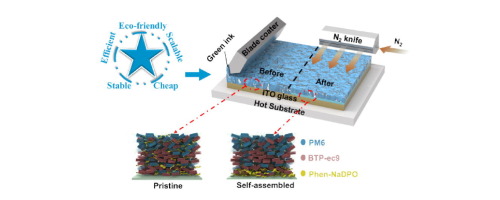
The ultimate goal of organic solar cells (OSCs) is to deliver cheap, stable, efficient, scalable, and eco-friendly solar-to-power products contributing to the global carbon neutral effort. This work demonstrates great potential to close the lab-to-fab gap of OSCs.
Elsevier, Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 6, 1 April 2022
Background: Community participation has the potential to improve the effects of interventions and reduce inequalities in child growth. Multidimensional indicators capture such effects and inequalities. Objectives: The objective of this study was to measure the association between multidimensional child growth and community participation in 2 nutrition-sensitive interventions. Methods: A Multidimensional Index of Child Growth was calculated with the 5-y-old cohort of the Vietnam Young Lives Survey.
Elsevier,
The Lancet Regional Health - Americas, Volume 8, April 2022
This Article supports SDGs 3 and 16 by quantifying mortality risk after a dementia diagnosis, focusing specifically on differences across race and ethnicity. The authors discuss the implications for financial and health services planning, as well as quality of life.
Elsevier,
Current Developments in Nutrition, Volume 6, 1 April 2022
The authors conclude improved water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH activities) were successful in contributing to improved dietary diversity in women. Interventions aimed at enhancing the diet and nutritional status of women during and after pregnancy should include relevant WASH components as essential elements in multisector nutrition programming.
Elsevier,
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 115, 1 April 2022
The study presents a new approach to analyzing the relations between sustainability indicators, foods, and macronutrients and establishes that proteins, irrespective of the source of protein, are driving dietary environmental and economic impacts.